define in C
Learn C - C tutorial - Define in c - C examples - C programs
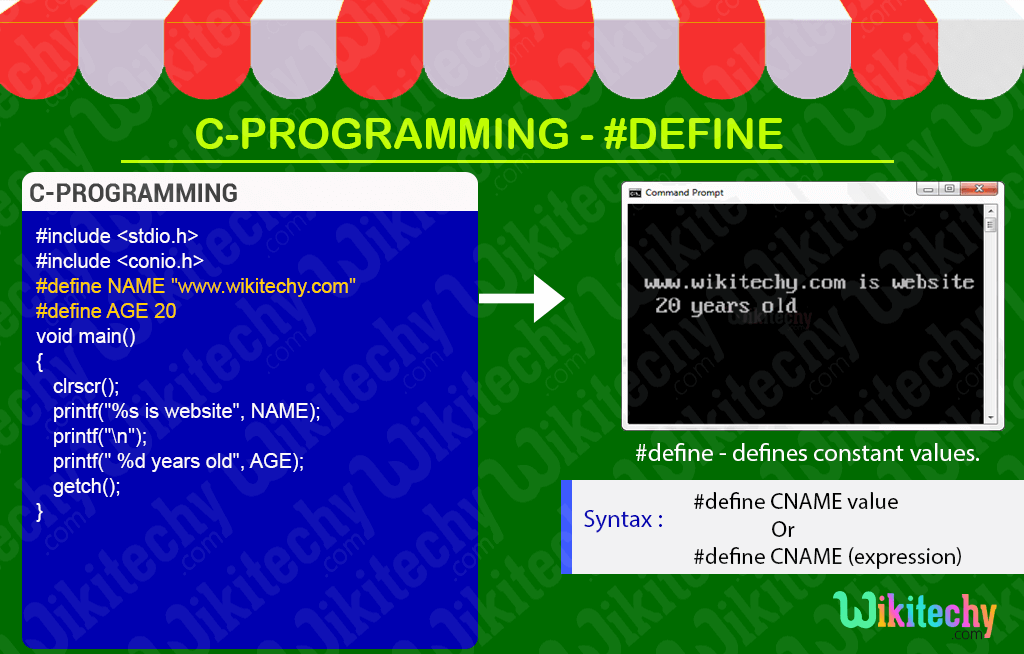
define in C - #define - Definition and Usage
- In C Language, the #define directive allows the definition of macros within your source code.
- These macro definitions allow constant values to be declared for use throughout your code.
- This macro defines constant value and can be any of the basic data types..
C Syntax
(#define CNAME value
or
#define CNAME (expression) );Syntax explanation:
- CNAME : CNAME is specified as a name of the constant. Most of the C programmers define their constant names in uppercase , but it is not a requirement for the C Language .
- Value : Value is representing value of the constant.
- Expression : Expression (or Statements) is assigned to the constant. The expression must be enclosed in parentheses if it contains operators.
#include :
- In C Programming, #include directive tells the preprocessor to insert the contents of another file into the source code at the point where the #include directive is found.
- Include directives are typically used to include the C header files for C functions that are held outsite of the current source file.
- The source code of the file “file_name” is included in the main C program where “#include
” is mentioned.
C Syntax
(#include <header_file>
Or
#include "header_file");- header_file : A header file is a C file that typically ends in ".h" and contains declarations and macro definitions which can be shared between several source files .
Sample - C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define AGE 20
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("%s is website", NAME);
printf("\n");
printf(" %d years old", AGE);
getch();
}C Code - Explanation
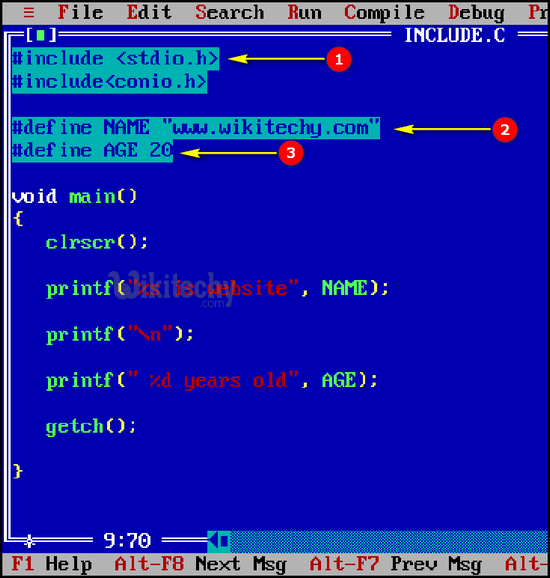
- In C programming #include<stdio.h> specifies the statement which tells the compiler to insert the contents of stdio at that particular place . A header file is a C file, that typically ends in ".h".
