Android tutorial - Android JSON Parser - android app development - android studio - android development tutorial
Learn android - android tutorial - Android json parser - android examples - android programs
- JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.
- It is an independent data exchange format and is the best alternative for XML.
- This chapter explains how to parse the JSON file and extract necessary information from it.
- Android provides four different classes to manipulate JSON data. These classes are JSONArray,JSONObject,JSONStringer and JSONTokenizer.

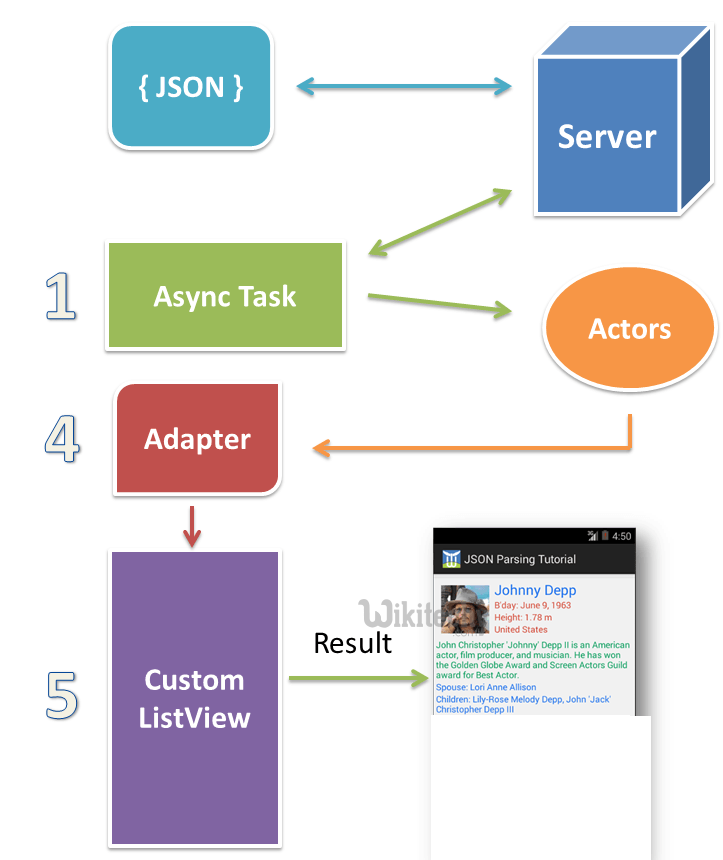
- JSON (Javascript Object Notation) is a programming language.
- It is minimal, textual, and a subset of JavaScript. It is an alternative to XML.
- Android provides support to parse the JSON object and array.
Advantage of JSON over XML
- JSON is faster and easier than xml for AJAX applications.
- Unlike XML, it is shorter and quicker to read and write.
- It uses array.
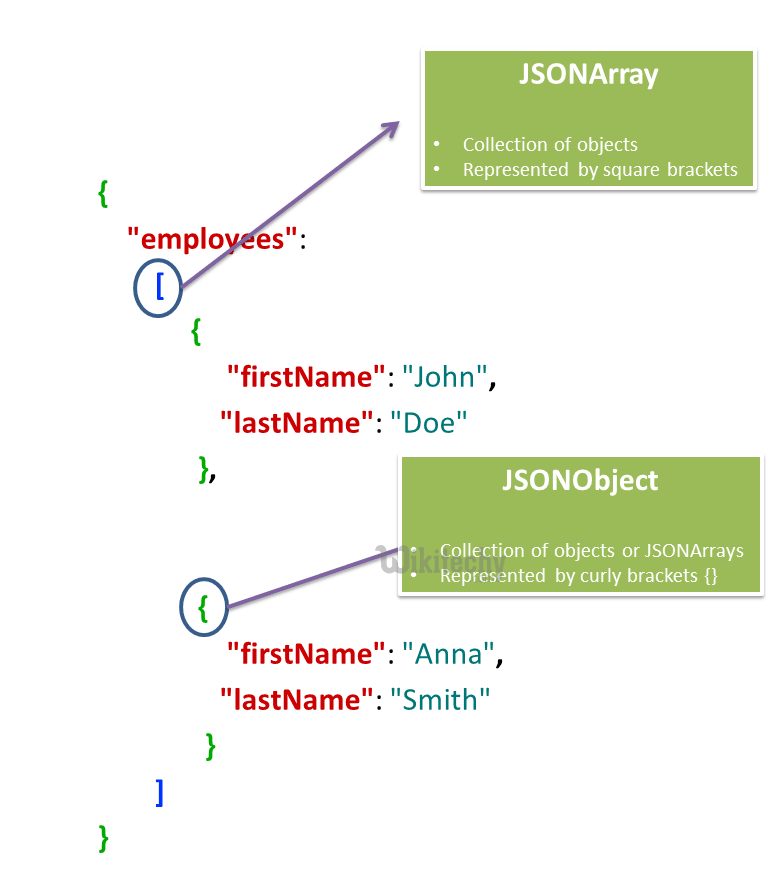
json object
- A JSON object contains key/value pairs like map.
