java tutorial - Java HashMap class - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
Java HashMap class implements the map interface by using a hashtable. It inherits AbstractMap class and implements Map interface.
The important points about Java HashMap class are:
- A HashMap contains values based on the key.
- It contains only unique elements.
- It may have one null key and multiple null values.
- It maintains no order.
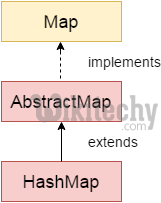
Hierarchy of HashMap class
As shown in the above figure, HashMap class extends AbstractMap class and implements Map interface.
Learn java - java tutorial - hashmap - java examples - java programs
HashMap class declaration
- Let's see the declaration for java.util.HashMap class.
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializableclick below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
HashMap class Parameters
- Let's see the Parameters for java.util.HashMap class.
- K: It is the type of keys maintained by this map.
- V: It is the type of mapped values.
Constructors of Java HashMap class
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| HashMap() | It is used to construct a default HashMap. |
| HashMap(Map m) | It is used to initializes the hash map by using the elements of the given Map object m. |
| HashMap(int capacity) | It is used to initializes the capacity of the hash map to the given integer value, capacity. |
| HashMap(int capacity, float fillRatio) | It is used to initialize both the capacity and fill ratio of the hash map by using its arguments. |
Methods of Java HashMap class
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void clear() | It is used to remove all of the mappings from this map. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | It is used to return true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | It is used to return true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| boolean isEmpty() | It is used to return true if this map contains no key-value mappings. |
| Object clone() | It is used to return a shallow copy of this HashMap instance: the keys and values themselves are not cloned. |
| Set entrySet() | It is used to return a collection view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| Set keySet() | It is used to return a set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| Object put(Object key, Object value) | It is used to associate the specified value with the specified key in this map. |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of key-value mappings in this map. |
| Collection values() | It is used to return a collection view of the values contained in this map. |
Java HashMap Example
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollection13{
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap<Integer,String> hm=new HashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(100,"Amit");
hm.put(101,"Vijay");
hm.put(102,"Rahul");
for(Map.Entry m:hm.entrySet()){
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output
102 Rahul
100 Amit
101 VijayJava HashMap Example: remove()
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create and populate hash map
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(101,"Let us C");
map.put(102, "Operating System");
map.put(103, "Data Communication and Networking");
System.out.println("Values before remove: "+ map);
// Remove value for key 102
map.remove(102);
System.out.println("Values after remove: "+ map);
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output:
Values before remove: {102=Operating System, 103=Data Communication and Networking, 101=Let us C}
Values after remove: {103=Data Communication and Networking, 101=Let us C}Difference between HashSet and HashMap
- HashSet contains only values whereas HashMap contains entry(key and value).
Java HashMap Example: Book
import java.util.*;
public class Book {
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
public class MapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating map of Books
Map<Integer,Book> map=new HashMap<Integer,Book>();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Let us C","Yashwant Kanetkar","BPB",8);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Data Communications & Networking","Forouzan","Mc Graw Hill",4);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Operating System","Galvin","Wiley",6);
//Adding Books to map
map.put(1,b1);
map.put(2,b2);
map.put(3,b3);
//Traversing map
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Book> entry:map.entrySet()){
int key=entry.getKey();
Book b=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+" Details:");
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+" "+b.quantity);
}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output:
1 Details:
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
2 Details:
102 Data Communications & Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
3 Details:
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6