oracle union all | Oracle UNION ALL Operator - oracle tutorial - sql tutorial
Learn oracle - oracle tutorial - Oracle union all - oracle examples - oracle programs
What is Oracle UNION ALL ?
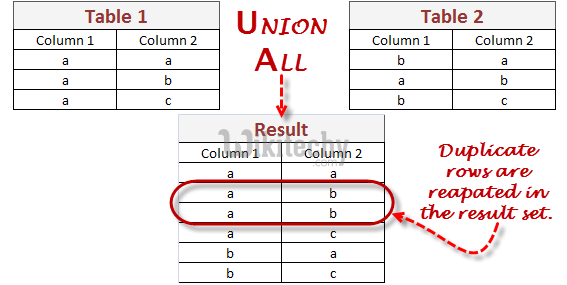
- In Oracle, the UNION ALL operator is used to combine the result sets of 2 or more SELECT statements.
- It is different from UNION operator in a way that it does not remove duplicate rows between the various SELECT statements.
- It returns all rows from the query and it does not remove duplicate rows between the various SELECT statements.
- Each SELECT statement within the Oracle UNION ALL operator must have the same number of fields in the result sets with similar data types.
Oracle Union All Query
Syntax
- The syntax for the UNION ALL operator in Oracle/PLSQL is:
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
UNION ALL
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];
click below button to copy the code. By - oracle tutorial - team
Parameters or Arguments
- expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
- The columns or calculations that you wish to retrieve.
Tables
