Relational operators in C - Relational operators Examples
Learn c - c tutorial - Relational operators in c - c examples - c programs
Relational operators in c
- The Relational operators is the C Programming Operator, which is mostly used either in If Conditions or Loops.
- Relational operators are commonly used to check the relationship between two variables.
- If the relation is true then it will return value 1 or if the relation is false then it will return value 0.
- Below table shows all the Relational Operators in C programming.
| Relational Operators In C | Usage | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| > | a > b | a is greater than b | 9 > 3 returns true (1) |
| < | a < b | a is less than b | 9 < 3 returns false (0) |
| >= | a >= b | a is greater than or equal to b | 9 >= 3 returns true (1) |
| <= | a <= b | a is less than or equal to b | 9 <= 3 return false (0) |
| == | a == b | a is equal to b | 9 == 3 returns false (0) |
| != | a != b | a is not equal to b | 9 != 3 returns true(1) |
a) Relational operators in c
Sample Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=b=c=100;
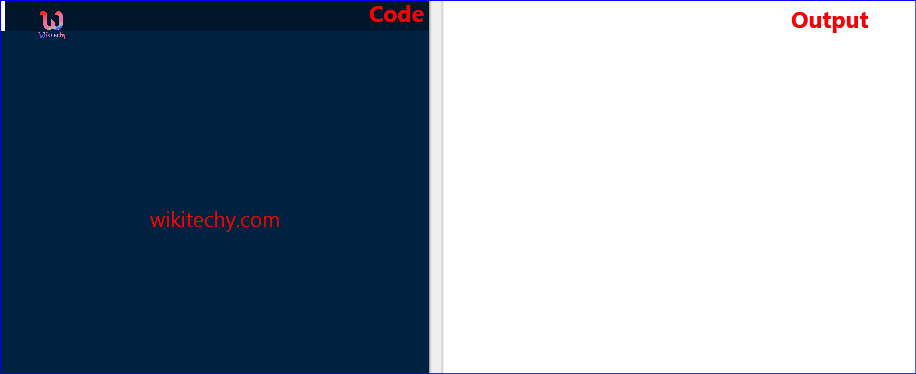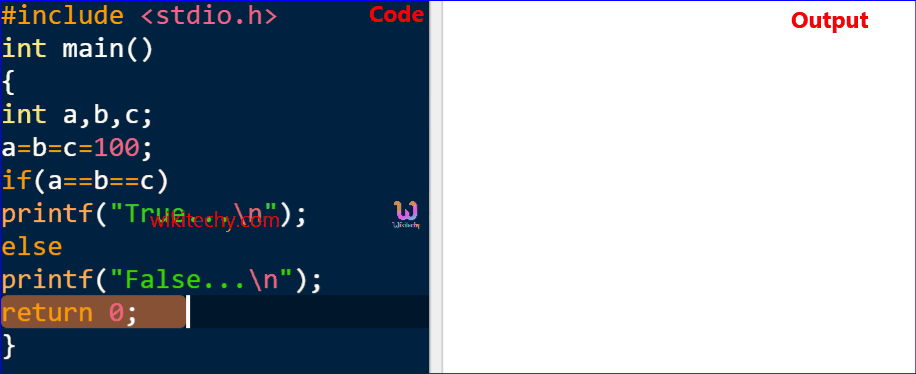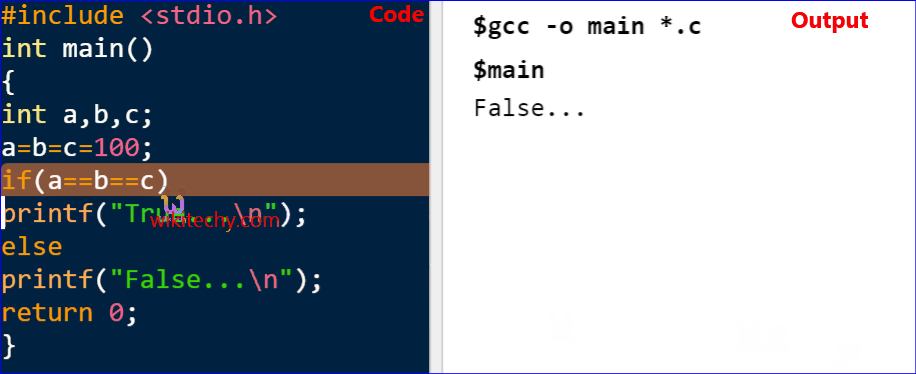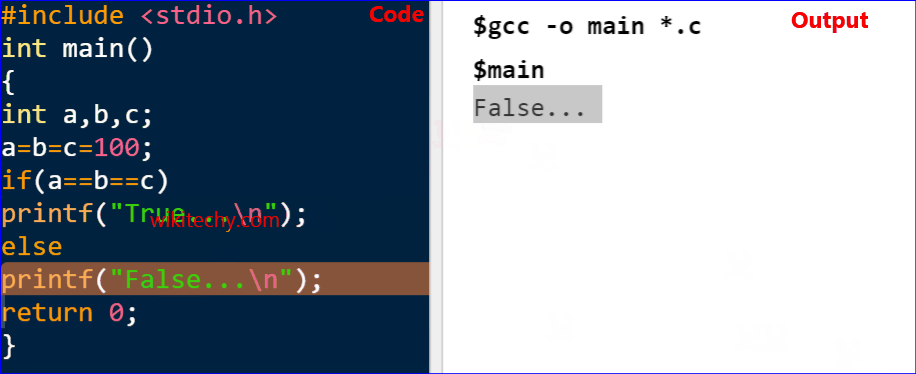
if(a==b==c)
printf("True...\n");
else
printf("False...\n");
return 0;
}
Output
False...
b) How Expression a=b=c (Multiple Assignment) Evaluates in C Programming

Learn c - c tutorial - Relational operators in c - c examples - c programs
Sample Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=0;
b=0;
c=100;
printf("Before Multiple Assignent a=%d,b=%d,c=%d\n",a,b,c);
//Multiple Assignent
a=b=c;
printf("After Multiple Assignent a=%d,b=%d,c=%d\n",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
Output
Before Multiple Assignent a=0,b=0,c=100
After Multiple Assignent a=100,b=100,c=100
