Android tutorial - XML Parsing in Android | Domparser - android app development - android studio - android development tutorial
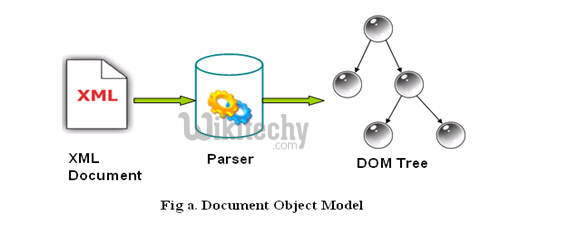
What is XML Parsing?
- Parsing XML refers to going through XML document to access data or to modify data in one or other way.
What is DOM Parser?
- The Document Object Model is an official recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
- It defines an interface that enables programs to access and update the style, structure and contents of XML documents.
- XML parsers that support the DOM implement that interface.
- We can parse the xml document by dom parser also. It can be used to create and parse the xml file.
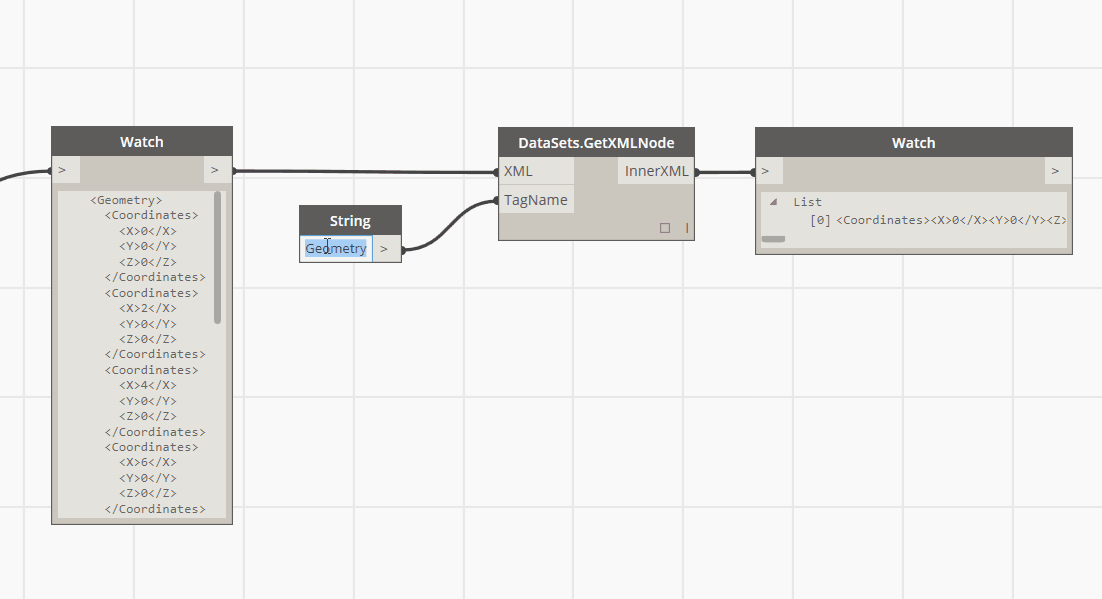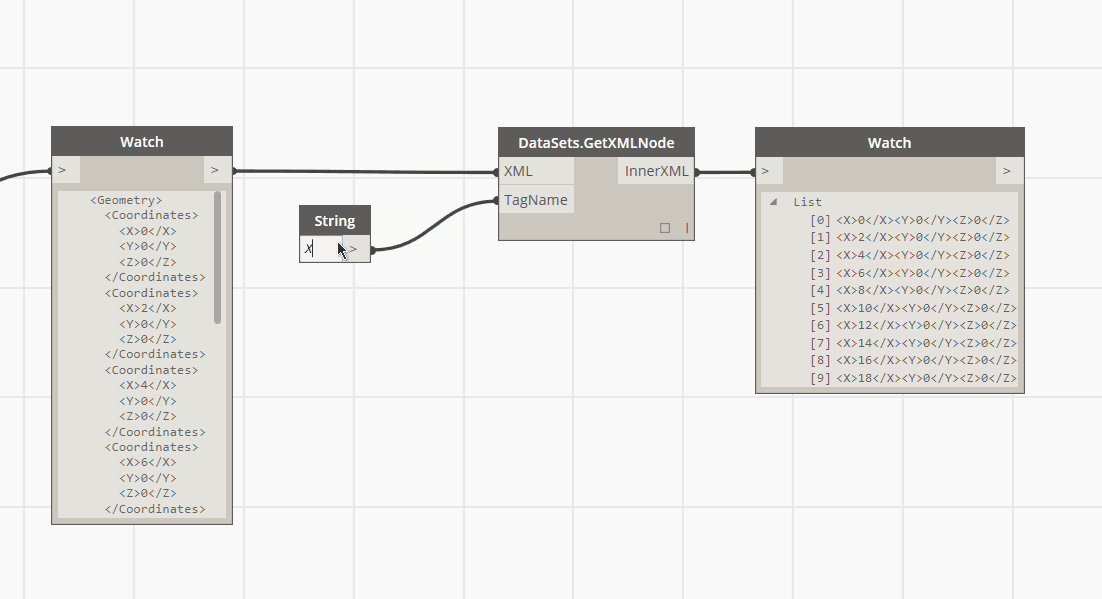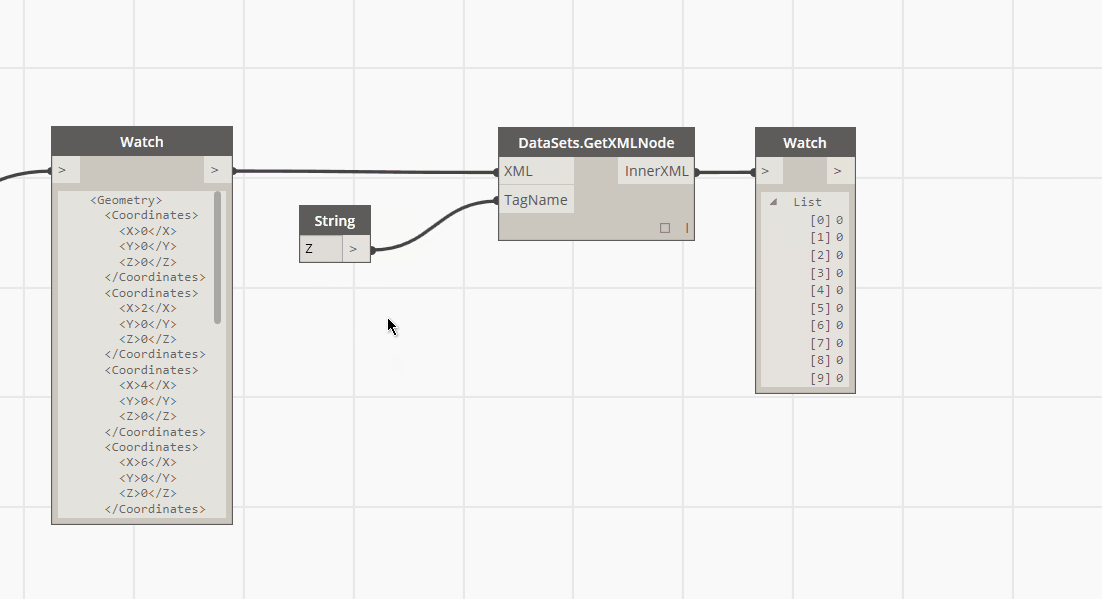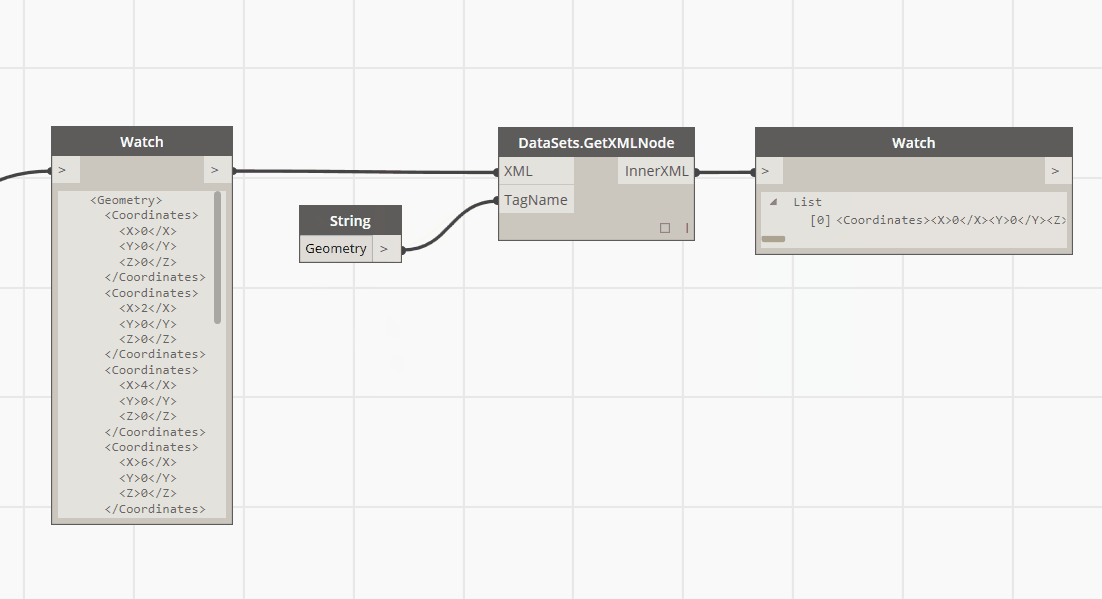
usage of dom?
