C - Switch Case
Learn C - C tutorial - Switch case - C examples - C programs
C - Switch Case - Definition and Usage
- In C- Programming the switch statement is used for defining multiple possibilities for the if statement.
- In general, the switch statement is executing only specific case statements based on the switch expression.
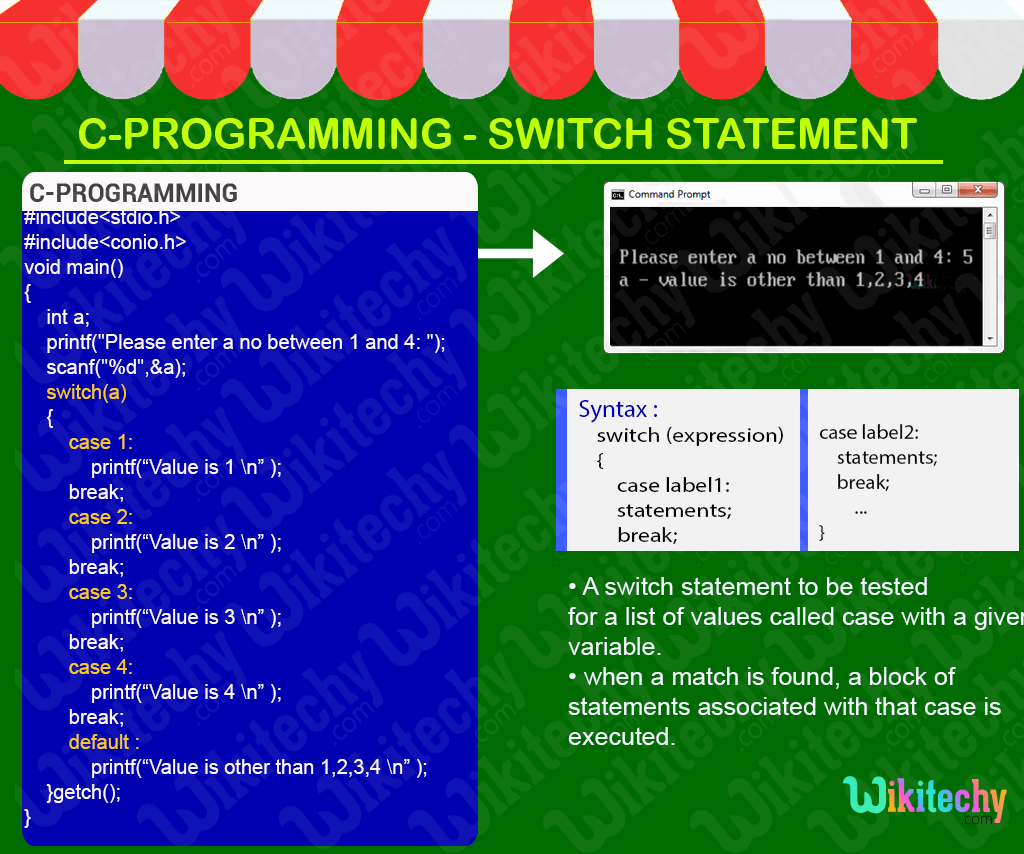
C Syntax
switch (expression)
{
case label1:
statements;
break;
case label2:
statements;
break;
default:
statements;
break;
} Sample - C Code
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a;
printf("Please enter a no between 1 and 4: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
switch(a)
{
case 1:
printf(“Value is 1 \n” );
break;
case 2:
printf(“Value is 2 \n” );
break;
case 3:
printf(“Value is 3 \n” );
break;
case 4:
printf(“Value is 4 \n” );
break;
default :
printf(“Value is other than 1,2,3,4 \n” );
}
getch();
}
C Code - Explanation :
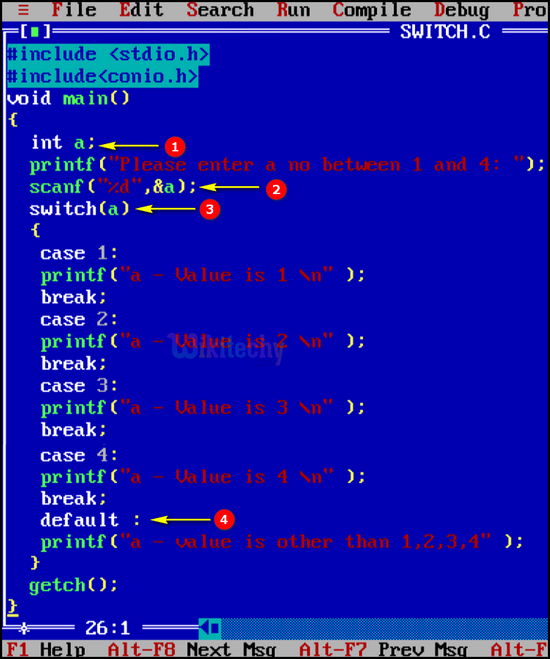
- Here we declare the variable “a” as integer.
