C - What is Pointer in C

Learn C - C tutorial - What is pointer in c - C examples - C programs
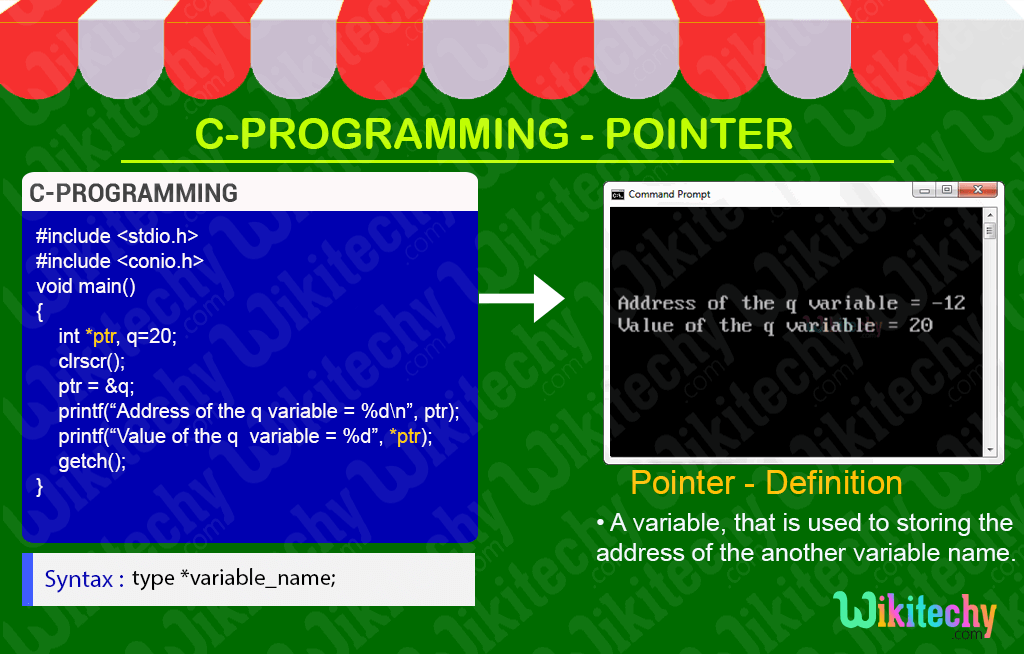
What is Pointer in C - Definition and Usage
- In C- Programming pointer is a variable, that is used for storing the address of the variable.
- In C-Programming Pointer is used for allocating the memory dynamically i.e. at run time.
C Syntax
type *variable_name; Note:
- The content of the C pointer is always the whole number i.e. address.
- Always C pointer is initialized to null, i.e. int *p = null.
- The value of null pointer is 0.
- “&” symbol is used to get the address of the variable.
- “*” symbol is used to get the value of the variable that the pointer is pointing to.
- If pointer is assigned to NULL, it means it is pointing to nothing.
- The size of pointer is 2 bytes (for 16 bit compiler).
Features of using pointers in C :
- Pointers allows passing of arrays and strings to functions more efficiently.
- Pointers makes possible to return more than one value from the function.
- Pointers reduce the length and complexity of program.
- Pointers increase the processing speed.
- Pointers save the memory.
Sample - C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int *ptr, q=20;
clrscr();
/* address of q is assigned to ptr */
ptr = &q;
printf(“Address of the q variable = %d\n”, ptr);
/* display q’s value using ptr variable */
printf(“Value of the q variable = %d”, *ptr);
getch();
}C Code - Explanation
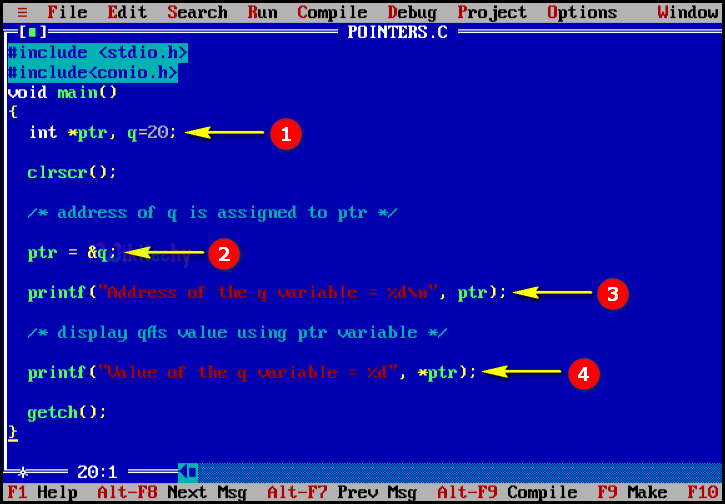
- In this statement we declare the pointer variable *ptr as integer and we assign the value for the variable “q=20” .
- In this statement we assign the address of the “q” variable to “ptr” .
- In this printf statement we print the address of the variable “q” .
- In this printf statement we print the value of the variable “q” .
Sample Output - Programming Examples
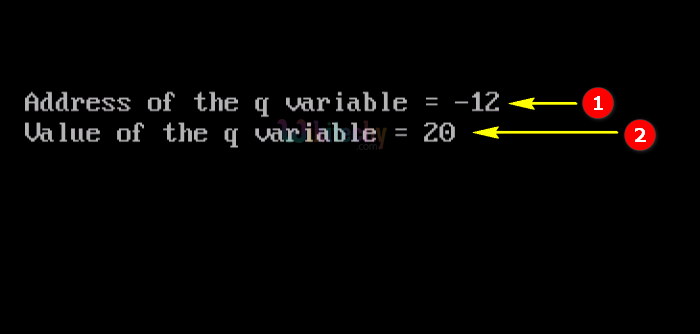
- Here in this output we display the address of the variable “q” as -12 shown in the console window.
- In this output we display the value of the variable “q” as 10 as shown in the console window.