- The keys are strings and the values are the JSON types.
- Keys and values are separated by comma.
- The { (curly brace) represents the json object.
{
"employee": {
"name": "sachin",
"salary": 56000,
"married": true
}
}
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
json array
- The [ (square bracket) represents the json array.
["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"]
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
- Let's take another example of json array.
{ "Employee" :
[
{"id":"101","name":"Sonoo Jaiswal","salary":"50000"},
{"id":"102","name":"Vimal Jaiswal","salary":"60000"}
]
}
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
Example of android JSON parsing
activity_main.xml
- Drag the one textview from the pallete. Now the activity_main.xml file will look like this:
- File: activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="75dp"
android:layout_marginTop="46dp"
android:text="TextView" />
</RelativeLayout>
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
Activity class
- Let's write the code to parse the xml using dom parser.
- File: MainActivity.java
package com.wikitechy.jsonparsing;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public static final String JSON_STRING="{\"employee\":{\"name\":\"Sachin\",\"salary\":56000}}";
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView textView1=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
try{
JSONObject emp=(new JSONObject(JSON_STRING)).getJSONObject("employee");
String empname=emp.getString("name");
int empsalary=emp.getInt("salary");
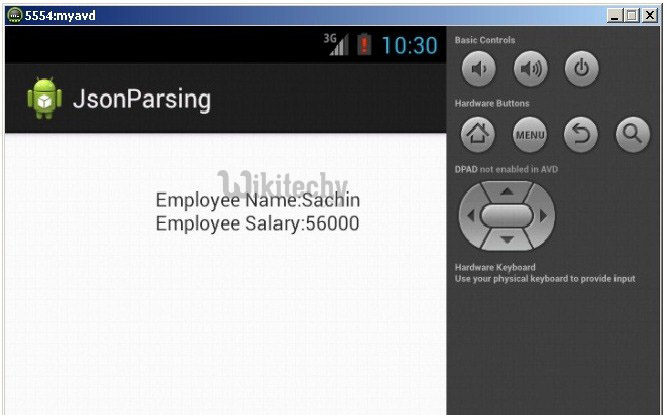
String str="Employee Name:"+empname+"\n"+"Employee Salary:"+empsalary;
textView1.setText(str);
}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
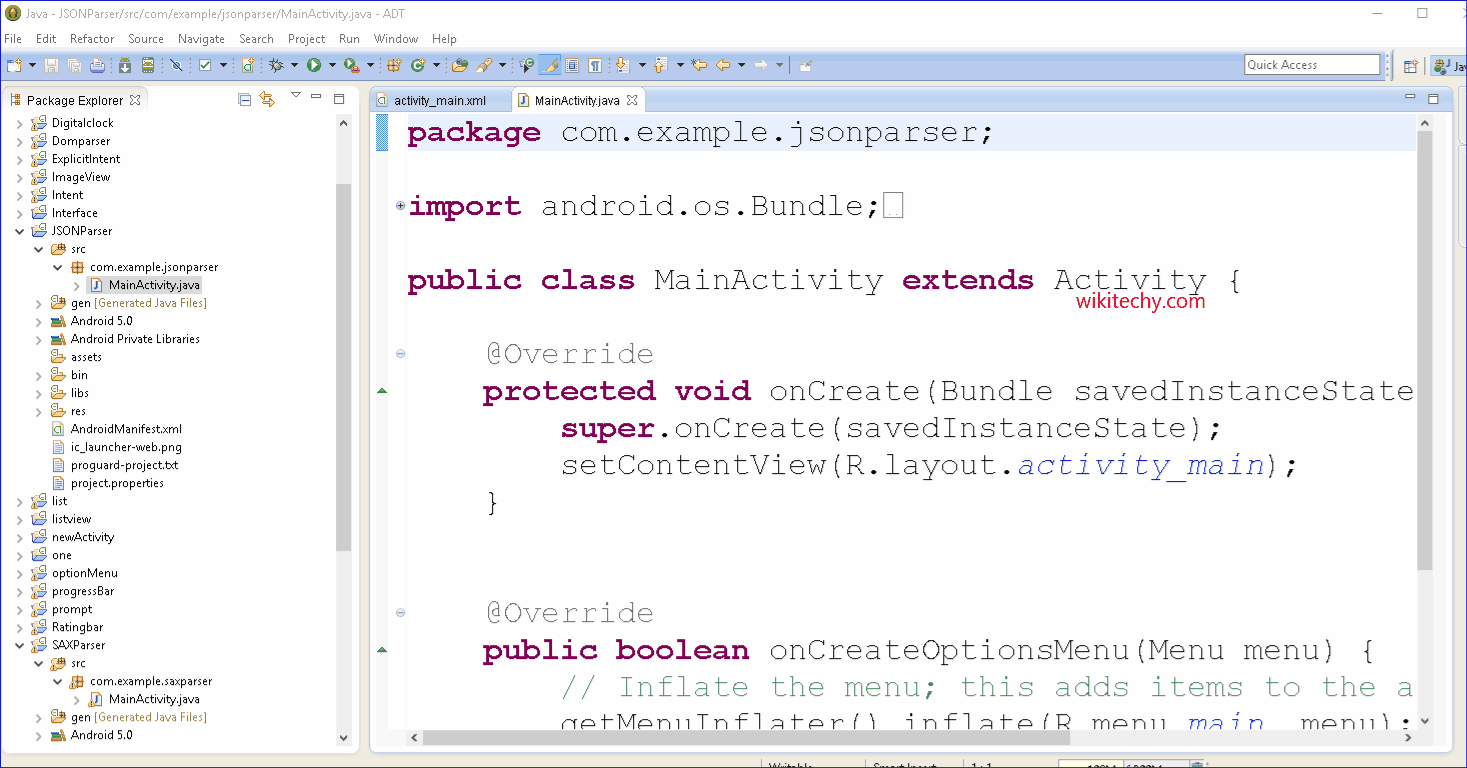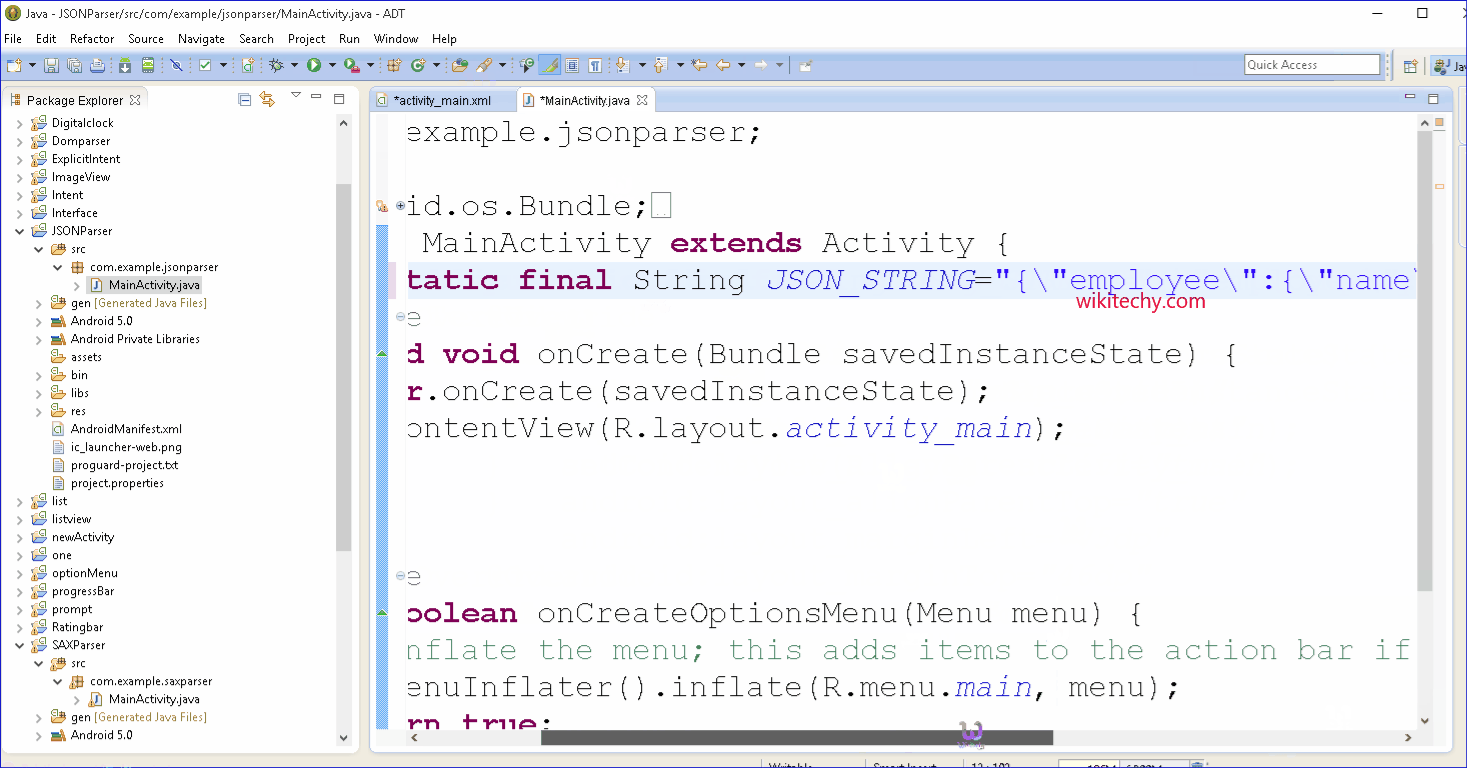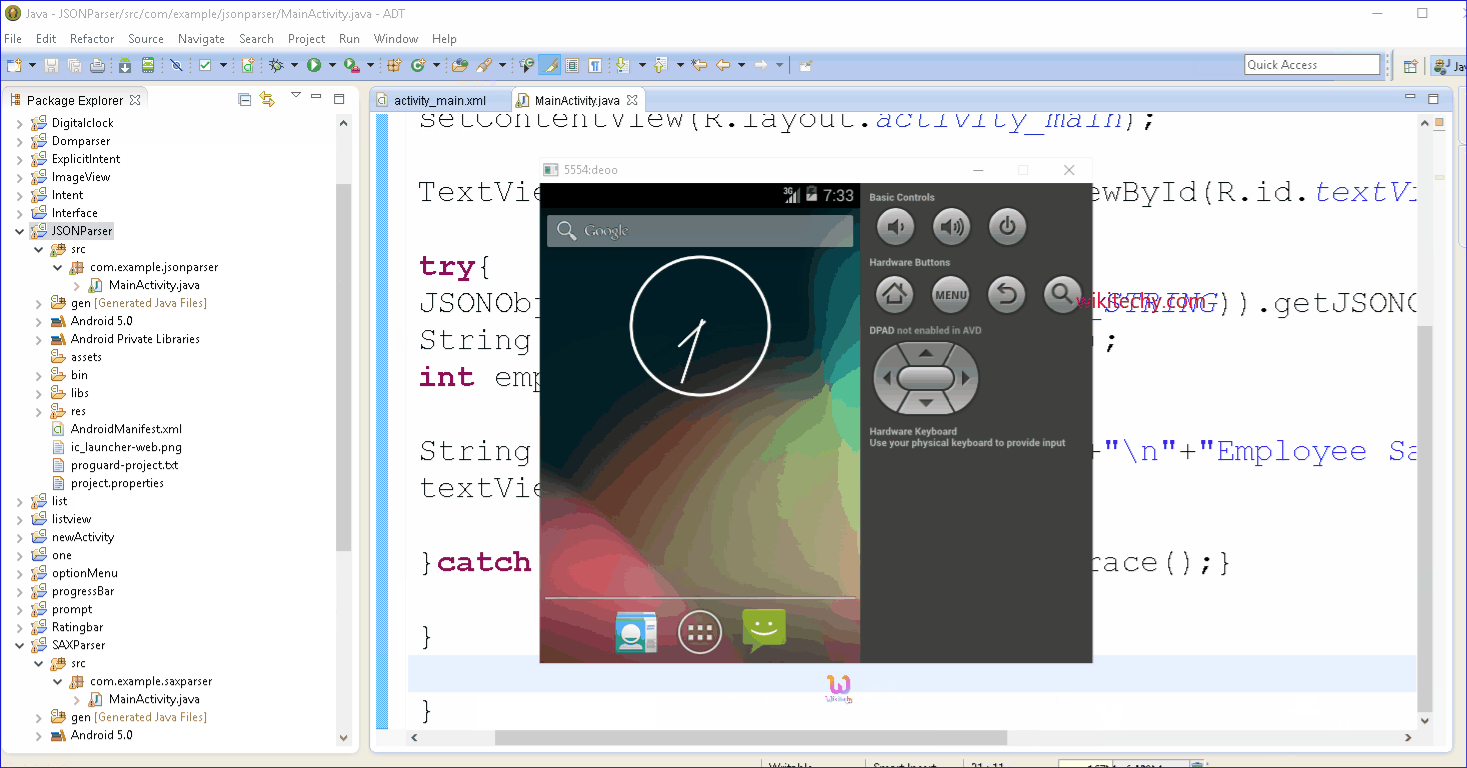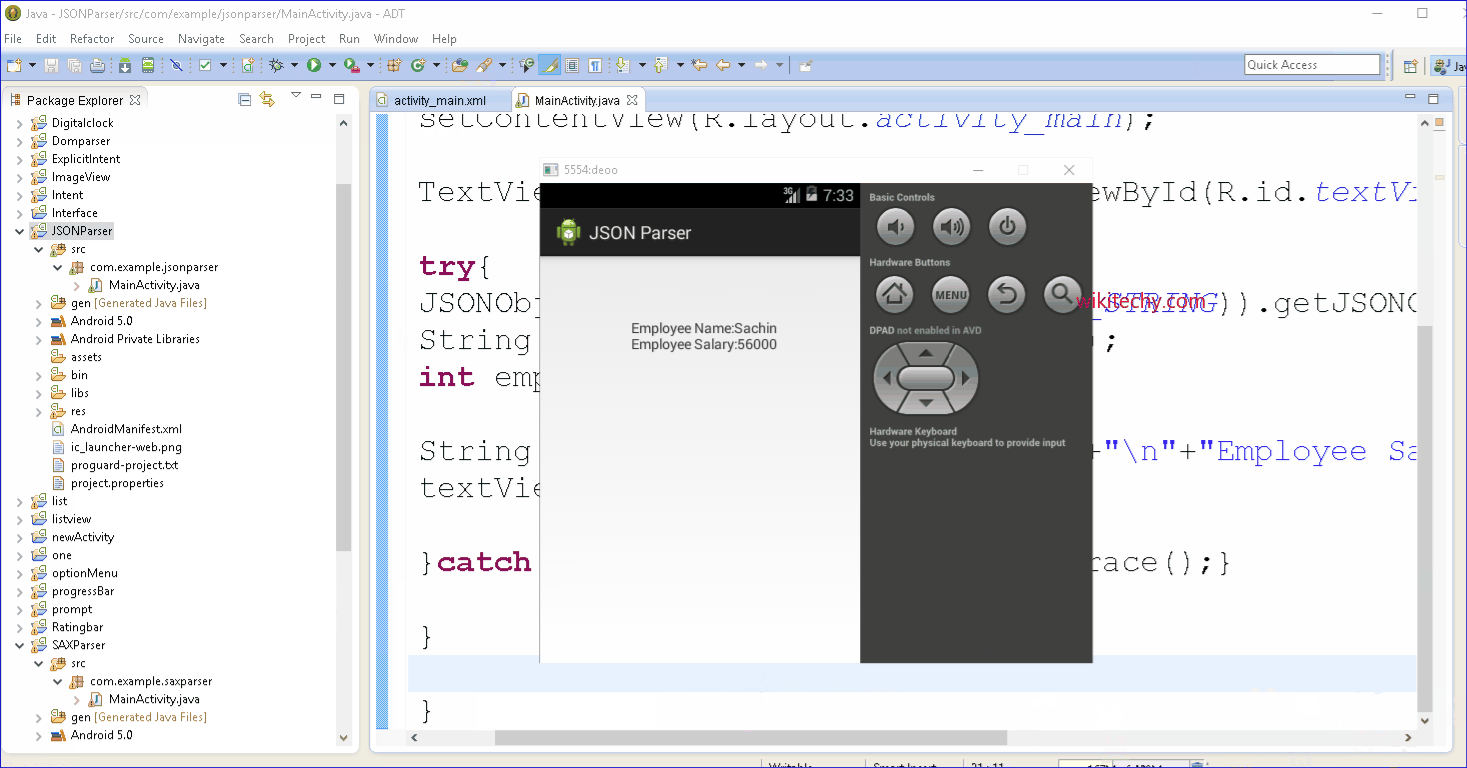
Output:
Parsing JSONArray in Android
Learn android - android tutorial - Json parser - android examples - android programs
- By the help of JSONArray class, you can parse the JSONArray containing the JSON Objects. Let's see the simple example to parse the json array.
- File: MainActivity.java
package com.example.jsonparsing2;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView output = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
String strJson="{ \"Employee\" :[{\"id\":\"101\",\"name\":\"Sonoo Jaiswal\",\"salary\":\"50000\"},{\"id\":\"102\",\"name\":\"Vimal Jaiswal\",\"salary\":\"60000\"}] }";
String data = "";
try {
// Create the root JSONObject from the JSON string.
