Drools Introduction - rules engine - drools tutorial - business rules engine
Drools Introduction
- Java enterprise level application can be divided into three parts
- UI - User Interface (Frontend)
- Service layer which is in turn connected to a database
- Business layer
- We have a number of frameworks that handle the UI and service layer together, for example, Spring and Struts.
- Yet, we did not have a standard way to handle the business logic until Drools came into existence.
learn drools tutorial - drools project - drools introduction - drools example programs
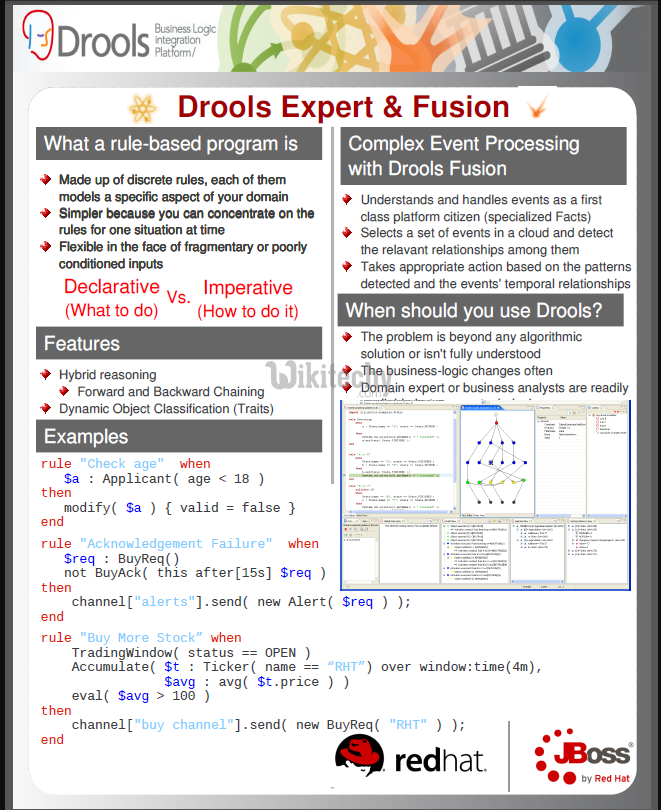
What is Drools?
- Drools is a Business Logic integration Platform (BLiP). It is written in Java.
- It is an open source project that is backed by JBoss and Red Hat, Inc.
- It extends and implements the Rete Pattern matching algorithm.
- In layman’s terms, Drools is a collection of tools that allow us to separate and reason over logic and data found within business processes.
- The two important keywords we need to notice are Logic and Data.
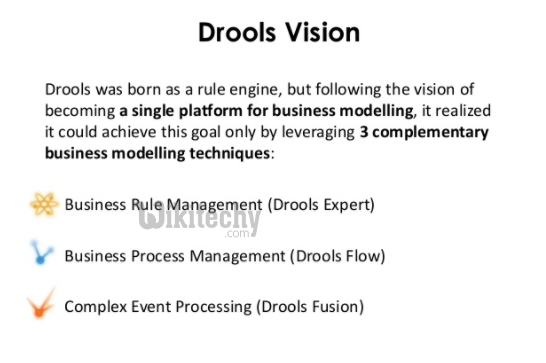
- Drools is split into two main parts: Authoring and Runtime.
- Authoring: Authoring process involves the creation of Rules files (.DRL files).
- Runtime: It involves the creation of working memory and handling the activation.
learn drools tutorial - drools project - drools rule engine introduction - drools types - drools example programs
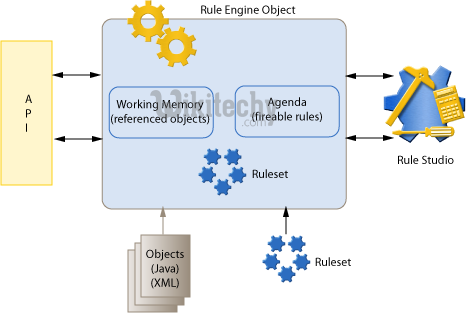
What is a Rule Engine?
- Drools is Rule Engine or a Production Rule System that uses the rule-based approach to implement and Expert System.
- Expert Systems are knowledge-based systems that use knowledge representation to process acquired knowledge into a knowledge base that can be used for reasoning.
- A Production Rule System is Turing complete with a focus on knowledge representation to express propositional and first-order logic in a concise, non-ambiguous and declarative manner.
- The brain of a Production Rules System is an Inference Engine that can scale to a large number of rules and facts.
- The Inference Engine matches facts and data against Production Rules - also called Productions or just Rules - to infer conclusions which result in actions.
- A Production Rule is a two-part structure that uses first-order logic for reasoning over knowledge representation.