- You should use a DOM parser when:
- You need to know a lot about the structure of a document
- You need to move parts of the document around (you might want to sort certain elements, for example)
- You need to use the information in the document more than once
Advantage of DOM Parser over SAX
- It can be used to create and parse the xml file both but SAX parser can only be used to parse the xml file.
Disadvantage of DOM Parser over SAX
- It consumes more memory than SAX.
Example of android DOM Xml parsing
activity_main.xml
- Drag the one textview from the pallete. Now the activity_main.xml file will look like this:
- File: activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="75dp"
android:layout_marginTop="46dp"
android:text="TextView" />
</RelativeLayout>
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
xml document
- Create an xml file named file.xml inside the assets directory of your project.
- File: file.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<records>
<employee>
<name>Sachin Kumar</name>
<salary>50000</salary>
</employee>
<employee>
<name>Rahul Kumar</name>
<salary>60000</salary>
</employee>
<employee>
<name>John Mike</name>
<salary>70000</salary>
</employee>
</records>
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
Activity class
- Let's write the code to parse the xml using dom parser.
- File: MainActivity.java
package com.wikitechy.domxmlparsing;
import java.io.InputStream;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
TextView tv1;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv1=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
try {
InputStream is = getAssets().open("file.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory dbFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder dBuilder = dbFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = dBuilder.parse(is);
Element element=doc.getDocumentElement();
element.normalize();
NodeList nList = doc.getElementsByTagName("employee");
for (int i=0; i<nList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element element2 = (Element) node;
tv1.setText(tv1.getText()+"\nName : " + getValue("name", element2)+"\n");
tv1.setText(tv1.getText()+"Salary : " + getValue("salary", element2)+"\n");
tv1.setText(tv1.getText()+"-----------------------");
}
}//end of for loop
} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
private static String getValue(String tag, Element element) {
NodeList nodeList = element.getElementsByTagName(tag).item(0).getChildNodes();
Node node = (Node) nodeList.item(0);
return node.getNodeValue();
}
}
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
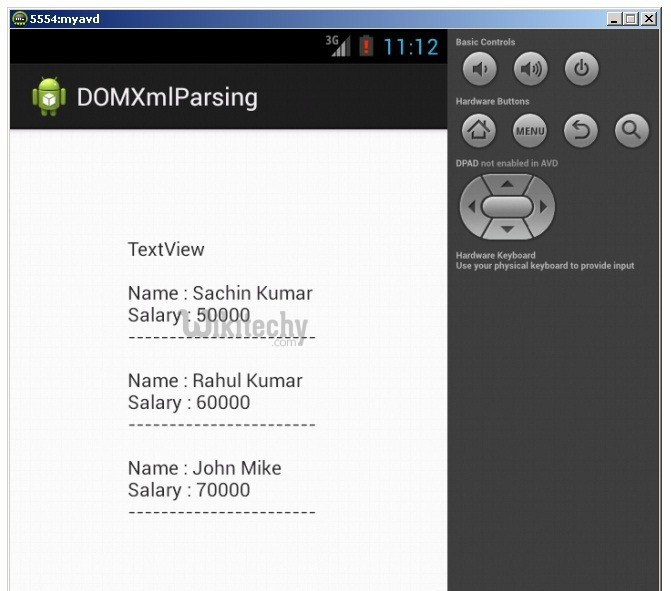
Output: