What is Document Database - MongoDB Tutorial
What is Document Database ?
- It is a type of nonrelational DB that is designed to store and query data as JSON-like documents.
- It becomes easier for developers to store and query data in a database while using the same document-model format they use in their application code.
- In document databases the data stored documents with their metadata.
- The key is the unique identifier of the document where the document stored is in key/value pair.
- Document databases are quicker to load, access, and parse.
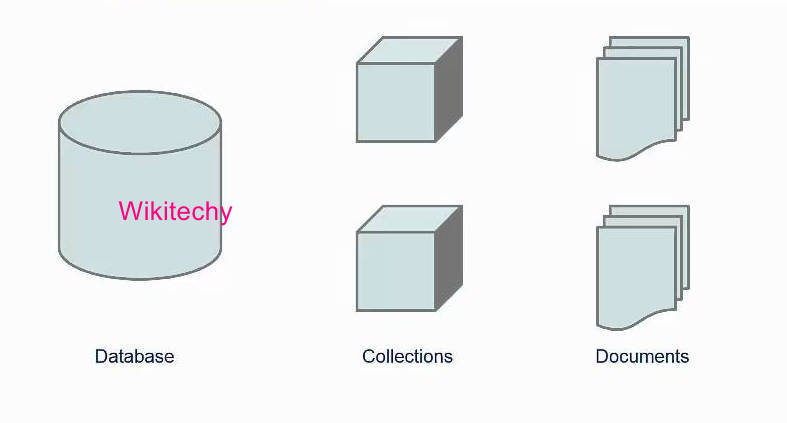
For Example