JSONObject jsonRootObject = new JSONObject(strJson);
//Get the instance of JSONArray that contains JSONObjects
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonRootObject.optJSONArray("Employee");
//Iterate the jsonArray and print the info of JSONObjects
for(int i=0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++){
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
int id = Integer.parseInt(jsonObject.optString("id").toString());
String name = jsonObject.optString("name").toString();
float salary = Float.parseFloat(jsonObject.optString("salary").toString());
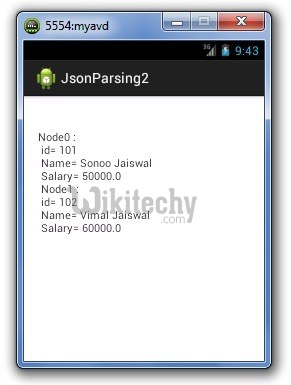
data += "Node"+i+" : \n id= "+ id +" \n Name= "+ name +" \n Salary= "+ salary +" \n ";
}
output.setText(data);
} catch (JSONException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
} click below button to copy the code from android tutorial team
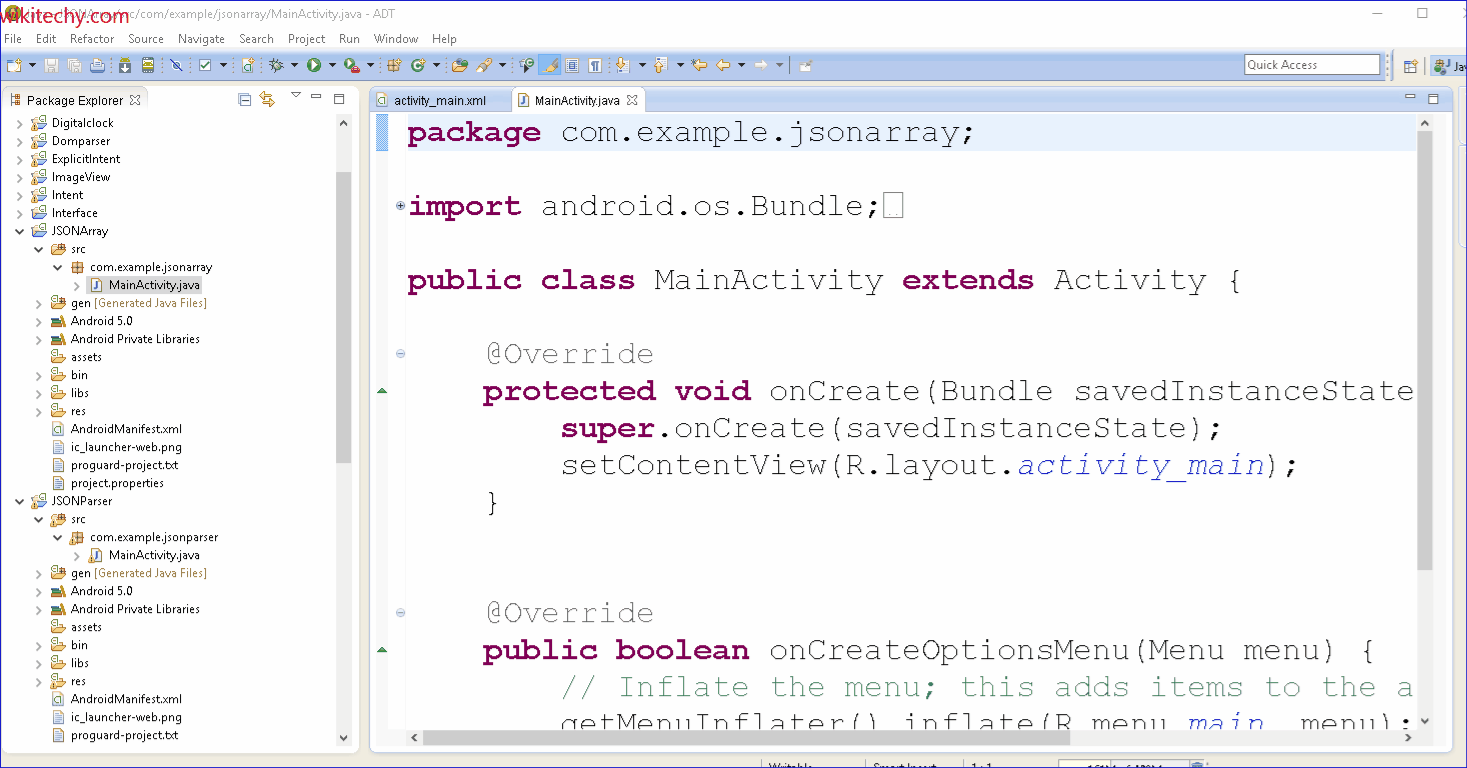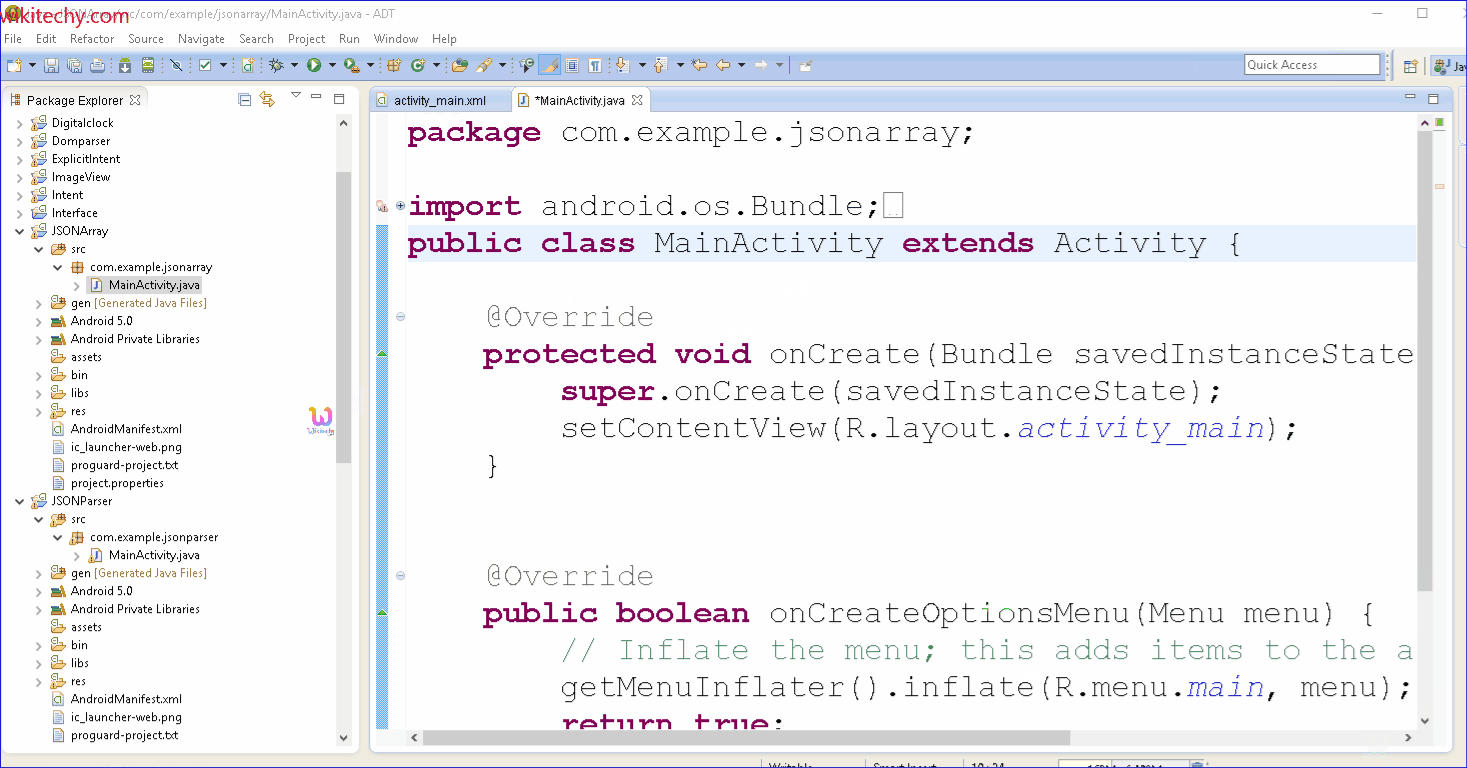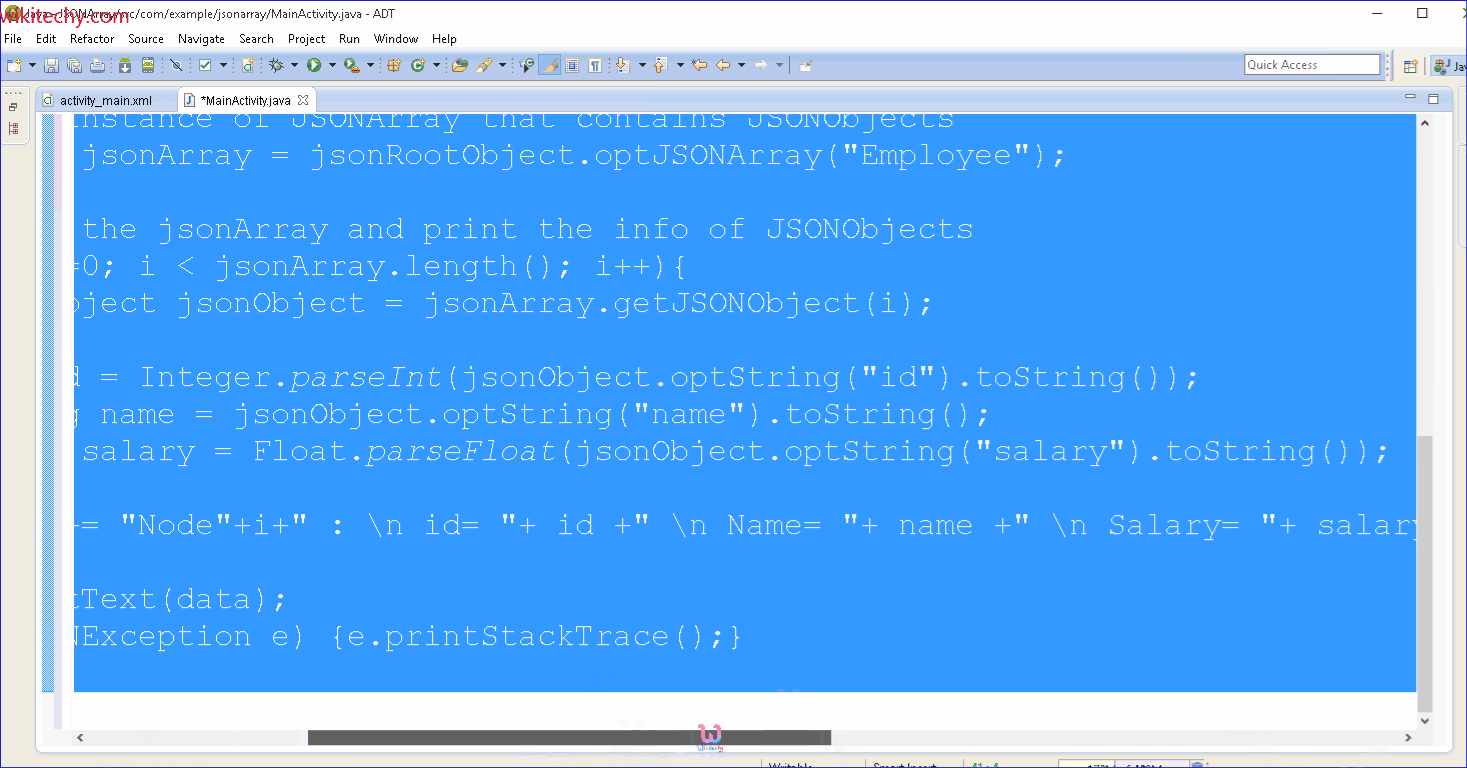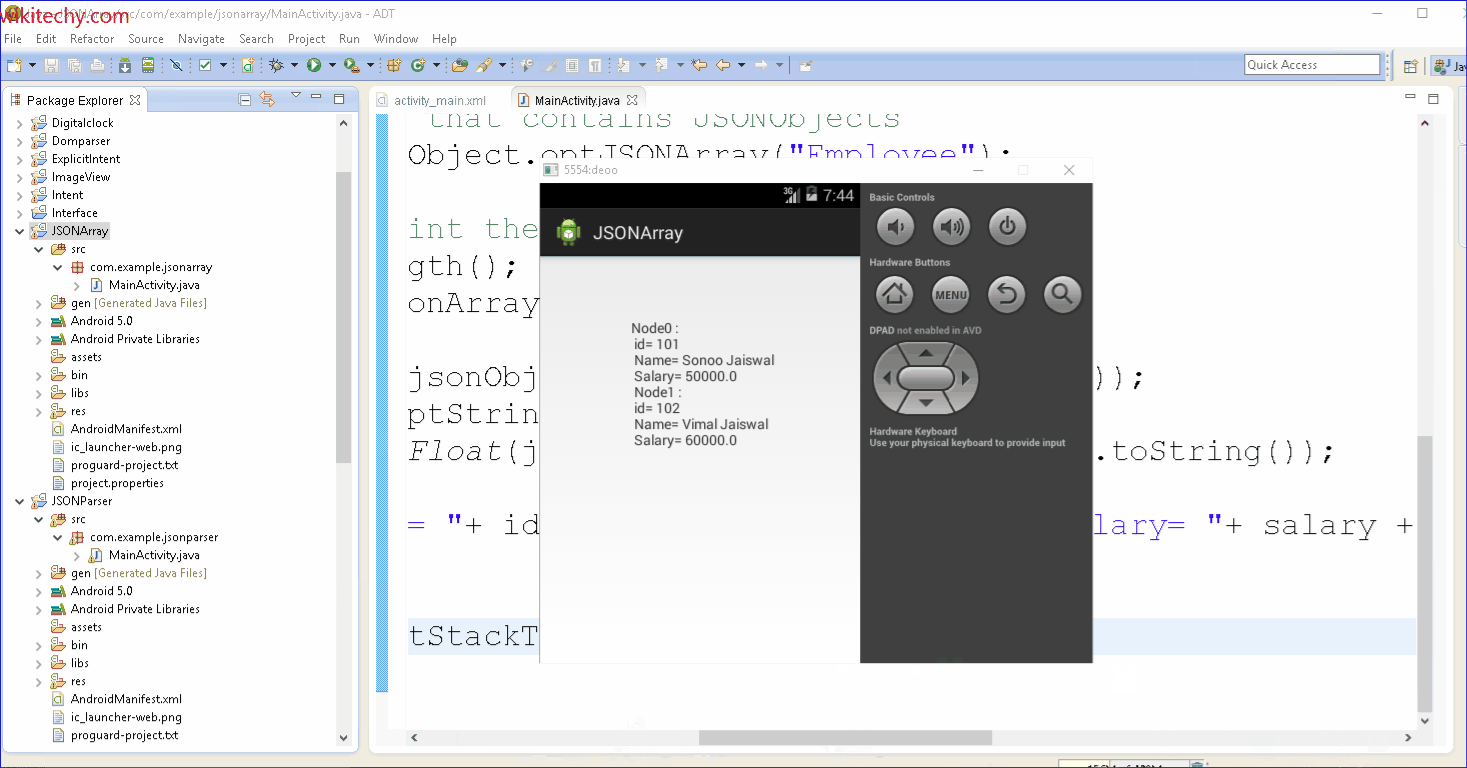
Output: