Ruby on Rails - Ruby on Rails - Controller - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - rails tutorial - ruby rails
What is rails Controller in ruby ?
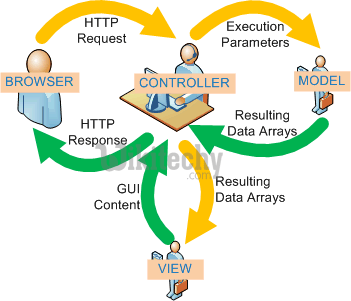
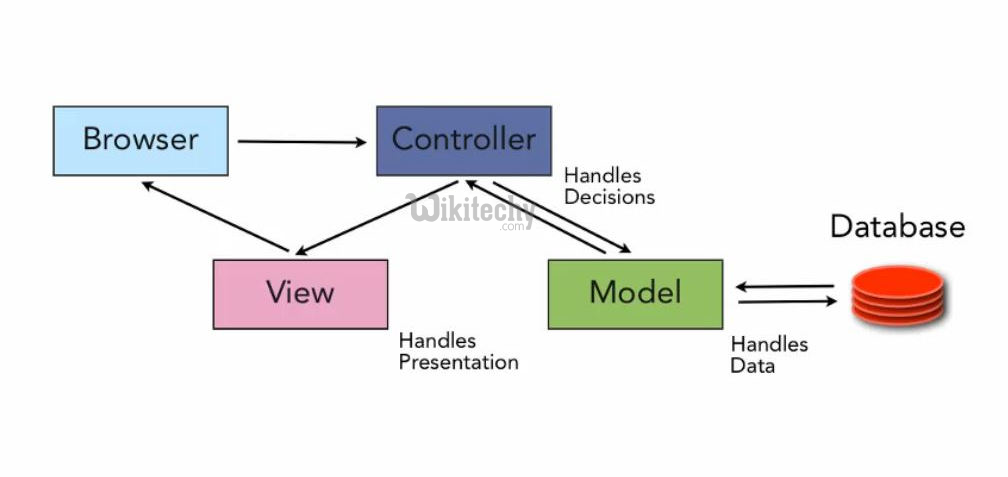
- The Rails controller is the normal center of your application. It coordinates the communication between the user, the views, and the model.
- The controller is also a home to a number of important additional services.
- It is responsible for routing external requests to inner actions. It handles people-friendly URLs extremely well.
- It attains caching, which can give applications orders-of-magnitude performance boosts.
- It accomplishes helper modules, which extend the abilities of the view templates without bulking up their code.
- It manages sessions, giving users the impression of an ongoing interaction with our applications.
- The process for creating a controller is easy. We will create just one controller here −
library\> rails generate controller Book
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
Learn Ruby On Rails Tutorials - Ruby On Rails Controller - Ruby On Rails Examples
- Notice that you are exploiting Book and using the particular form. This is a Rails standard that you should follow each time you create a controller.
- This command understands several tasks, of which the following are relevant here −
- It creates a file called app/controllers/book_controller.rb
- If you look at book_controller.rb, you will find it as follows −
class BookController < ApplicationController
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- Controller classes inherit from ApplicationController, which is the other file in the controllers folder: application.rb.
- The Application Controller holds code that can be run in all your controllers and it inherits from Rails ActionController::Base class.
- You don't need to worry with the ApplicationController as of yet, so let's just define a few method stubs in book_controller.rb. Based on your requirement, you could define any number of functions in this file.
- Modify the file to look like the following and save your changes. Note that it is upto you what name you want to give to these methods, but better to give relevant names.
Ruby on Rails - Controllers in mvc :




Implementing the list Method:
- The list process gives you a list of all the books in the record. This functionality will be achieved by the following lines of code.
- Edit the following lines in book_controller.rb file.
def list
@books = Book.all
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The @books = Book.all line in the list method tells Rails to search the books table and store each row it finds in the @books instance object.
Implementing the show Method:

- The show method displays only further details on a single book. This functionality will be achieved by the following lines of code.
def show
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The show method's @book = Book.find(params[:id]) line tells Rails to find only the book that has the id defined in params[:id].
- The params object is a container that enables you to pass values between method calls.
- For example, when you're on the page called by the list method, you can click a link for a specific book, and it passes the id of that book via the params object so that show can find the specific book.
Implementing the new Method:
- The new system lets Rails know that you will create a new object. So just add the following code in this method.
def new
@book = Book.new
@subjects = Subject.all
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The overhead method will be called when you will display a page to the user to take user input. Here second line grabs all the subjects from the database and puts them in an array called @subjects.
Implementing the create Method
- Once you take user input using HTML form, it is time to create a record into the database. To achieve this, edit the create method in the book_controller.rb to match the following −
def create
@book = Book.new(book_params)
if @book.save
redirect_to :action => 'list'
else
@subjects = Subject.all
render :action => 'new'
end
end
def book_params
params.require(:books).permit(:title, :price, :subject_id, :description)
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The first line creates a new occasion variable called @book that holds a Book object built from the data, the user submitted. The book_params method is used to collect all the fields from object :books.
- The data was passed from the new method to create using the params object.
- The next line is a provisional statement that redirects the user to the list method if the object saves correctly to the database.
- If it doesn't save, the user is sent back to the new method. The redirect_to method is similar to performing a meta refresh on a web page: it automatically forwards you to your destination without any user interaction.
- Then @subjects = Subject.all is required in case it does not save data successfully and it becomes similar case as with new option.
Implementing the edit Method
- The edit method looks nearly similar to the show method. Both methods are used to retrieve a single object based on its id and display it on a page. The only difference is that the show method is not editable.
def edit
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
@subjects = Subject.all
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- This method will be called to display data on the screen to be modified by the user. The second line grabs all the subjects from the database and puts them in an array called @subjects.
Implementing the update Method
- This method will be called after the edit method, when the user modifies a data and wants to update the changes into the database.
- The update method is similar to the create method and will be used to update existing books in the database.
def update
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
if @book.update_attributes(book_param)
redirect_to :action => 'show', :id => @book
else
@subjects = Subject.all
render :action => 'edit'
end
end
def book_param
params.require(:book).permit(:title, :price, :subject_id, :description)
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The update_attributes method is similar to the save method used by create but instead of creating a new row in the database, it overwrites the attributes of the existing row.
- Then @subjects = Subject.all line is required in case it does not save the data successfully, then it becomes similar to edit option.
Implementing the delete Method
- If you want to delete a record from the database then you will use this method. Implement this method as follows.
def delete
Book.find(params[:id]).destroy
redirect_to :action => 'list'
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- The first line finds the classified based on the parameter passed via the params object and then deletes it using the destroy method. The second line redirects the user to the list method using a redirect_to call.
Additional Methods to Display Subjects
- Assume you want to give a facility to your users to browse all the books based on a given subject. So, you can create a method inside book_controller.rb to display all the subjects. Assume the method name is show_subjects −
def show_subjects
@subject = Subject.find(params[:id])
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- Finally your book_controller.rb file will look as follows −
class BooksController < ApplicationController
def list
@books = Book.all
end
def show
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
end
def new
@book = Book.new
@subjects = Subject.all
end
def book_params
params.require(:books).permit(:title, :price, :subject_id, :description)
end
def create
@book = Book.new(book_params)
if @book.save
redirect_to :action => 'list'
else
@subjects = Subject.all
render :action => 'new'
end
end
def edit
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
@subjects = Subject.all
end
def book_param
params.require(:book).permit(:title, :price, :subject_id, :description)
end
def update
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
if @book.update_attributes(book_param)
redirect_to :action => 'show', :id => @book
else
@subjects = Subject.all
render :action => 'edit'
end
end
def delete
Book.find(params[:id]).destroy
redirect_to :action => 'list'
end
def show_subjects
@subject = Subject.find(params[:id])
end
end
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
- Then save your controller file.
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Validations :
- validate
- Generic validation method that can be used for custom validation
- validates_uniqueness_of :name
- validates_numericality_of :age
- validates_presence_of :address
- validates_format_of :email, :with => <regex>
ruby on rails tutorial tags - ruby , rail , ruby on rails , rail forum , ruby on rails tutorial , ruby tutorial , rails guides , rails tutorial , learn ruby
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Callbacks :
- before_create
- after_create
- before_save
- after_save
- before_update
- after_update
- before_destroy
- after_destroy
- before_validation
- after_validation
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Relations :
- has_many
- 1 ↔ m relationship with child
- belongs_to
- 1 ↔ 1 relationship with parent
- has_one
- 1 ↔ 1 relationship with child
- has_many :through =>
- Earlier versions: has_and_belongs_to_many
- m ↔ m relationship with peer
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Relations - has_one ↔ belongs_to :
class Customer < ActiveRecord::Base
has_one :address
end
class Address < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :customer
end
cust = Customer.new(:name => ‘Gautam Rege’)
address = Address.new(:customer => cust,
:street => ‘SB Road’, :zip => ‘411016’)
cust.address => #<Address object>
address.customer => # <Customer object>
Cust.address.zip => Zip code of address for this customerClicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
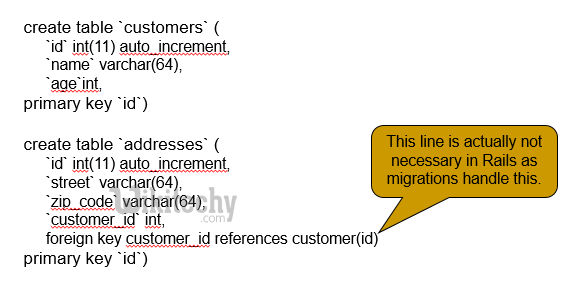
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Relations - has_many ↔ belongs_to :
create table `bank_accounts` (
`id` int(11) auto_increment,
`acc_number` varchar(64),
`branch` varchar(64),
`customer_id` int,
foreign key customer_id references customer(id)
primary key `id`)
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
class Customer < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many :bank_accounts
end
class BankAccount < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :customer
end
cust = Customer.new(:name => ‘Gautam Rege’)
bank = BankAccount.new(:customer => cust,
:acc_number => ‘123456’, :branch => ‘XYZ’)
