C - Dynamic Malloc Function - malloc in C
Structure and Linked List with C Programming in Tamil

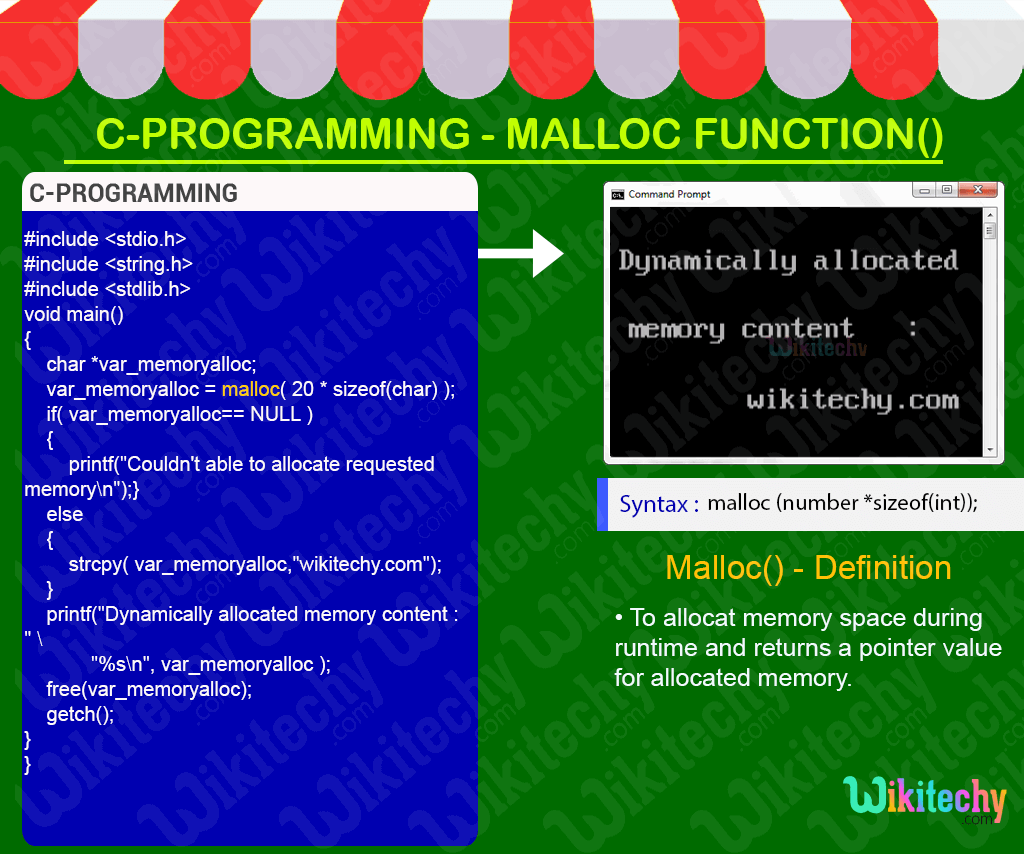
Learn C - C tutorial - Malloc in c - C examples - C programs
C Dynamic malloc() Function - Definition and Usage
- In C- Programming the malloc () function is used to allocate space in memory during the execution/runtime of the program.
- malloc () does not initialize the memory allocated during execution,It carries garbage value.
- malloc () function returns null pointer if it couldn’t able to allocate requested amount of memory.
