- There is no guaranteed way for any organization to prevent a cyber attack, but there are numerous Cyber Security best practices that organizations can follow to reduce the risk.
- Reducing the risk of a cyber attack relies on using a combination of skilled security professionals, processes and technology.
Types of cyber threats and how to deal with them
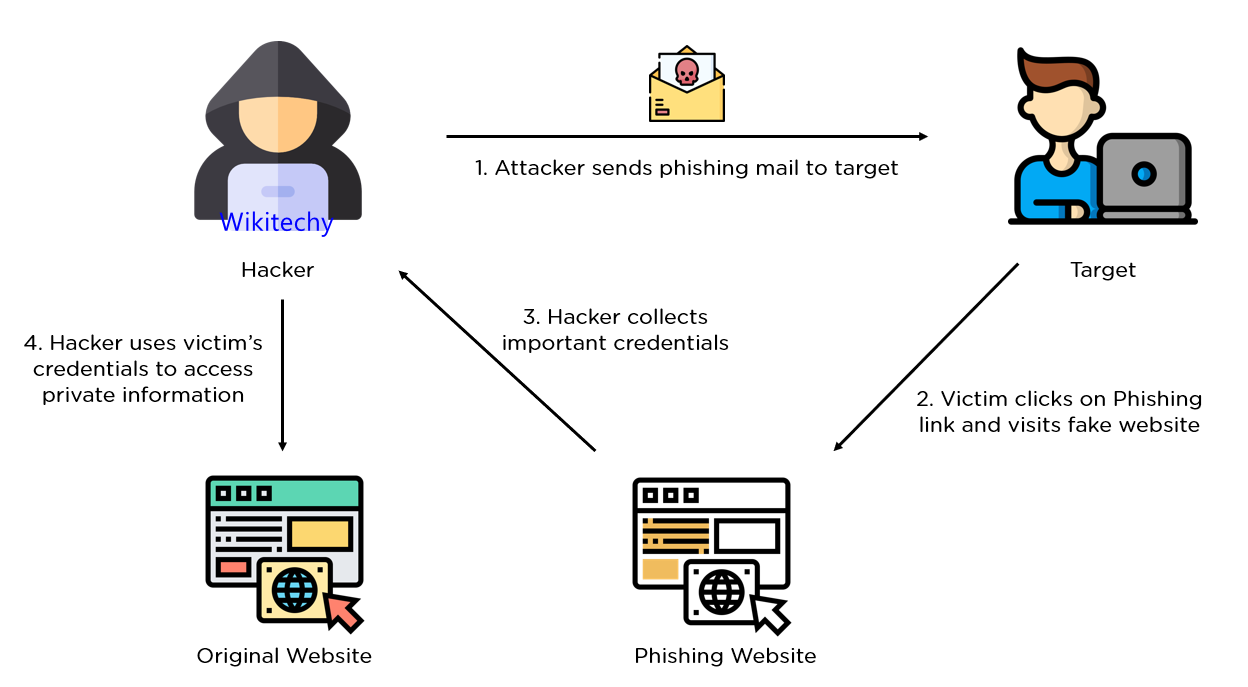
Phishing
- This is the term used to describe the process of trying to get private information by pretending to be a legitimate enquirer.
- A malicious individual or organisation may ‘fish’ for information by using fake communications, such as emails, to try and gain login credentials or other sensitive information
How to deal with phishing
- There are several ways you can identify and avoid phishing attacks. Here are some top tips:
- Make sure your IT equipment is updated and installed with the necessary Security Software.
- Be suspicious of emails and calls that seem overly alarming or slightly odd.
- For example, an email might warn you of a breached password, but there could be spelling errors, an unusual email address, or an unprofessional layout. Don’t click on links unless you’re sure of the authenticity of a message.
- If you’re unsure whether a call or email is legitimate, contact the company before you respond. They’ll be able to verify whether it’s real or not.
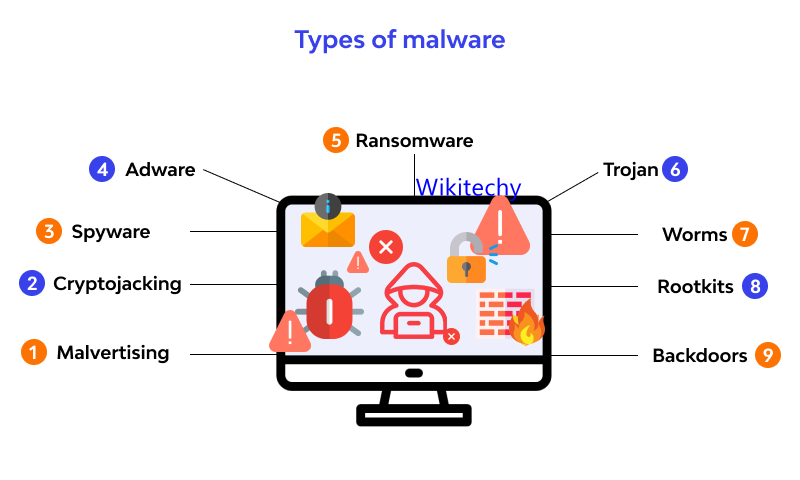
Malwares
- You’ll often find that malware and phishing scams go hand in hand.
