Cyber Security Goals
Cyber Security Goals
- Cyber security is to protect information from being stolen, compromised or attacked. Cyber Security three goals are "
- Protect - Confidentiality of data.
- Preserve - Integrity of data.
- Promote - Availability of data for authorized users.
- CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availabilty) is a security model that is designed to guide policies for information security within the premises of an organization or company. Elements of the triad are considered the three most crucial components of security.
- The CIA criteria are one that most of the organizations and companies use when they have installed a new application, creates a database or when guaranteeing access to some data.
The CIA triad are :
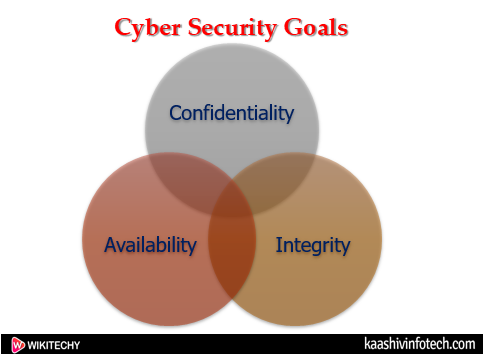
Cyber Security Goals
Confidentiality
It involves the protection of data, providing access for those who are allowed to see it while disallowing others from learning anything about its content.
Tools for Confidentiality

Confidentiality Tools
Encryption
- Encryption is a method of transforming information to make it unreadable for unauthorized users by using an algorithm. Asymmetric-key and symmetric-key are the two primary types of encryption.
Access control
- In access control systems, users need to present credentials before they can be granted access such as a person's name or a computer's serial number.
Authentication
- An authentication is a process that ensures and confirms a user's identity or role that someone has. It can be done in a number of different ways, but it is usually based on a combination of-
- something the person has (storing secret keys),
- something the person knows (like a password),
- something the person is (like a human with a fingerprint).
- Authentication is the necessity of every organizations because it enables organizations to keep their networks secure by permitting only authenticated users to access its protected resources.
Authorization
- Authorization is a security mechanism which gives permission to do or have something. It is used to determine a person or system is allowed access to resources, based on an access control policy, including computer programs, files, services, data and application features.
Physical Security
- Physical security describes measures designed to deny the unauthorized access of IT assets like facilities, equipment, personnel, resources and other properties from damage. It protects these assets from physical threats including theft, vandalism, fire and natural disasters.
Integrity
- Integrity refers to the methods for ensuring that data is real, accurate and safeguarded from unauthorized user modification.
Tools for Integrity
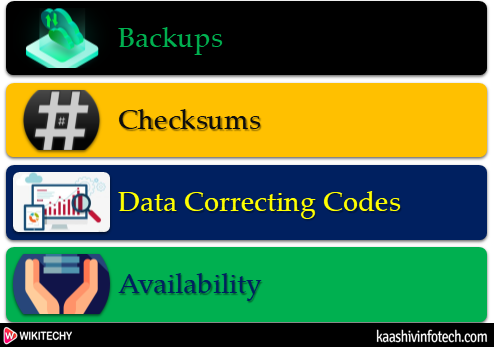
Integrity Tools
Backups
- Backup is the periodic archiving of data. It is a process of making copies of data or data files to use in the event when the original data or data files are lost or destroyed.
Checksums
- A checksum is a numerical value used to verify the integrity of a file or a data transfer. A checksum function depends on the entire contents of a file.
Data Correcting Codes
- It is a method for storing data in such a way that small changes can be easily detected and automatically corrected.
Availability
- Availability is the property in which information is accessible and modifiable in a timely fashion by those authorized to do so.
Tools for Availability
- Physical Protections
- Computational Redundancies
Physical Protections
Physical safeguard means to keep information available even in the event of physical challenges.
Computational redundancies
- It is applied as fault tolerant against accidental faults.
- It protects computers and storage devices that serve as fallbacks in the case of failures.
