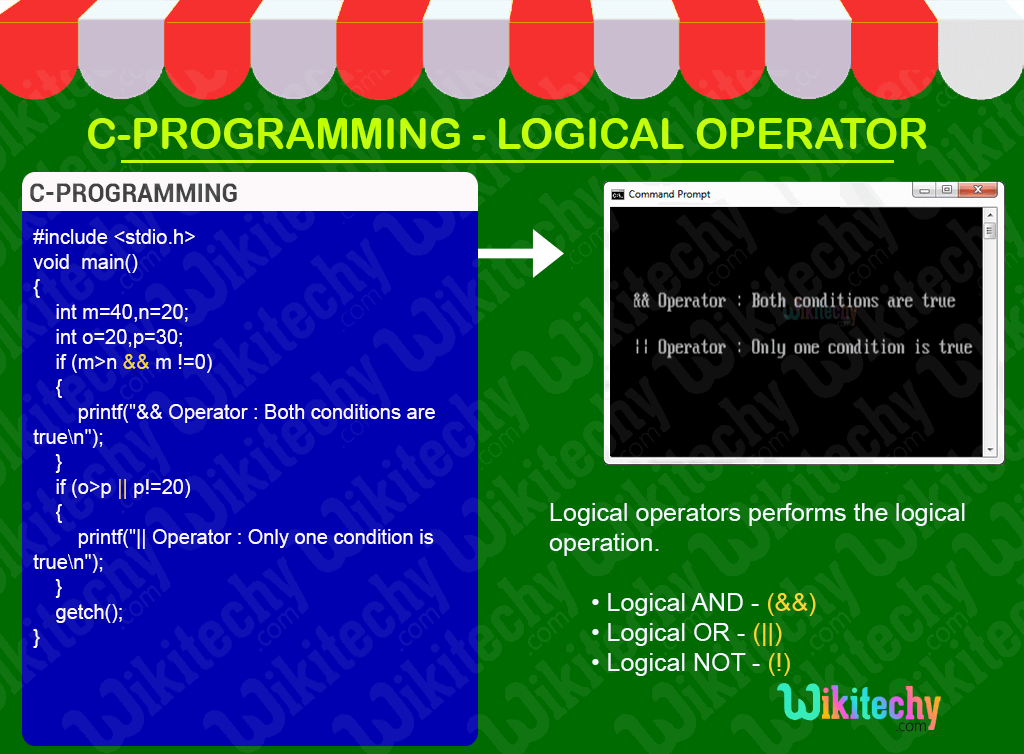
C - Logical Operators

Learn C - C tutorial - C logical operators - C examples - C programs
C Logical Operators - Definition and Usage
- In C-Programming the logical operators are used for defining the logical operation.
- Generally, there are three logical operators in c language.
- logical AND (&&)
- logical OR (||)
- logical NOT (!)
| Operators | Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| && | logical AND | (x>5)&&(y<5) | It returns true when both conditions are true |
| || | logical OR | (x>=10)||(y>=10) | It returns true when atleast one of the condition is true |
| ! | logical NOT | !((x>5)&&(y<5)) | It reverses the state of the operand “((x>5) && (y<5))”If “((x<5) && (y<5))” is true, logical NOT operator makes it false |
Sample - C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int m=40,n=20;
int o=20,p=30;
if (m>n && m !=0)
{
printf("&& Operator : Both conditions are true\n");
}
if (o>p || p!=20)
{
printf("|| Operator : Only one condition is true\n");
}
getch();
}C Code - Explanation
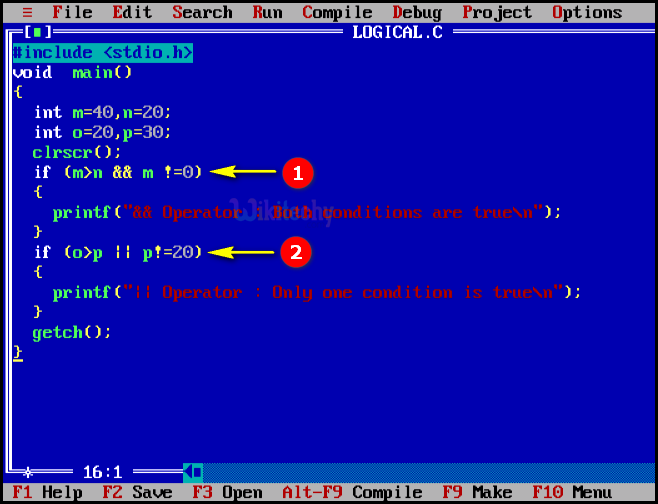
- In this statement we are using the logical operator AND(&&) if both conditions are true. Here m>n condition will be satisfied because m=40 and n=20 and the next condition is that m not equals to “0” is satisfied so the print statement prints the output as “&& operator: Both condition is true” .
- In this statement we are using the logical operator OR (||) so only one condition is satisfied. Here o>p condition will not be satisfied because o=20 and p=30 and also the next condition “m” is not equals to “20” so the print statement prints the output as “||operator: only one condition is true” .
Sample Output - Programming Examples
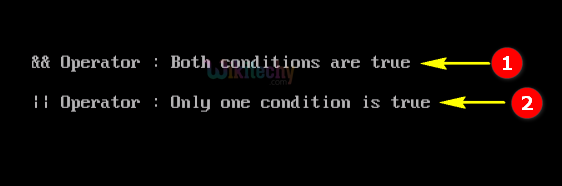
- Here in this output the “if” condition satisfy both condition so output will be displayed as “&& Operator: Both conditions are true” in the output window.
- Here in this output the “if” condition satisfy only one condition so output will be displayed as “|| Operator: Only one condition is true” in the output window.