- The term is used to describe malicious software designed to perform an attack on the device or server that downloads or runs it.
- Malware attacks can cause a corruption of data or even take down an entire system.
How to deal with malware
- Again, there are several steps you can take to prevent and deal with potential malware cyber threats. We’ve picked out some essential advice below:
- Ensure you have anti-malware software installed and updated on your device.
- Back up your data, especially your important files, and make sure you can store them in an offline location.
- Only open files and software that you know is from a trusted source.
- Inspect content and correspondence to identify any features that seem amiss (as you would with phishing scams).
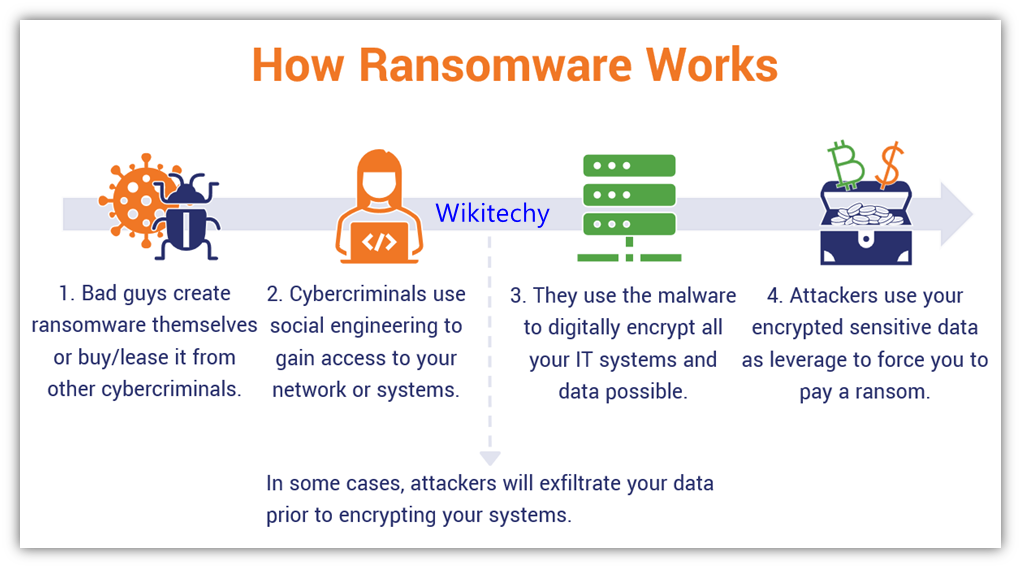
Ransomware
- Ransomware is a type of malware that essentially locks down a victim’s files, Encrypting them so they cannot be accessed.
- Usually, the attacker will then demand a fee (often to be paid anonymously via cryptocurrency) to decrypt the data.
- It’s perhaps the biggest cyber security threat in the current landscape.
How to deal with ransomware
- Victims of ransomware attacks can often feel helpless once they’re left without access to their files. As with many of the cyber security threats on this list, prevention is often the best way of dealing with them:
- Ensure you have antivirus software installed and up to date. The same applies to your IT devices.
- Set up your devices so that only authorised software and applications can run on them. Avoid opening applications and files from unknown sources.
- If you fall victim to a ransomware attack, notify your IT security team immediately (if at work).
- Disconnect the affected machine from your network.
- Notify the authorities of the breach.
- Do not pay the ransom, but ensure the relevant organisations are informed – they can advise you further.
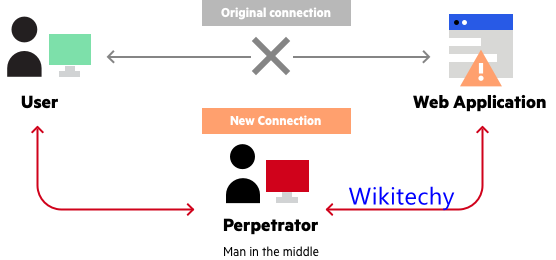
MITM
- A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is when an attacker establishes a position between the sender of a message or information and the recipient, allowing them to intercept any correspondence.
- The MITM attacker could even alter the contents of a message without either sender or recipient knowing.
How to deal with MITM attacks
- These types of attacks can be difficult to detect, so once again, prevention is a far easier method at dealing with MITM attacks:
- Ensure access points are secure. Wi-Fi networks are often particularly vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, so making sure passwords are strong and secure is essential.