- The tables that you wish to retrieve records from. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause.
WHERE conditions
- Optional. The conditions that must be met for the records to be selected.
Note
- There must be same number of expressions in both SELECT statements.
Example 1 - Return single field
- The following is an example of the Oracle UNION ALL operator that returns one field from multiple SELECT statements (and both fields have the same data type):
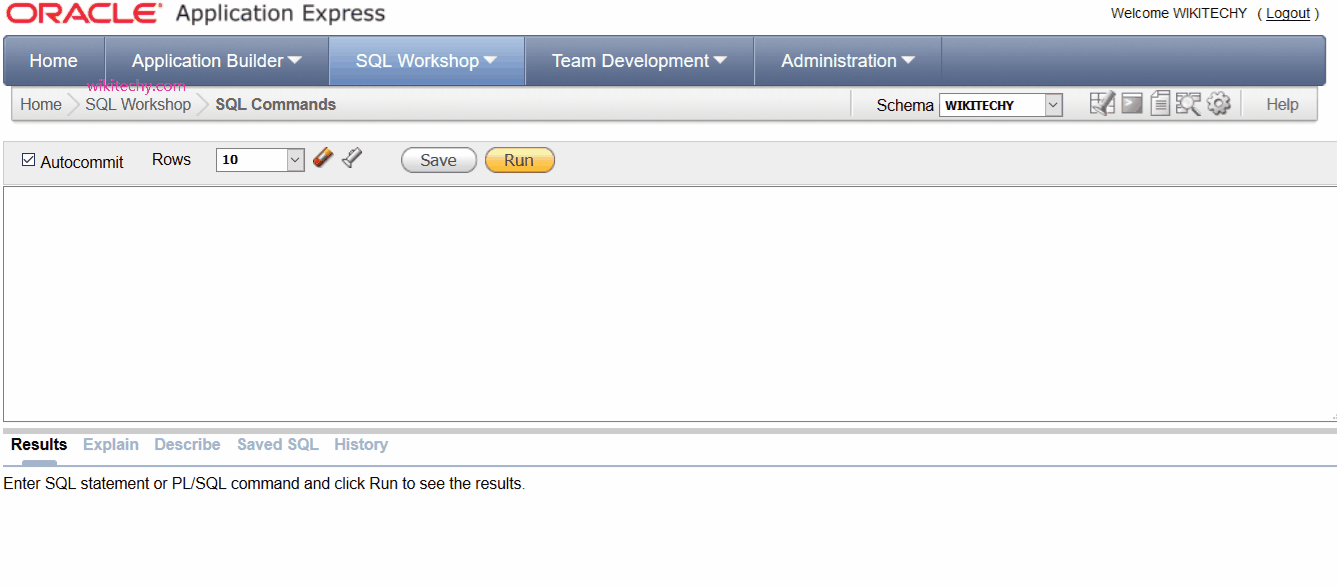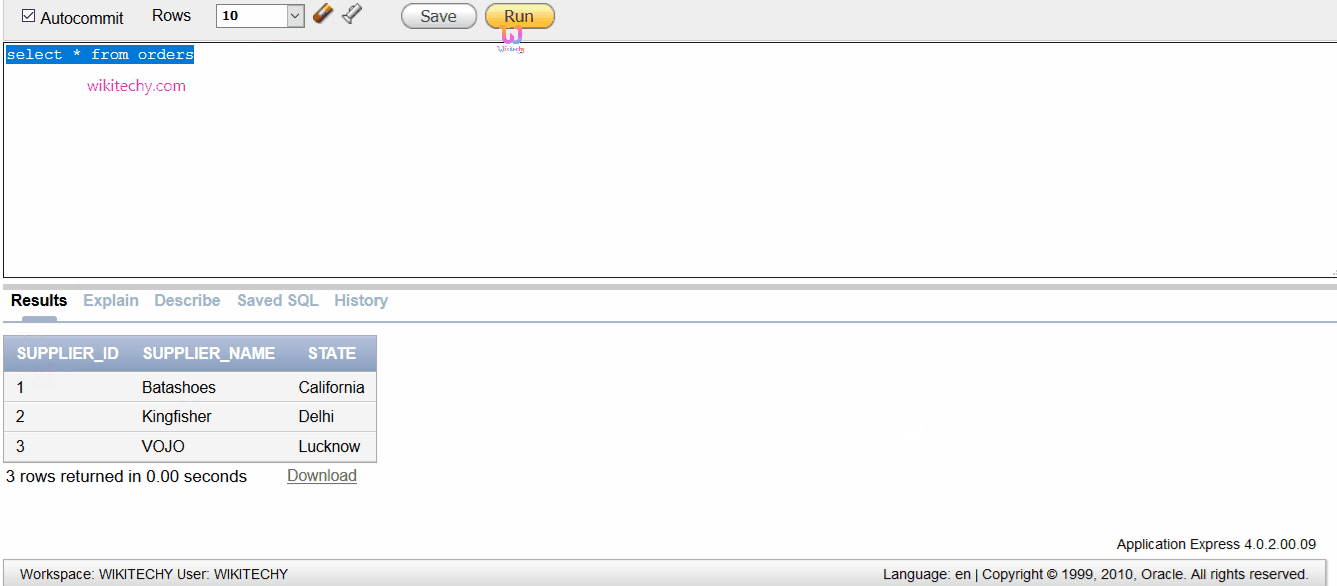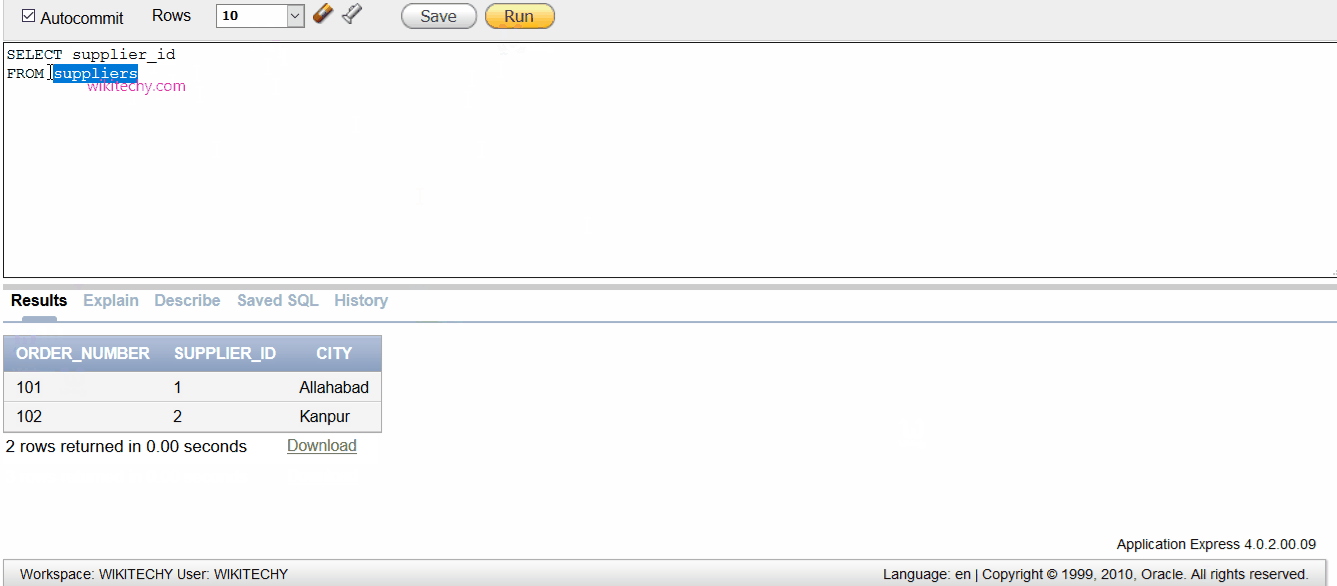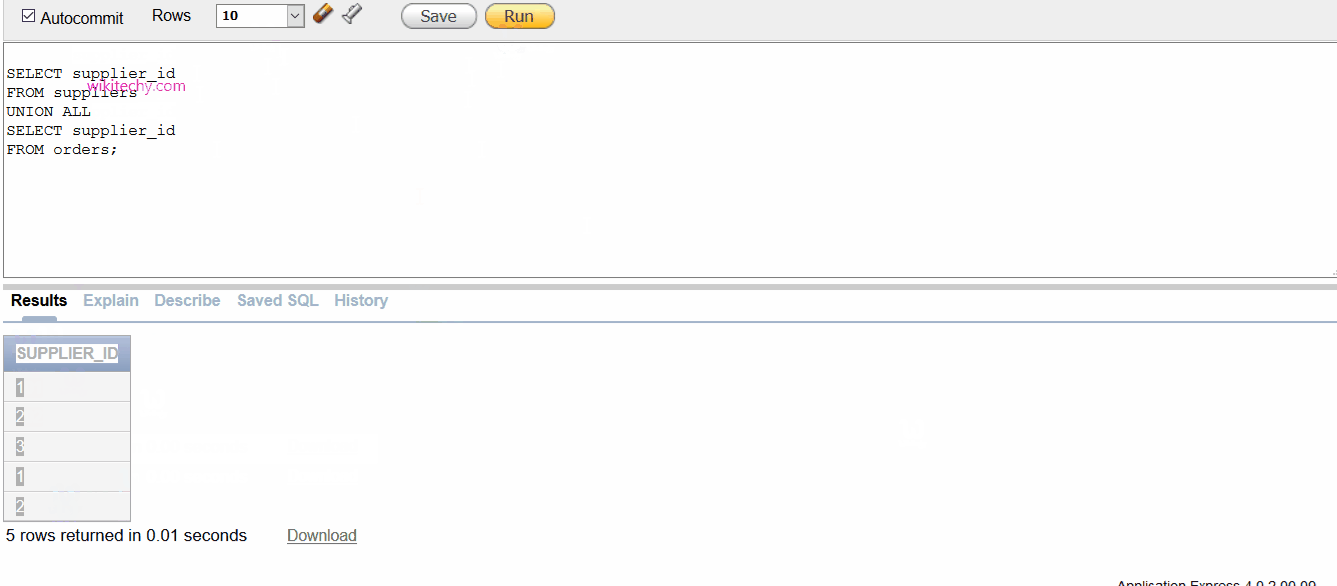
