C++ Classes and Objects - Learn C++ - C++ Tutorial - C++ programming
Learn c++ - c++ tutorial - c++ classes and -objects - c++ examples - c++ programs
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
C++ Class:
- Before you create an object in C++, you need to define a class.
- A class is a blueprint for the object.
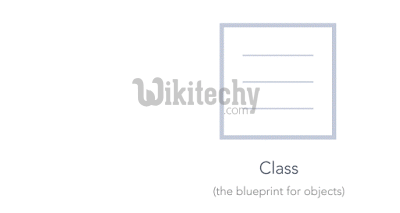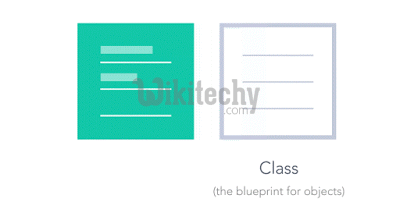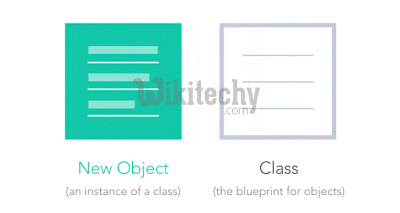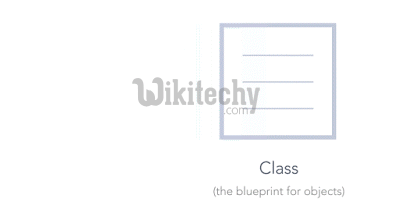
- We can think of class as a sketch (prototype) of a house. It contains all the details about the floors, doors, windows etc. Based on these descriptions we build the house. House is the object.
- As, many houses can be made from the same description, we can create many objects from a class.
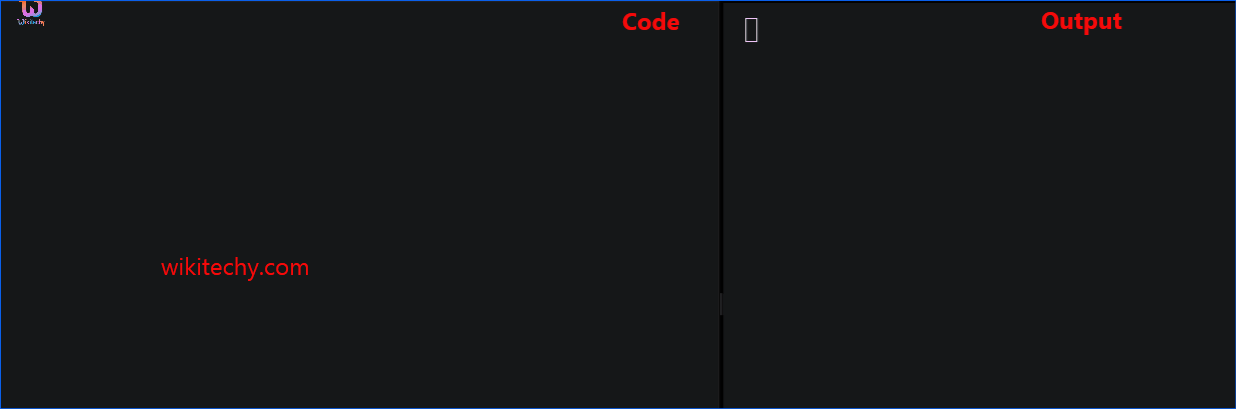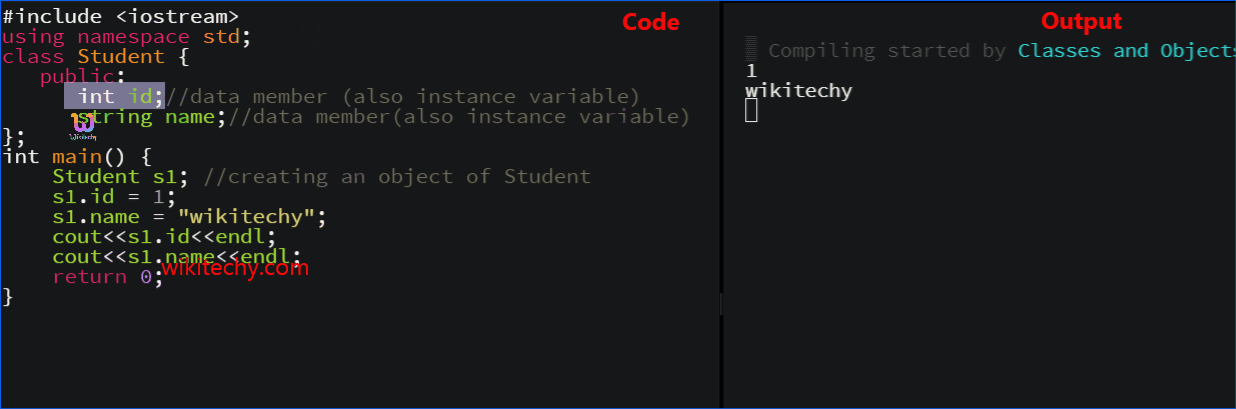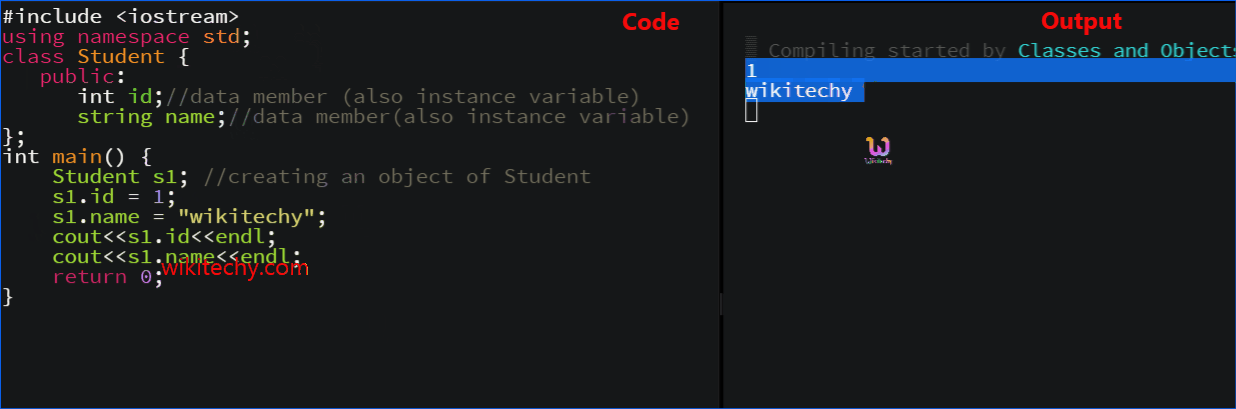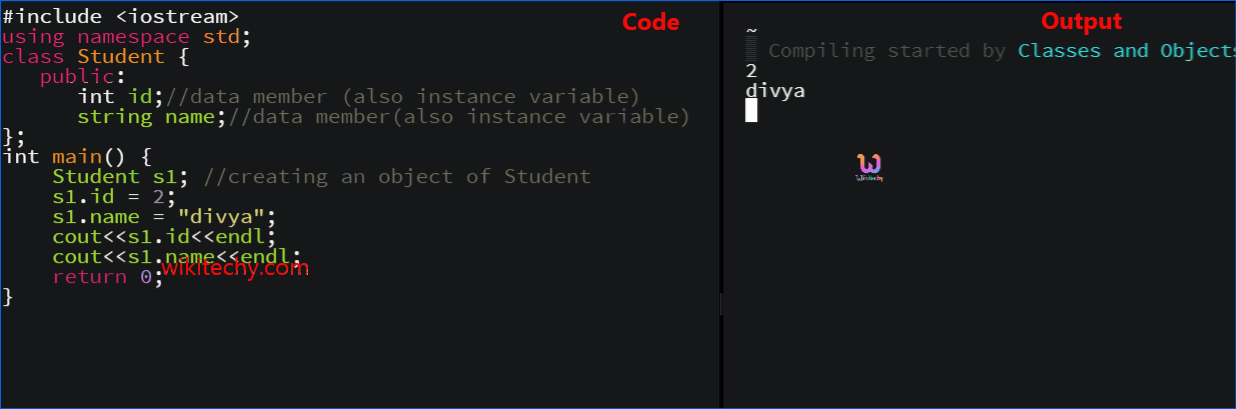
learn c++ tutorials - class object model in c++ Example
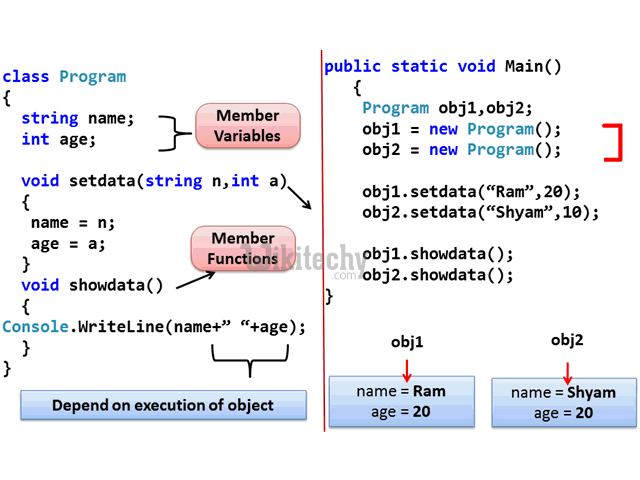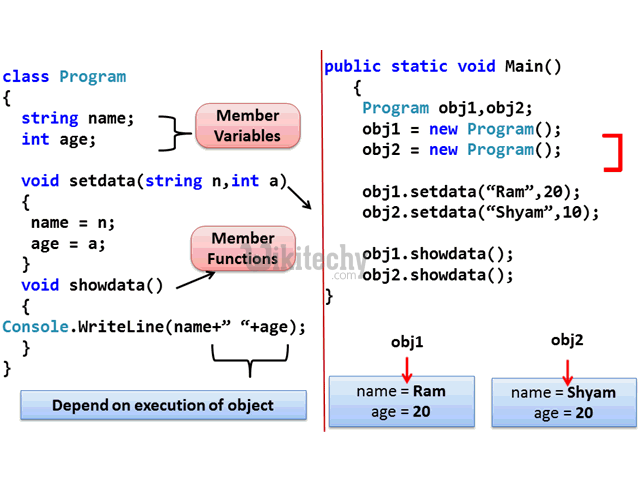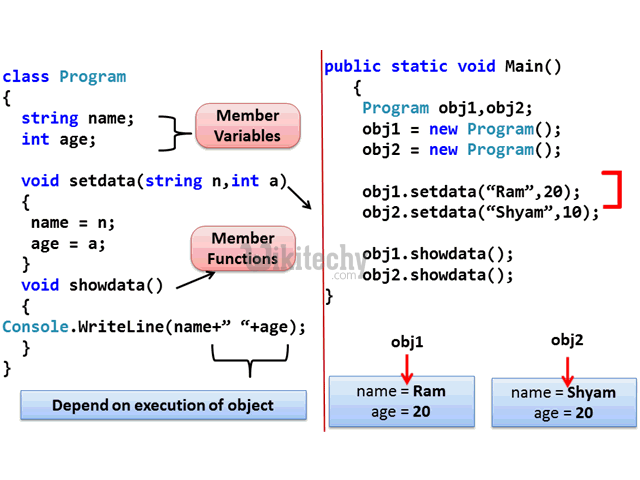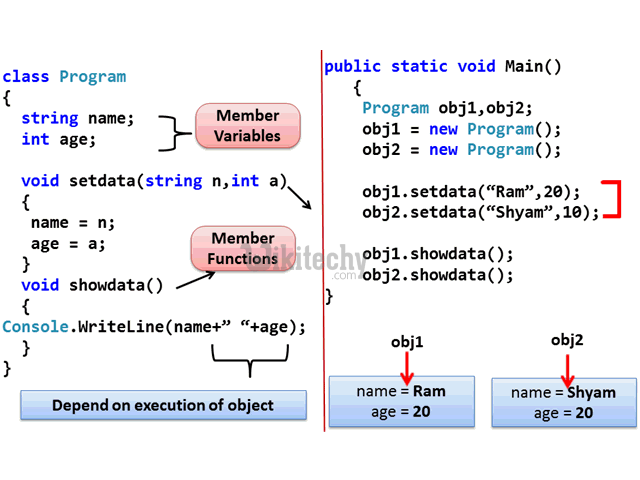
learn c++ tutorials - class and object in c++ Example
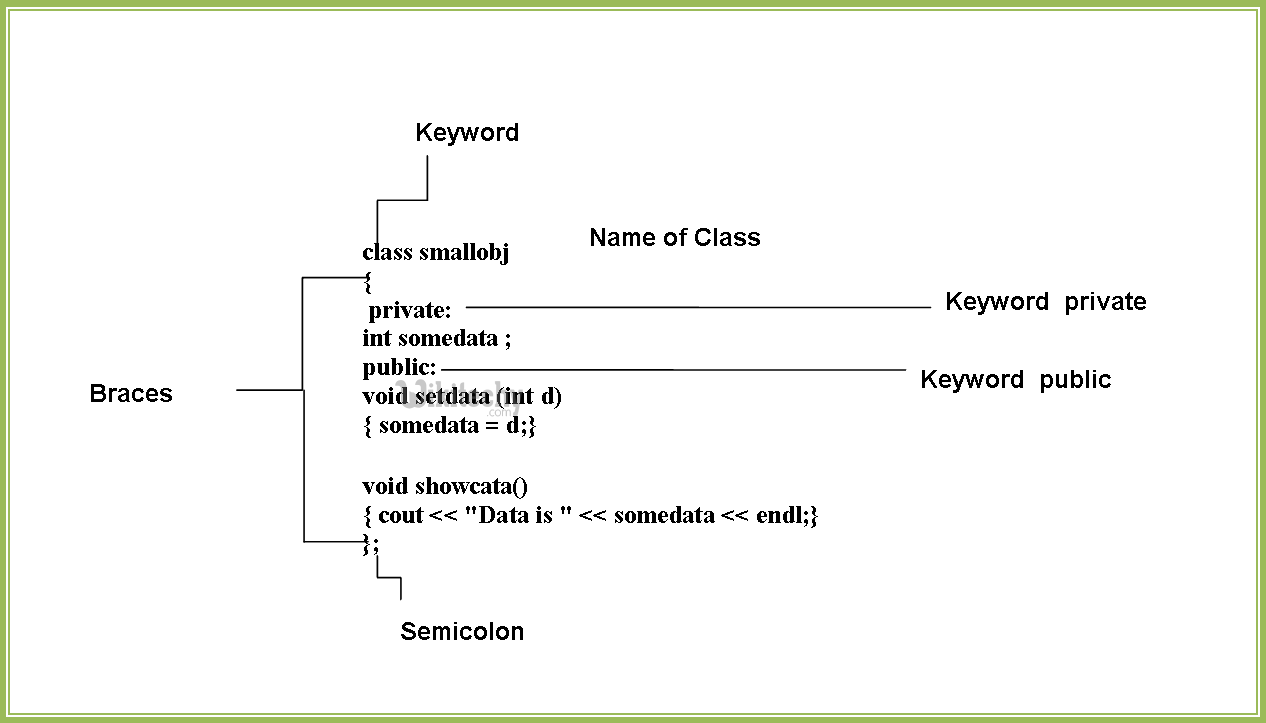
How to define a class in C++?