- Use VPNs for sensitive information. A virtual private network (VPN) can create a secure environment that you can use when handling valuable data.
- Make sure your web browsers are updated regularly – patches are released often to close any security vulnerabilities.
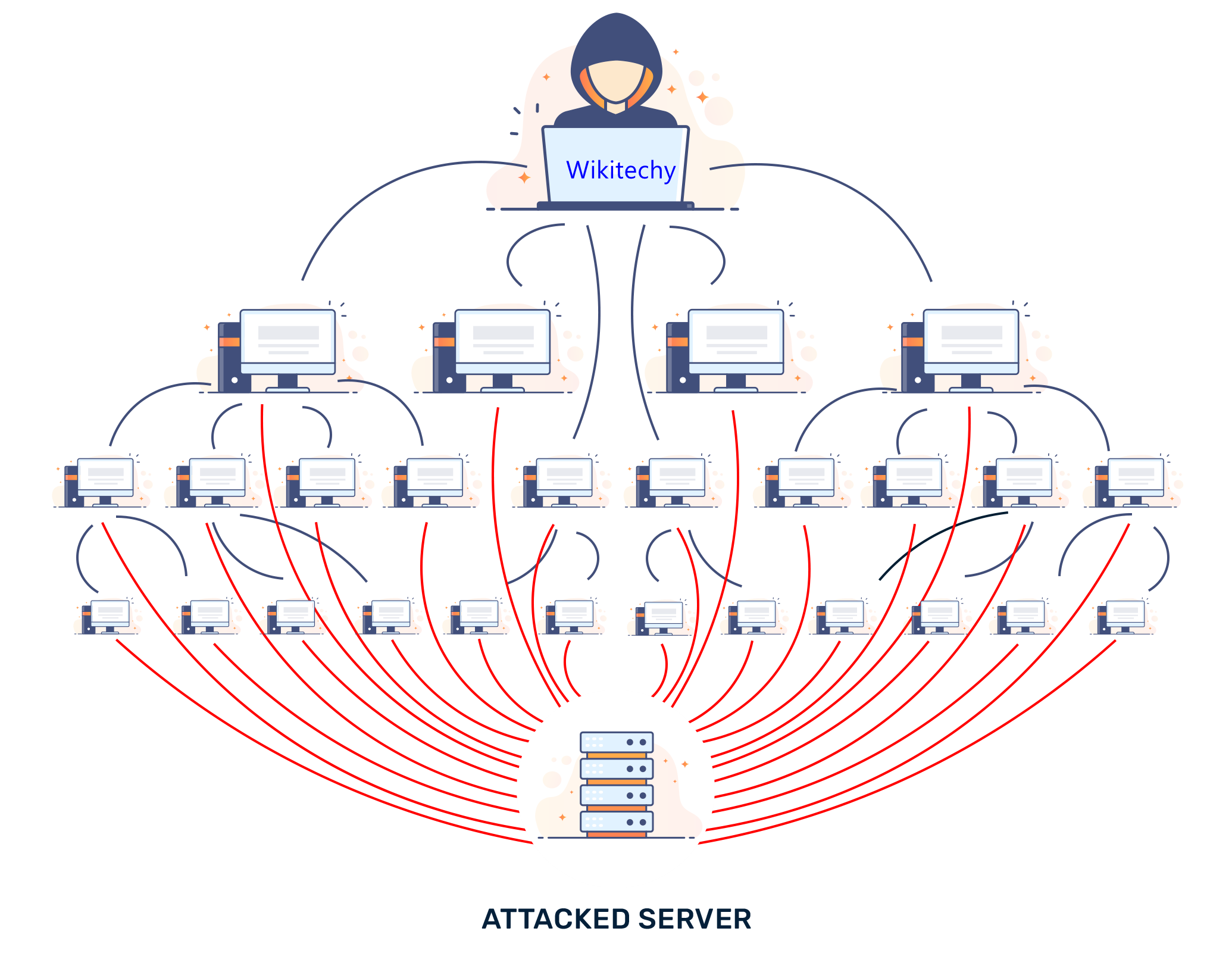
DDoS attacks
- A Denial of Service/Distributed Denial of Service Attack (DDoS) occurs when a hacker uses multiple devices (often numbering in the thousands) and uses them to overload target systems.
- Usually, the attacker will target websites, which can only usually cope with a set number of users at any one time.
- This renders the website (and associated services) unusable for some time.
How to deal with DDoS attacks
- A lot of preventing and dealing with DDoS attacks is handled by IT professionals with access to servers and networks.
- They will often ensure that cyber security solutions are in place.
- However, average users can help by following similar procedures and precautions as they would with malware prevention.
UP NEXT IN Cyber Security