SELECT supplier_id
FROM suppliers
UNION ALL
SELECT supplier_id
FROM orders;
click below button to copy the code. By - oracle tutorial - team
- This Oracle UNION ALL operator would return a supplier_id multiple times in your result set if the supplier_id appeared in both the suppliers and orders table. The Oracle UNION ALL operator does not remove duplicates. If you wish to remove duplicates, try using the Oracle UNION operator
oracle tutorial , sql tutorial , sql , pl sql tutorial , oracle , pl sql , plsql
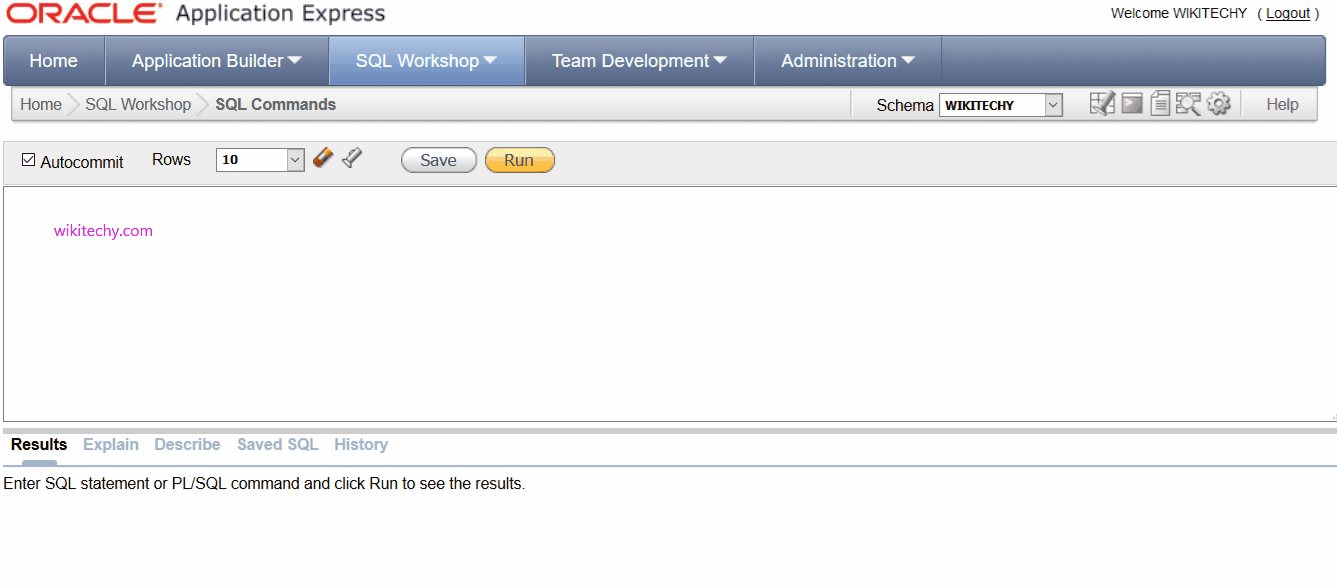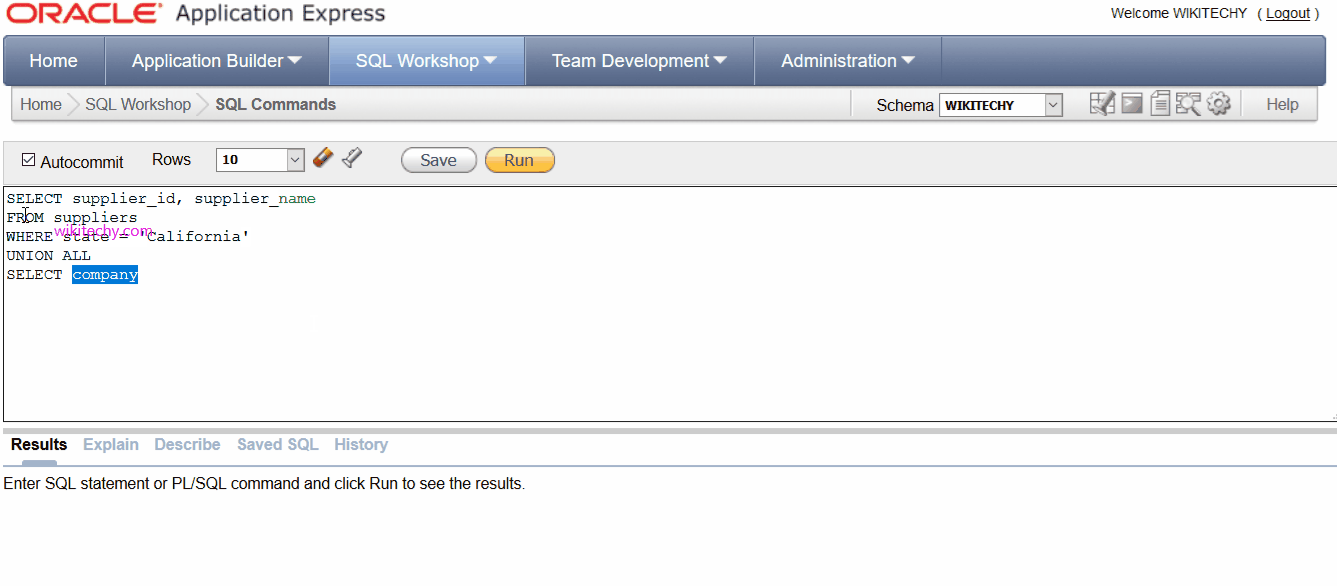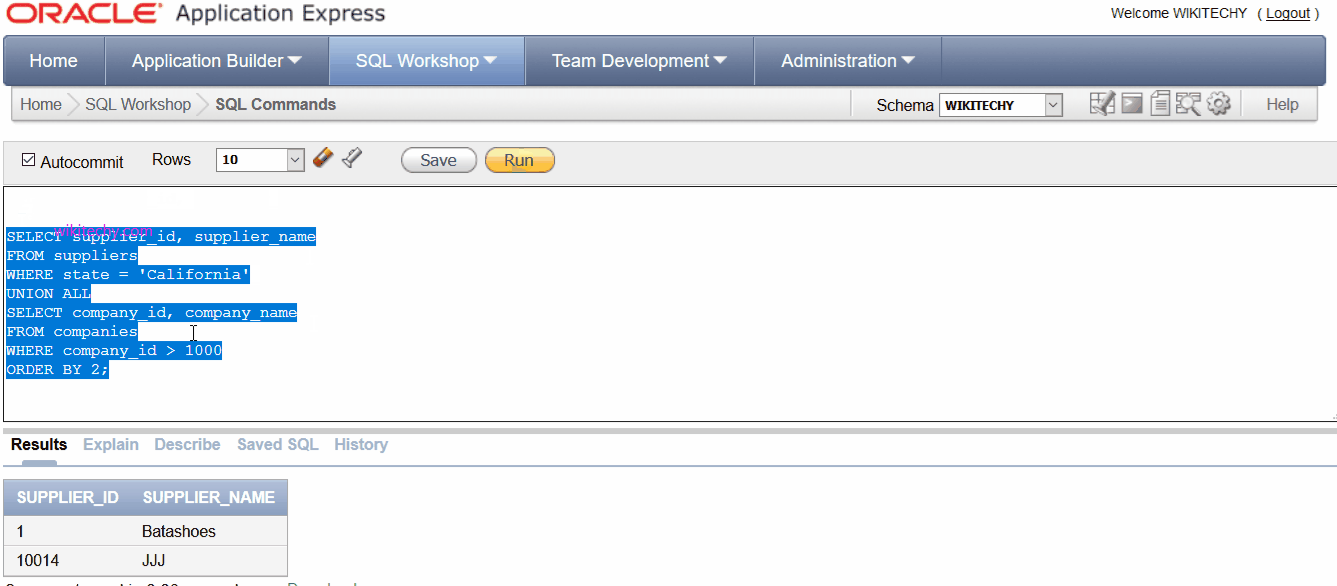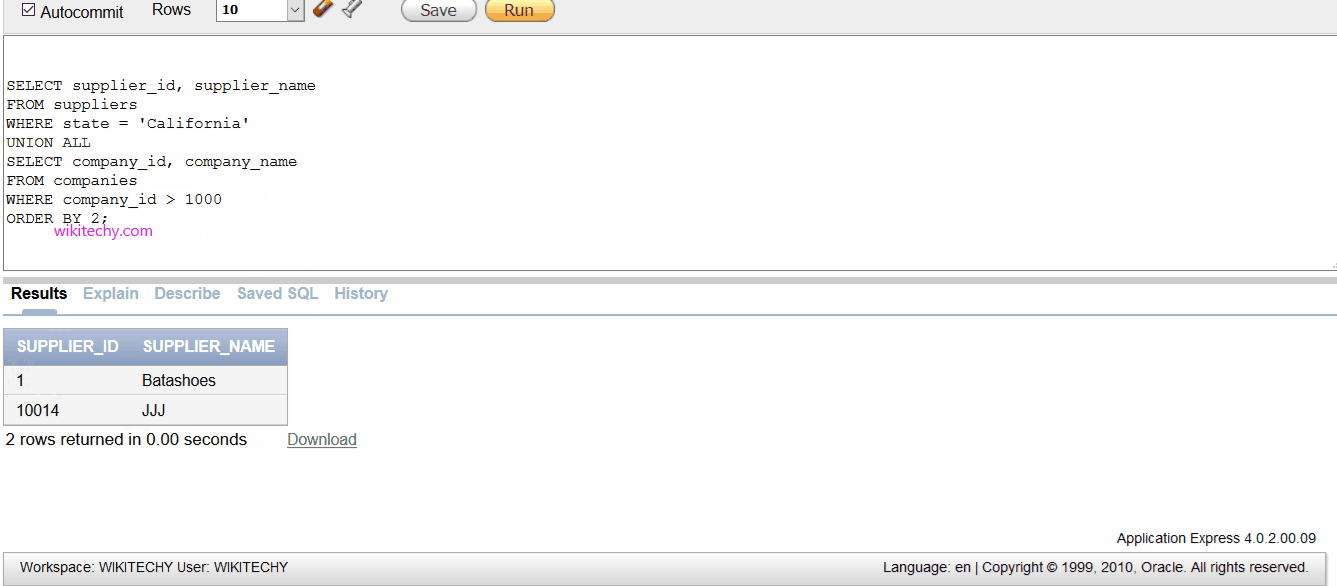
Example 2 - Using ORDER BY
- The Oracle UNION ALL operator can use the Oracle ORDER BY clause to order the results of the query.
SELECT supplier_id, supplier_name
FROM suppliers
WHERE state = 'California'
UNION ALL
SELECT company_id, company_name
FROM companies
WHERE company_id > 1000
ORDER BY 2;
click below button to copy the code. By - oracle tutorial - team
Learn oracle - oracle tutorial - Oracle union all order by - oracle examples - oracle programs
