java tutorial - Java Socket Programming - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
- A socket is one of the most fundamental technologies of computer network programming . It is a way of connecting two nodes on a network to communicate with each other. Socket-based software usually runs on two separate computers on the network, but sockets can also be used to communicate locally (interprocess) on a single computer. The Java Socket Programming has two sections.
- Java Server Socket Program
- Java Client Socket Program
Learn Java - Java tutorial - Sockets programming in Java - Java examples - Java programs
- Java Socket programming is used for communication between the applications running on different JRE. Java Socket programming can be connection-oriented or connection-less. Socket and ServerSocket classes are used for connection-oriented socket programming and DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket classes are used for connection-less socket programming. The client in socket programming must know two information:
- IP Address of Server, and
- Port number.
Socket class
- A socket is simply an endpoint for communications between the machines. The Socket class can be used to create a socket.
Socket class
- Socket is an endpoint for communications between the machines.
- The Socket class can be used to create a socket.
Methods
ServerSocket class
- The ServerSocket class can be used to create a server socket. This object is used to establish communication with the clients.
Methods
Sample Code
- Java socket programming in which client sends a text and server receives it.
File: MyServer.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
ServerSocket wiki=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket a=wiki.accept();//establishes connection
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(a.getInputStream());
String str=(String)dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("message= "+str);
wiki.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
File: MyClient.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket a=new Socket("localhost",6666);
DataOutputStream dout=new DataOutputStream(a.getOutputStream());
dout.writeUTF("Hello Wikitechy Server");
dout.flush();
dout.close();
s.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
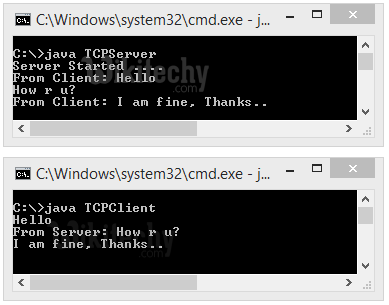
Java Socket Programming (Read-Write both side)
- Client will write first to the server then server will receive and print the text.
- Then server will write to the client and client will receive and print the text.
File: MyServer.java
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
class MyServer{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
ServerSocket wiki=new ServerSocket(3333);
Socket a=wiki.accept();
DataInputStream din=new DataInputStream(a.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream dout=new DataOutputStream(a.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str="",str2="";
while(!str.equals("stop")){
str=din.readUTF();
System.out.println("client says: "+str);
str2=br.readLine();
dout.writeUTF(str2);
dout.flush();
}
din.close();
a.close();
wiki.close();
}} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
File: MyClient.java
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
class MyClient{
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
Socket a=new Socket("localhost",3333);
DataInputStream din=new DataInputStream(a.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream dout=new DataOutputStream(a.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str="",str2="";
while(!str.equals("stop")){
str=br.readLine();
dout.writeUTF(str);
dout.flush();
str2=din.readUTF();
System.out.println("Server says: "+str2);
}
dout.close();
a.close();
}} 