C++ Struct | Structures in C++ - Learn C++ - C++ Tutorial - C++ programming

Learn c++ - c++ tutorial - c++ struct - c++ examples - c++ programs
What is Structure in C++
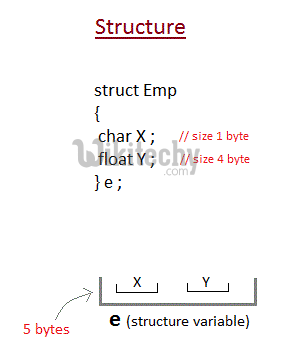
- Structure is a collection of variables of different data types under a single name. It is similar to a class in that, both holds a collection of data of different data types.
- For example: You want to store some information about a person: his/her name, citizenship number and salary. You can easily create different variables name, citNo, salary to store this information separately.
- However, in the future, you would want to store information about multiple persons. Now, you'd need to create different variables for each information per person: name1, citNo1, salary1, name2, citNo2, salary2
- You can easily visualize how big and messy the code would look. Also, since no relation between the variables (information) would exist, it's going to be a daunting task.
- A better approach will be to have a collection of all related information under a single name Person, and use it for every person. Now, the code looks much cleaner, readable and efficient as well.
- This collection of all related information under a single name Person is a structure.
learn c++ tutorials - structure Example
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
How to declare a structure in C++ programming?
- The struct keyword defines a structure type followed by an identifier (name of the structure).
- Then inside the curly braces, you can declare one or more members (declare variables inside curly braces) of that structure. For example:
struct Person
{
char name[50];
int age;
float salary;
};- Here a structure person is defined which has three members: name, age and salary.
- When a structure is created, no memory is allocated.
- The structure definition is only the blueprint for the creating of variables. You can imagine it as a datatype. When you define an integer as below:
int foo;- The int specifies that, variable foo can hold integer element only. Similarly, structure definition only specifies that, what property a structure variable holds when it is defined.
- Note: Remember to end the declaration with a semicolon (;)
How to define a structure variable?
- Once you declare a structure person as above. You can define a structure variable as:
Person bill;- Here, a structure variable bill is defined which is of type structure Person.
- When structure variable is defined, only then the required memory is allocated by the compiler.
- Considering you have either 32-bit or 64-bit system, the memory of float is 4 bytes, memory of int is 4 bytes and memory of char is 1 byte.
- Hence, 58 bytes of memory is allocated for structure variable bill.
How to access members of a structure?
- The members of structure variable are accessed using a dot (.) operator.
- Suppose, you want to access age of structure variable bill and assign it 50 to it. You can perform this task by using following code below:
bill.age = 50;Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Example: C++ Structure
- C++ Program to assign data to members of a structure variable and display it.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person
{
char name[50];
int age;
float salary;
};
int main()
{
Person p1;
cout << "Enter Full name: ";
cin.get(p1.name, 50);
cout << "Enter age: ";
cin >> p1.age;
cout << "Enter salary: ";
cin >> p1.salary;
cout << "\nDisplaying Information." << endl;
cout << "Name: " << p1.name << endl;
cout <<"Age: " << p1.age << endl;
cout << "Salary: " << p1.salary;
return 0;
}
Output
Enter Full name: Magdalena Dankova
Enter age: 27
Enter salary: 1024.4
Displaying Information.
Name: Magdalena Dankova
Age: 27
Salary: 1024.4
- Here a structure Person is declared which has three members name, age and salary.
- Inside main() function, a structure variable p1 is defined. Then, the user is asked to enter information and data entered by user is displayed.