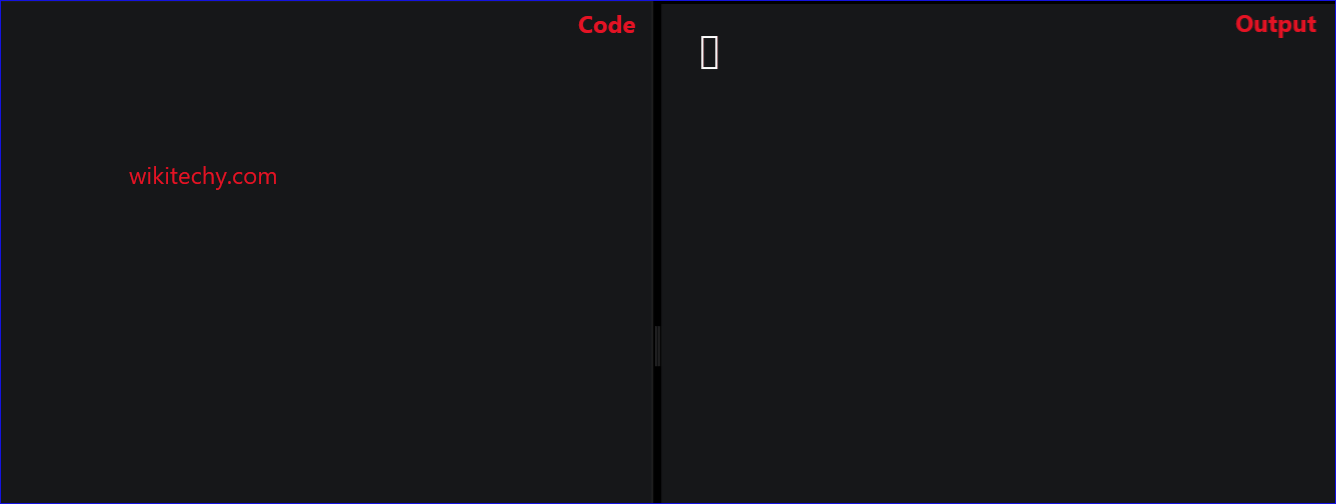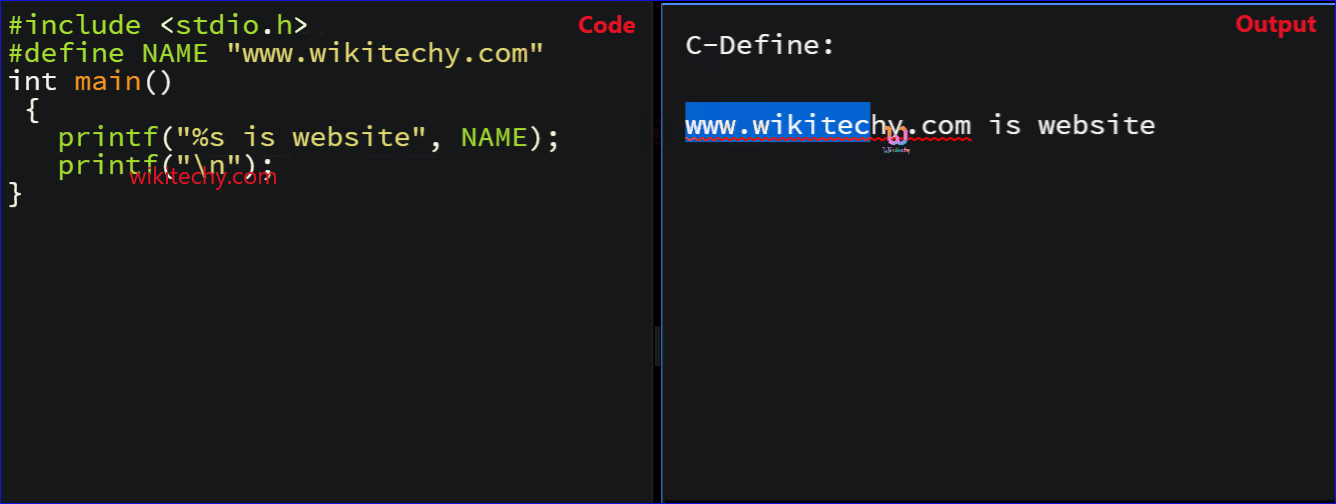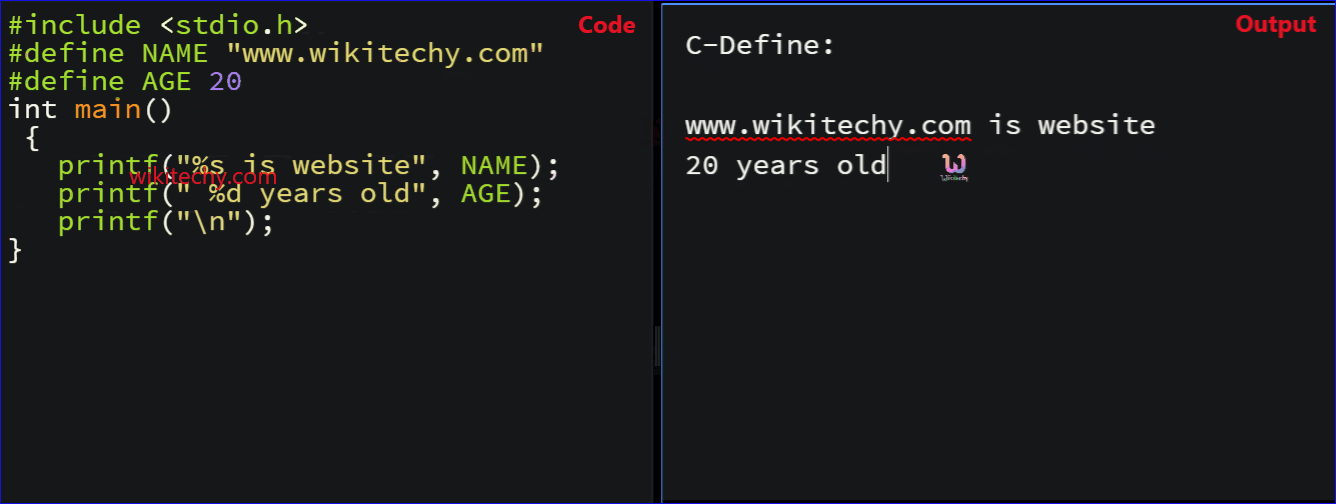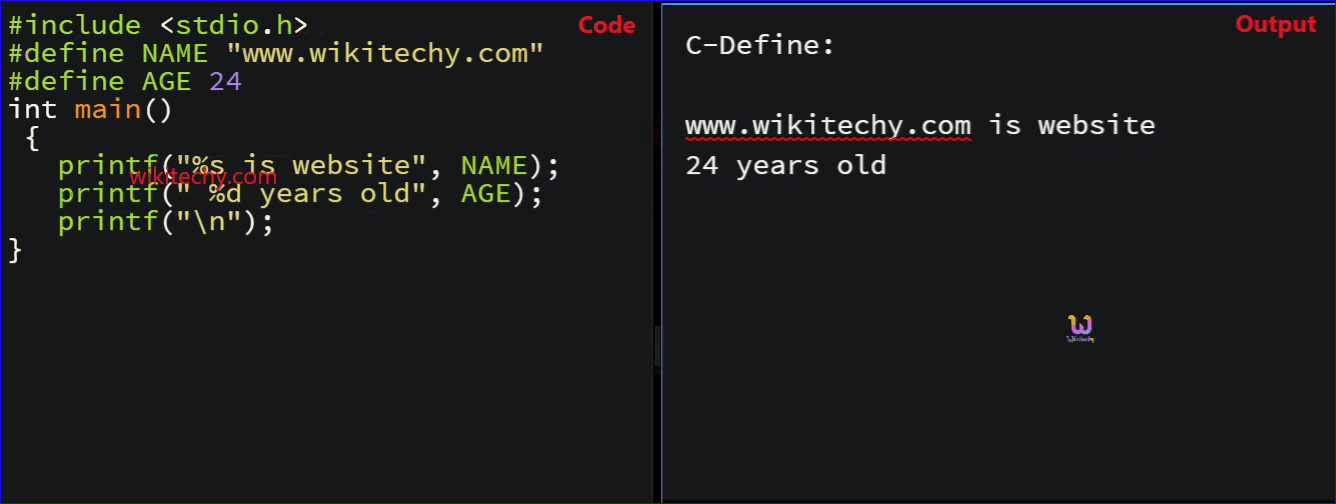
- In this example, #define NAME “www.wikitechy.com” specifies the constant “NAME” which contains the value “www.wikitechy.com”.
- In this example, #define AGE 20 specifies the constant name as AGE containing the value “20”.
Sample Output - Programming Examples
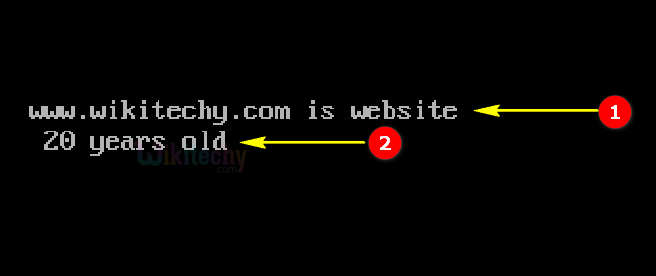
- Here “www.wikitechy.com is website” represents the print statement which defines the Constant NAME .
- Here “20 years old” represents the print statement which defines the Constant AGE .