C Syntax
malloc (number *sizeof(int));
or
ptr=(cast-type*)malloc(byte-size)
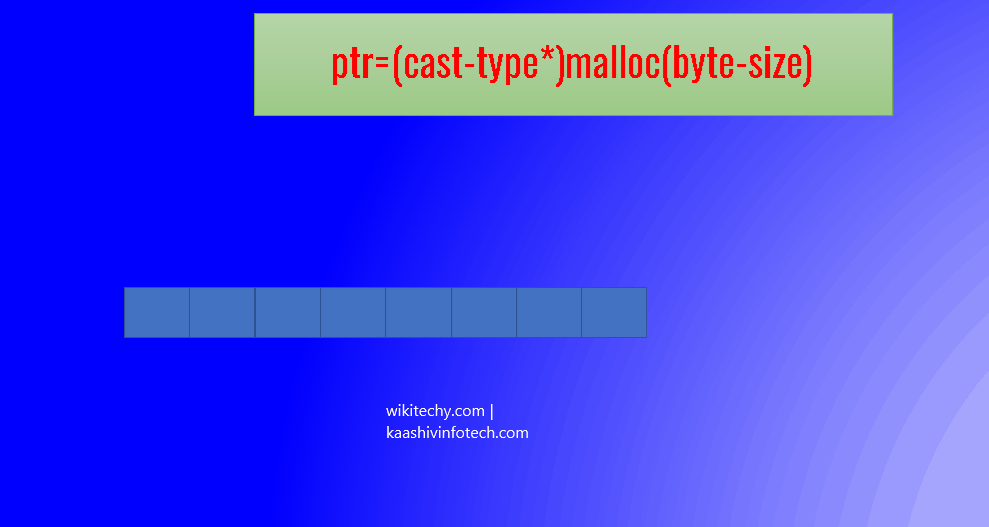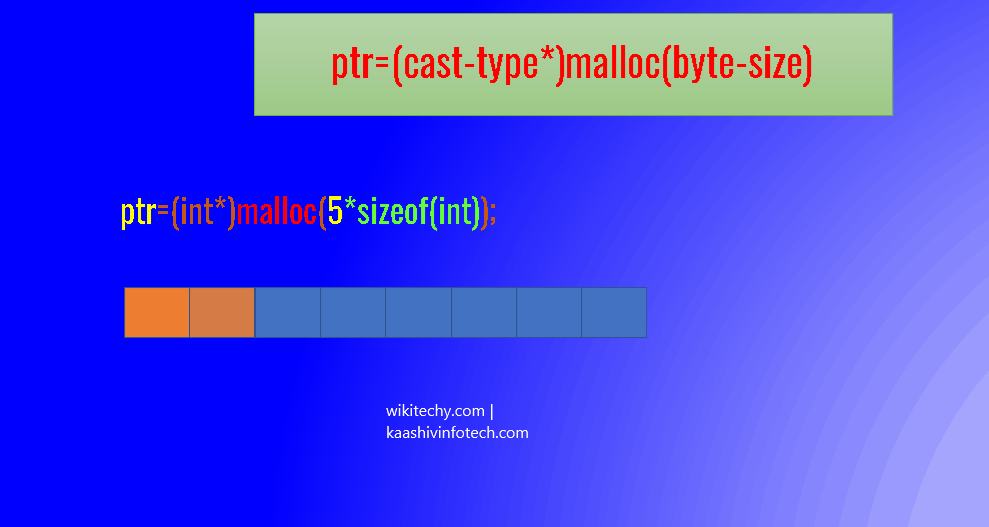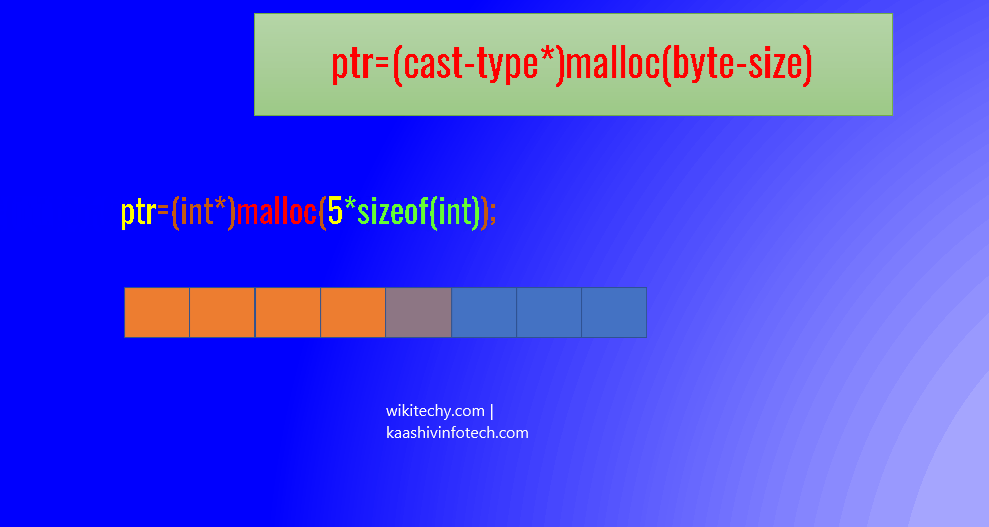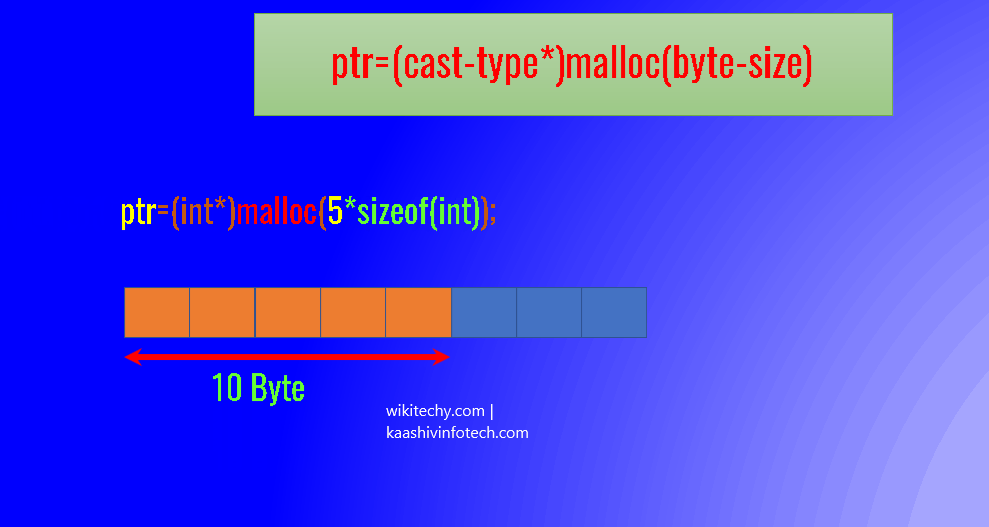
Example 1
Sample - C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main()
{
char *var_memoryalloc;
/* memory is allocated dynamically */
var_memoryalloc = malloc( 20 * sizeof(char) );
if( var_memoryalloc== NULL )
{
printf("Couldn't able to allocate requested memory\n");}
else
{
strcpy( var_memoryalloc,"wikitechy.com");
}
printf("Dynamically allocated memory content : " \
"%s\n", var_memoryalloc );
free(var_memoryalloc);
getch();
}C Code - Explanation
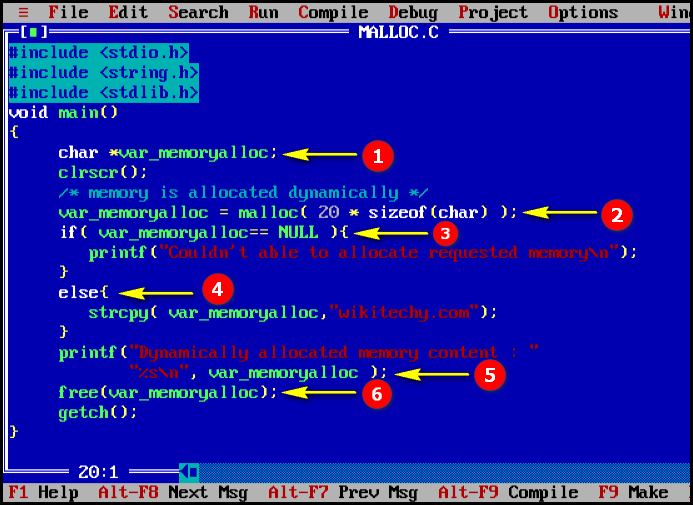
- In this statement we declare the pointer variable “var_memoryalloc” as character datatype.
- In this statement we allocate the memory space dynamically.
- In this condition we check whether the memory space is empty or not.