- A business rule engine is a software system that executes one or more business rules in a runtime production environment.
- A Rule Engine allows you to define “What to Do” and not “How to do it.”
learn drools tutorial - drools rule engine - drools example
What is a Rule?
- Rules are pieces of knowledge often expressed as, "When some conditions occur, then do some tasks."
learn drools tutorial - drools project - drools sample rule engine - drools example programs
When
<Condition is true>
Then
<Take desired Action>
- The most important part of a Rule is it’s when part. If the when part is satisfied, the then part is triggered.
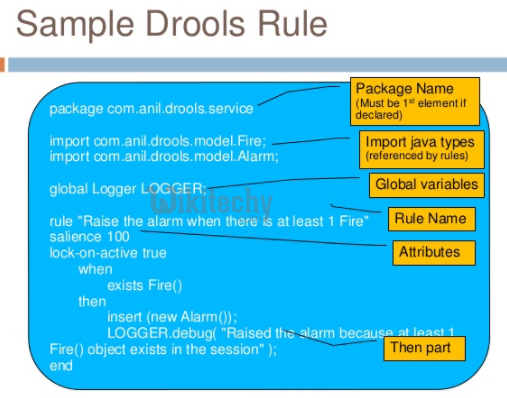
rule <rule_name>
<attribute> <value>
when
<conditions>
then
<actions>
end
Pattern Matching:
- The process of matching the new or existing facts against Production Rules is called Pattern Matching, which is performed by the Inference Engine.
- There are a number of algorithms used for Pattern Matching including:
- Linear
- Rete
- Treat
- Leaps
- Drools Implements and extends the Rete Algorithm.
- The Drools Rete implementation is called ReteOO, signifying that Drools has an enhanced and optimized implementation of the Rete algorithm for object-oriented systems.
Advantages of a Rule Engine :
Declarative Programming:
- Rules make it easy to express solutions to difficult problems and get the solutions verified as well.
- Unlike codes, Rules are written in less complex language; Business Analysts can easily read and verify a set of rules.
Logic and Data Separation:
- The data resides in the Domain Objects and the business logic resides in the Rules.
- Depending upon the kind of project, this kind of separation can be very advantageous.
Speed and Scalability:
- The Rete OO algorithm on which Drools is written is already a proven algorithm.
- With the help of Drools, your application becomes very scalable.
- If there are frequent change requests, one can add new rules without having to modify the existing rules.
Centralization of Knowledge:
- By using Rules, you create a repository of knowledge (a knowledge base) which is executable.
- It is a single point of truth for business policy.
- Ideally, Rules are so readable that they can also serve as documentation.
Tool Integration:
- Tools such as Eclipse provide ways to edit and manage rules and get immediate feedback, validation, and content assistance. Auditing and debugging tools are also available.
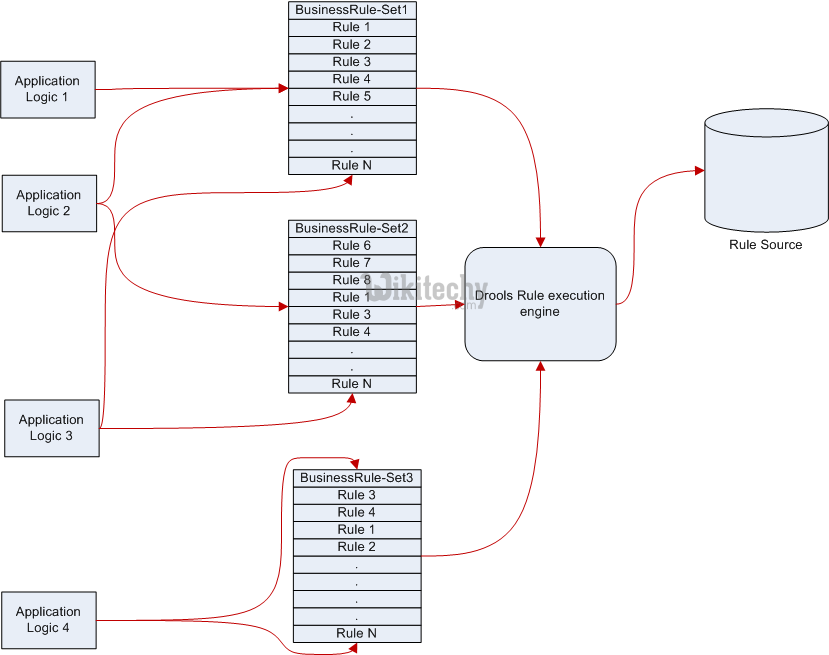
learn drools tutorial - drools project - drools rule execution engine - drools example programs