Mongodb Create Table Collection

Mongodb Insert Collection

Features of Document Databases
- It provides fast queries, a structure well suited for handling big data.
- Flexible indexing and a simplified method of maintaining the database.
- It has been fully integrated by large-scale IT companies like Amazon and it is efficient for web apps.
- It easy to query data with the same document-model used to code the application.
Advantages of Document Databases:
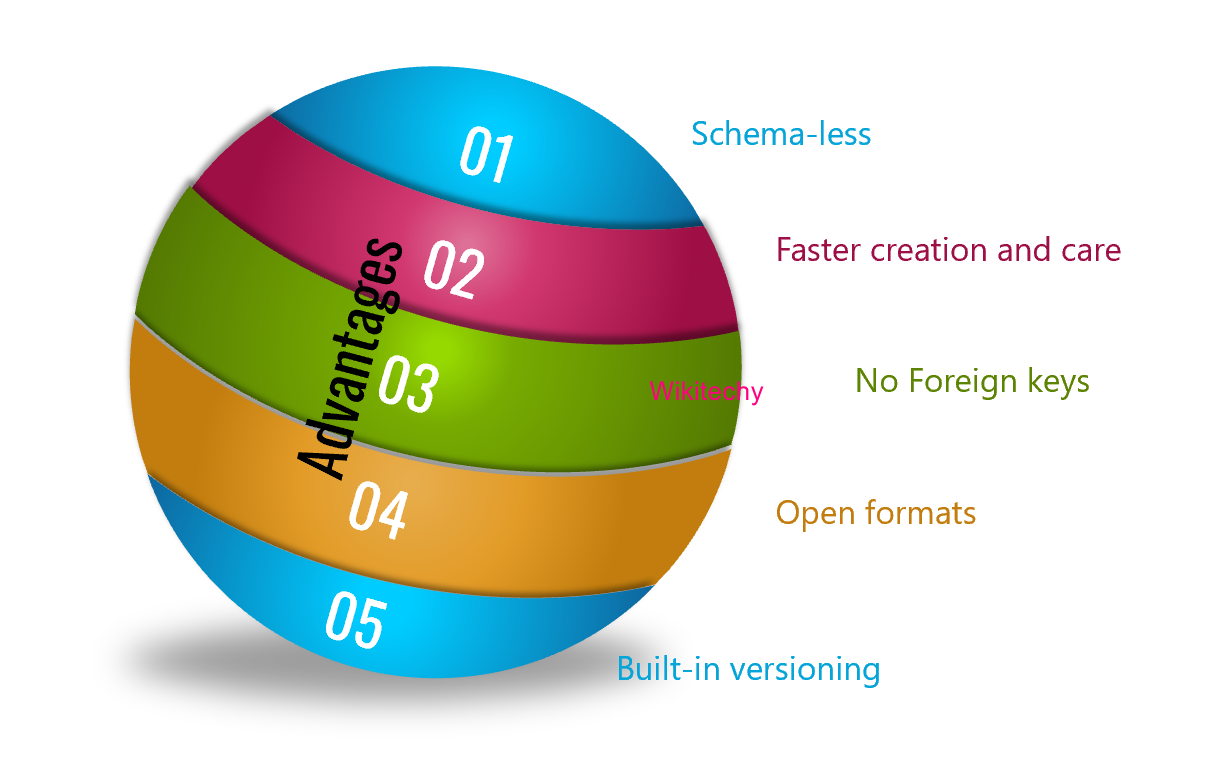
Schema-less
- No restrictions in the format and structure of data storage.
- It is good for retaining existing data at big volumes and different structural states, especially in a constantly transforming system.
Faster creation and care
- Minimal maintenance is required once you create the document, which can be as simple as adding your complex object once.
No foreign keys
- The absence of this relationship dynamic, documents can be independent of one another.
Open formats
- A clean build process that uses XML, JSON and other derivatives to describe documents.
Built-in versioning
- While documents grow in size they can also grow in complexity. It decreases conflicts.
Disadvantages of Document Databases
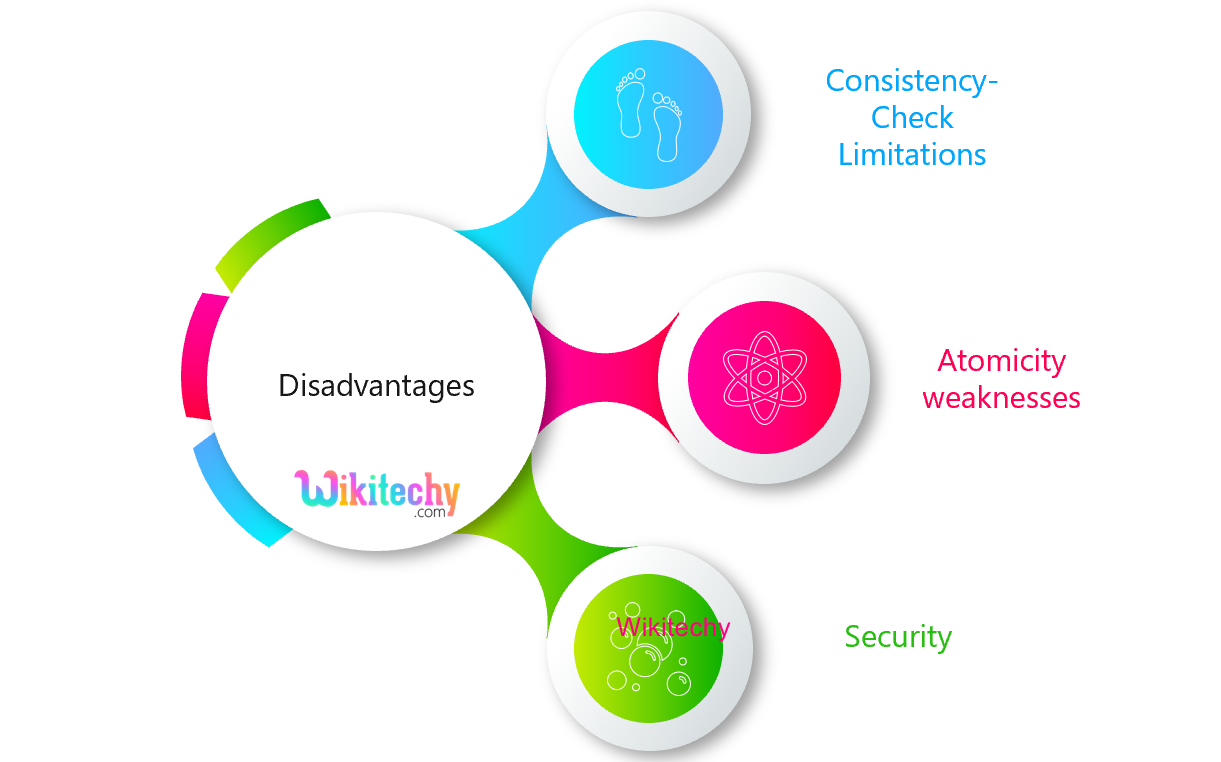
Consistency-Check Limitations
- In database we use case example above, it would be possible to search for books from a non-existent author.
- You should search the book collection and discover files that aren't linked to an author series.
- These inconsistencies aren’t significant in a few contexts, however at upper-tier standards of RDB consistency audits, they seriously hamper database performance.
Atomicity Weakness
- Relational systems also allow you to modify data from one place without the need for JOINs.
- A change involving two collections will require you to run two separate queries (per collection) for document databases.
- Breaks atomicity requirements.
Security
- For Web application security owners of NoSQL databases, therefore, want to pay careful attention.
- Nearly half of web applications today actively leak sensitive data.