- In this statement the memory space will be allocated where the content will be assigned for the certain variable.
- Here in this statement we print the value of the variable “var_memoryalloc”.
- After the process gets completed, we free dynamically allocate memory space.
Sample Output - Programming Examples
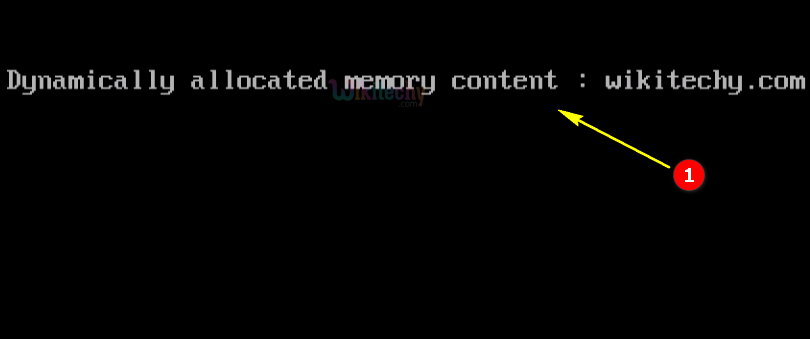
- Here in this output the dynamic memory will be allocated and the string “wikitechy.com” will be copied and printed as shown in the console window.
Example 2
Sample Code
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int n,i,*ptr,sum=0;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
ptr=(int*)malloc(n*sizeof(int));
if(ptr==NULL)
{
printf("Sorry! unable to allocate memory");
exit(0);
}
printf("Enter elements of array:");
for(i=0;i<n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",ptr+i);
sum+=*(ptr+i);
}
printf("Sum=%d",sum);
free(ptr);
getch();
}
Output
Enter number of elements :3
Enter elements of array:10
10
10
sum=30