Ruby on Rails - Ruby on Rails Migrations - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - rails tutorial - ruby rails
What is Ruby on Rails Migrations?
- Rails Migration define changes to your database schema, making it possible to use a version control system to keep things synchronized with the actual code.
- They use a Ruby DSL through which there is no need to write SQL by hand.
- SQL fragments can be edited by hand but then you have to tell other developers about the changes you made and then run them.
- You need to keep track of changes that need to be run against production machines next time you deploy.
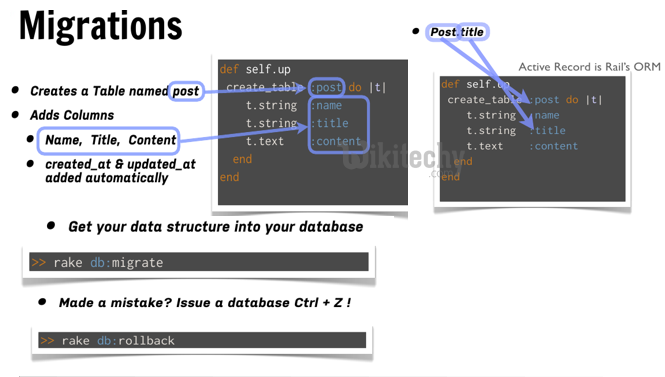
- Each migration is a new version of the database. Each migration modifies database by adding or removing tables, columnns or entries.
- Active record will update your db/schema.rb file to match up-to-date structure of your database.
What does Rails Migration Do?
- create_table(name, options)
- drop_table(name)
- rename_table(old_name, new_name)
- add_column(table_name, column_name, type, options)
- rename_column(table_name, column_name, new_column_name)
- change_column(table_name, column_name, type, options)
- remove_column(table_name, column_name)
- add_index(table_name, column_name, index_type)
- remove_index(table_name, column_name)
Migrations support all the basic data types:
The following is the list of data types that migration supports −
- string − for small data types such as a title.
- text − for longer pieces of textual data, such as the description.
- integer − for whole numbers.
- float − for decimals.
- datetime and timestamp − store the date and time into a column.
- date and time − store either the date only or time only.
- binary − for storing data such as images, audio, or movies.
- Boolean − for storing true or false values.
What are the Valid column options?
The following is the list of valid column options.
- limit ( :limit => “50” )
- default (:default => “blah” )
- null (:null => false implies NOT NULL)
NOTE − The activities done by Rails Migration can be done using any front-end GUI or directly on SQL prompt, but Rails Migration makes all those activities very easy.
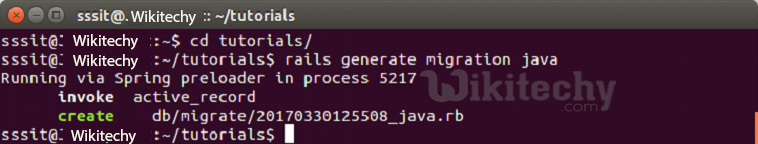
How to Create a Migration file?
Syntax to create a migration file:
application_dir> rails generate migration table_name
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
This will create a file with the name db/migrate/001_table_name.rb. A migration file contains the basic Ruby syntax that describe the data structure of a database table.
NOTE − Before running the migration generator, it is recommended to clean the existing migrations generated by model generators.
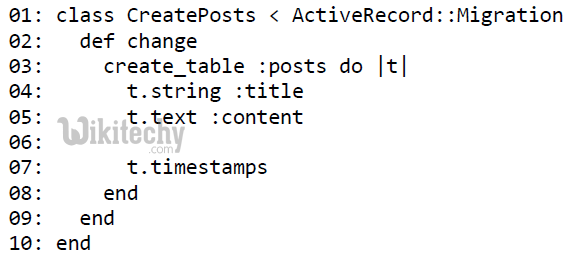
We will create two migrations corresponding to our three tables − books and subjects. Books migration should be as follows
tp> cd library
library> rails generate migration books
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
Above command generates the following code.
Learn ruby - ruby tutorial - create migration file in ruby on rail migration - ruby examples - ruby programs
ruby on rails tutorial tags - ruby , rail , ruby on rails , rail forum , ruby on rails tutorial , ruby tutorial , rails guides , rails tutorial , learn ruby
What are Editing Codes?
Go to db/migrate directory in the tutorials application. Write the following code in the present file 001_java.rb,
class Java < ActiveRecord::Migration
def self.up
create_table :java do |t|
t.column :title, :string, :limit => 32, :null => false
t.column :fee, :float
t.column :duration, :integer
t.column :index, :string
t.column :created_at, :timestamp
end
end
def self.down
drop_table :java
end
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
The method self.up is used during migrating to a new version and self.down is used to roll back any changes if needed.
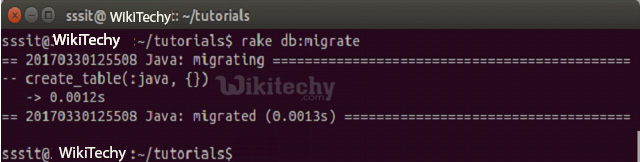
What is Run Migration?
- After creating all the required migration files you need to execute them. To execute migration file against database, run the following code:
rake db:migrate
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
It will create a "schema_info" table if doesn't exist. It tracks the current version of the database. If new migration will be created then that will be a new version for the database.