One of the major advantages of Object Oriented Programming is re-use. Inheritance is one of the mechanisms to achieve the same. In inheritance, a class (usually called superclass) is inherited by another class (usually called subclass). The subclass adds some attributes to superclass.
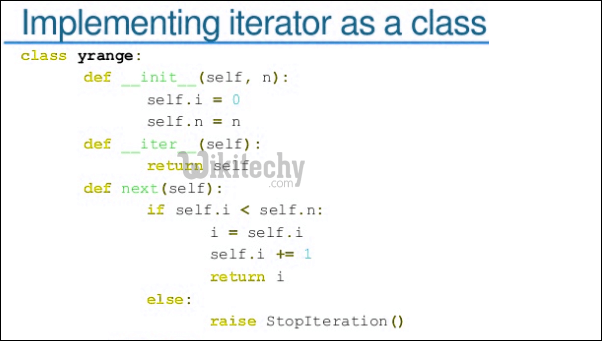
Below is a sample Python program to show how inheritance is implemented in Python.
python - Sample - python code :
# A Python program to demonstrate inheritance
# Base or Super class. Note object in bracket.
# (Generally, object is made ancestor of all classes)
# In Python 3.x "class Person" is
# equivalent to "class Person(object)"
class Person(object):
# Constructor
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
# To get name
def getName(self):
return self.name
# To check if this person is employee
def isEmployee(self):
return False
# Inherited or Sub class (Note Person in bracket)
class Employee(Person):
# Here we return true
def isEmployee(self):
return True
# Driver code
emp = Person("wikitechy1") # An Object of Person
print(emp.getName(), emp.isEmployee())
emp = Employee("wikitechy12") # An Object of Employee
print(emp.getName(), emp.isEmployee())python programming - Output :
wikitechy1 False wikitechy2 True
How to check if a class is subclass of another?
Python provides a function issubclass() that directly tells us if a class is subclass of another class.

python - Sample - python code :
# Python example to check if a class is
# subclass of another
class Base(object):
pass # Empty Class
class Derived(Base):
pass # Empty Class
# Driver Code
print(issubclass(Derived, Base))
print(issubclass(Base, Derived))
d = Derived()
b = Base()
# b is not an instance of Derived
print(isinstance(b, Derived))
# But d is an instance of Base
print(isinstance(d, Base))python programming - Output :
True False False True
What is object class?
Like Java Object class, in Python (from version 3.x), object is root of all classes.
In Python 3.x, “class Test(object)” and “class Test” are same.
In Python 2.x, “class Test(object)” creates a class with object as parent (called new style class) and “class Test” creates old style class (without object parent).
Does Python support Multiple Inheritance?
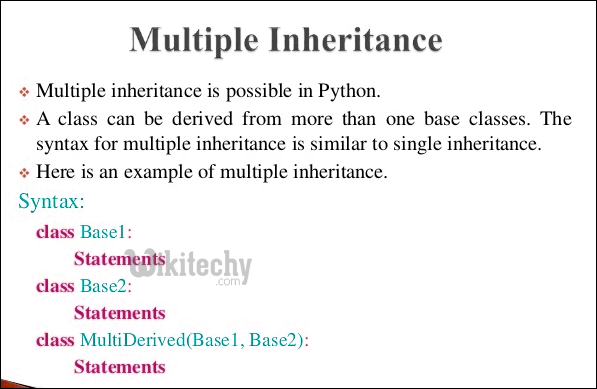
Unlike Java and like C++, Python supports multiple inheritance. We specify all parent classes as comma separated list in bracket.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python example to show working of multiple
# inheritance
class Base1(object):
def __init__(self):
self.str1 = "wikitechy1"
print "Base1"
class Base2(object):
def __init__(self):
self.str2 = "wikitechy2"
print "Base2"
class Derived(Base1, Base2):
def __init__(self):
# Calling constructors of Base1
# and Base2 classes
Base1.__init__(self)
Base2.__init__(self)
print "Derived"
def printStrs(self):
print(self.str1, self.str2)
ob = Derived()
ob.printStrs()python programming - Output :
wikitechy1 True E101
How to access parent members in a subclass?
- Using Parent class name
python - Sample - python code :
# Python example to show that base
# class members can be accessed in
# derived class using base class name
class Base(object):
# Constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.x = x
class Derived(Base):
# Constructor
def __init__(self, x, y):
Base.x = x
self.y = y
def printXY(self):
# print(self.x, self.y) will also work
print(Base.x, self.y)
# Driver Code
d = Derived(10, 20)
d.printXY()python programming - Output :
10, 20
- Using super()
We can also access parent class members using super.
python - Sample - python code :
# Python example to show that base
# class members can be accessed in
# derived class using super()
class Base(object):
# Constructor
def __init__(self, x):
self.x = x
class Derived(Base):
# Constructor
def __init__(self, x, y):
''' In Python 3.x, "super().__init__(name)"
also works'''
super(Derived, self).__init__(x)
self.y = y
def printXY(self):
# Note that Base.x won't work here
# because super() is used in constructor
print(self.x, self.y)
# Driver Code
d = Derived(10, 20)
d.printXY()python programming - Output :
(10, 20)
Note that the above two methods are not exactly same. In the next article on inheritance, we will covering following topics.
1) How super works? How accessing a member through super and parent class name are different?
2) How Diamond problem is handled in Python?