- In this statement we get the value of the variable “a” using scanf statement.
- In this statement we get the switch case expression value of the variable “a”. and based on the variable value the case statement will be executed.
- If no case statement is matched it execute the default case statement.
Sample Output - Programming Examples
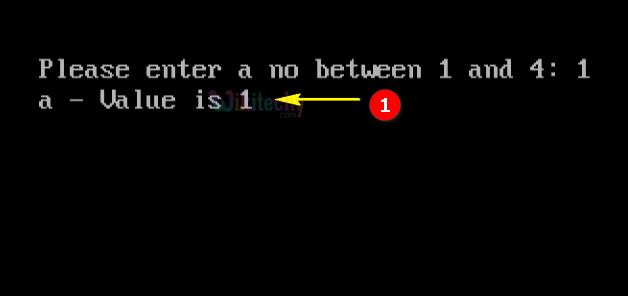
- Here in this output we have entered the number 1, which will switch to “Case 1” so the output of “a-value is 1” .
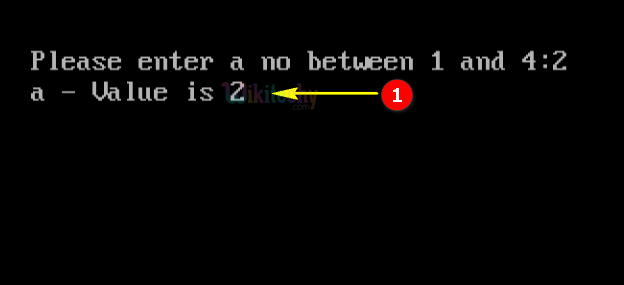
- Here in this output we have entered the number 2, which will switch to “Case 2” so the output of “a-value is 2” .
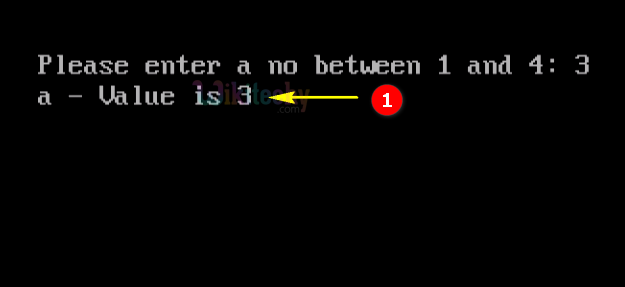
- Here in this output we have entered the number 3, which will switch to “Case 3” so the output of “a-value is 3” .
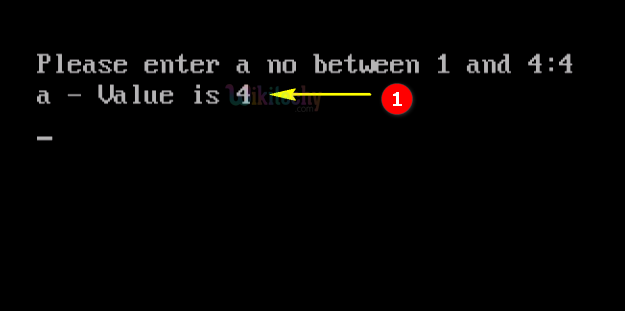
- Here in this output we have entered the number 4, which will switch to “Case 4” so the output of “a-value is 4” .
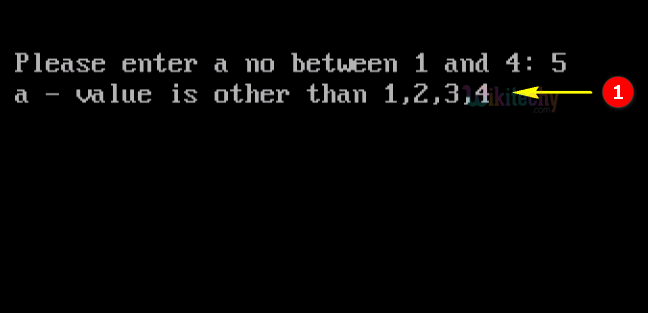
- Here in this output we have entered the number 5, which will switch to “default” so the output of “a-value is other than 1,2,3,4”.