cust.bank_accounts =>[ #<BankAccount object> array ]
bank.customer => # <Customer object> Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
Ruby on Rails - ActiveRecord Relations - has_many :through => :
create table `products` (
`id` int(11) auto_increment,
`cost` varchar(64),
primary key `id`)
create table `categories` (
`id` int(11) auto_increment,
`name` varchar(64),
primary key `id`)
create table `product_categories` (
`id` int(11) auto_increment,
`product_id` int,
`category_id` int
primary key `id`)
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
class Customer < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many :bank_account_customers
has_many :bank_accounts :through => :bank_account_customers
end
class BankAccount < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many : bank_account_customers
has_many :customers :through => : bank_account_customers
end
class BankAccountCustomer < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :bank_account
belongs_to :customer
end
customer.bank_accounts => [ #<BankAccount object> array ]
acc.customers => [ #<Customer object> array ]
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy - ruby on rails tutorial - rails guides - ruby rails - rubyonrails - learn ruby on rails - team
ruby on rails tutorial tags - ruby , rail , ruby on rails , rail forum , ruby on rails tutorial , ruby tutorial , rails guides , rails tutorial , learn ruby
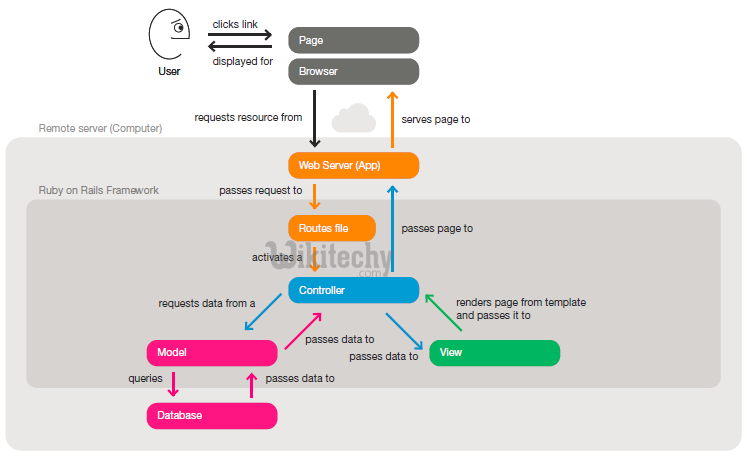
Web Application Process in ruby on rails - MVC web server access :
Step 1 : A user clicks a link to a page in a web application
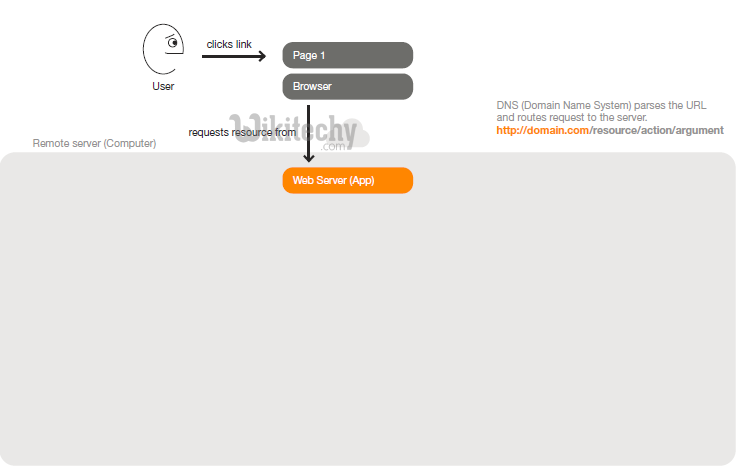
Step 2: The web server recieves the request URL (Universal Resource Location - Uniform Resource Locator). Rails uses a routes file to match the URL with a controller action.
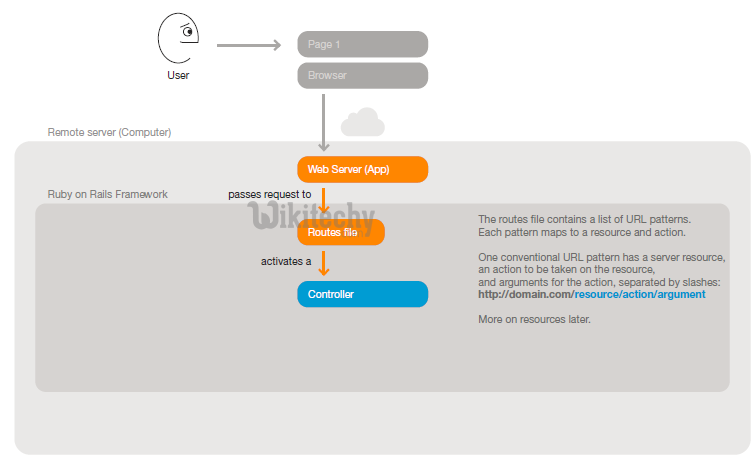
Step 3: The invoked controller action requests data from a model. The model queries the database and hands data back to the controller
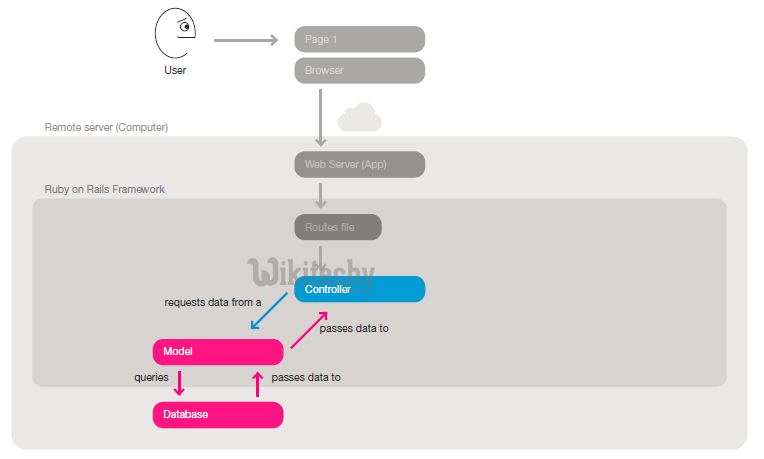
Step 4: The controller action then passes data to a corresponding view. The view uses the data and a template to compose a page.