- In this Oracle UNION ALL operator, since the column names are different between the two SELECT statements, it is more advantageous to reference the columns in the ORDER BY clause by their position in the result set. In this example, we've sorted the results by supplier_name / company_name in ascending order, as denoted by the ORDER BY 2.
- The supplier_name / company_name fields are in position #2 in the result set.
Oracle Union Vs UnionAll Vs Except Vs Intersect

Oracle Union Vs UnionAll Performance
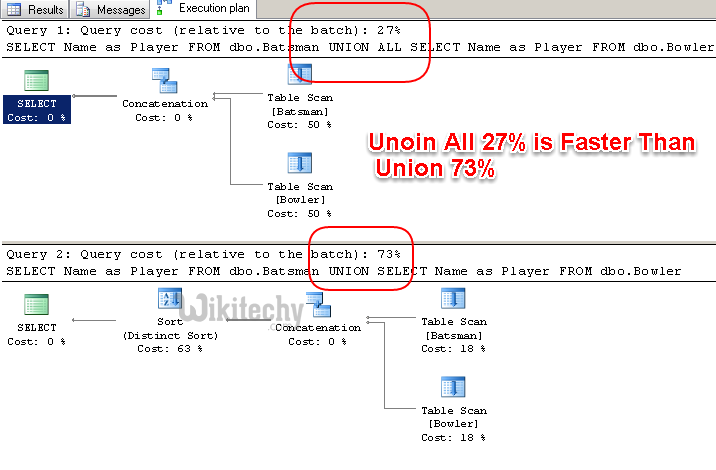
Oracle Union Vs Union all query performance