- A class is defined in C++ using keyword class followed by the name of class.
- The body of class is defined inside the curly brackets and terminated by a semicolon at the end.
class className
{
// some data
// some functions
};Example: Class in C++
class Test
{
private:
int data1;
float data2;
public:
void function1()
{ data1 = 2; }
float function2()
{
data2 = 3.5;
return data2;
}
};- Here, we defined a class named Test.
- This class has two data members: data1 and data2 and two member functions:function1() and function2().
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Keywords: private and public
- You may have noticed two keywords: private and public in the above example.
- The private keyword makes data and functions private. Private data and functions can be accessed only from inside the same class.
- The public keyword makes data and functions public. Public data and functions can be accessed out of the class.
- Here, data1 and data2 are private members where as function1() and function2() are public members.
- If you try to access private data from outside of the class, compiler throws error. This feature in OOP is known as data hiding.
learn c++ tutorials - class and object definition in c++ Example
C++ Objects
- When class is defined, only the specification for the object is defined; no memory or storage is allocated.
- To use the data and access functions defined in the class, you need to create objects.
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Syntax to Define Object in C++
className objectVariableName;- You can create objects of Test class (defined in above example) as follows:
class Test
{
private:
int data1;
float data2;
public:
void function1()
{ data1 = 2; }
float function2()
{
data2 = 3.5;
return data2;
}
};
int main()
{
Test o1, o2;
}- Here, two objects o1 and o2 of Test class are created.
- In the above class Test, data1 and data2 are data members and function1() andfunction2() are member functions.
How to access data member and member function in C++?
- You can access the data members and member functions by using a . (dot) operator. For example,
o2.function1();- This will call the function1() function inside the Test class for objects o2.
- Similarly, the data member can be accessed as:
o1.data2 = 5.5;- It is important to note that, the private members can be accessed only from inside the class.
- So, you can use o2.function1(); from any function or class in the above example. However, the code o1.data2 = 5.5; should always be inside the class Test.
Example: Object and Class in C++ Programming
// Program to illustrate the working of objects and class in C++ Programming
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:
int data1;
float data2;
public:
void insertIntegerData(int d)
{
data1 = d;
cout << "Number: " << data1;
}
float insertFloatData()
{
cout << "\nEnter data: ";
cin >> data2;
return data2;
}
};
int main()
{
Test o1, o2;
float secondDataOfObject2;
o1.insertIntegerData(12);
secondDataOfObject2 = o2.insertFloatData();
cout << "You entered " << secondDataOfObject2;
return 0;
}Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Output
Number: 12
Enter data: 23.3
You entered 23.3- In this program, two data members data1 and data2 and two member functions insertIntegerData() and insertFloatData() are defined under Test class.
- Two objects o1 and o2 of the same class are declared.
- The insertIntegerData() function is called for the o1 object using:
o1.insertIntegerData(12);- This sets the value of data1 for object o1 to 12.
- Then, the insertFloatData() function for object o2 is called and the return value from the function is stored in variable secondDataOfObject2 using:
secondDataOfObject2 = o2.insertFloatData();
- In this program, data2 of o1 and data1 of o2 are not used and contains garbage value.