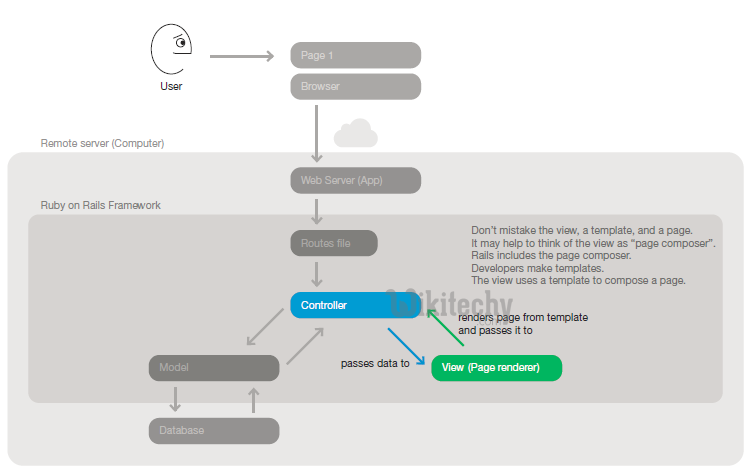
Step 5: The controller passes the complete page to the web server.
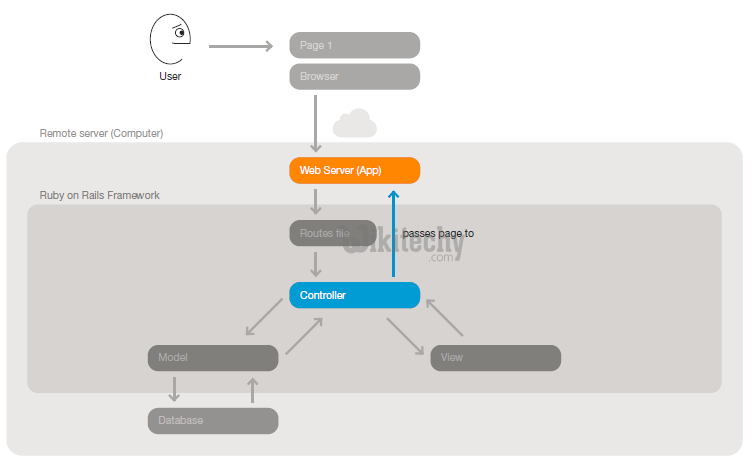
ruby on rails tutorial tags - ruby , rail , ruby on rails , rail forum , ruby on rails tutorial , ruby tutorial , rails guides , rails tutorial , learn ruby
Step 6: The web server serves the page to the browser. The browser renders the new page in place of the first one.
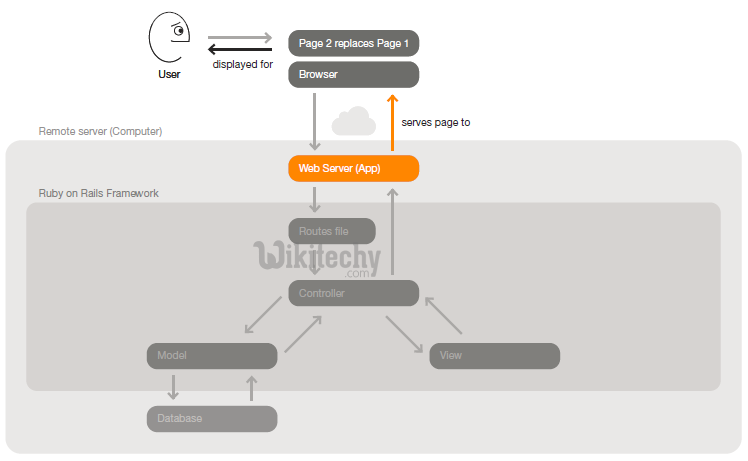
Step 7: Ruby on Rails provides a framework for this MVC flow. It enables developers to work on what makes their apps unique rather than spend time re-implementing conventions.