SQL Primary Key Constraint - Create primary keys in SQL Server
PRIMARY KEY Constraint
- PRIMARY KEY is like the superstar of a table, ensuring that each row gets a unique identification.
- Just like there's only one superstar in the show, there can be only one PRIMARY KEY in a table.
- It's a special column that sets each row apart, making sure there's no confusion about who's who.
PRIMARY KEY on CREATE TABLE
-
The following SQL establishes a PRIMARY KEY on the 'ID' column during the creation of the 'Persons' table:
Syntax
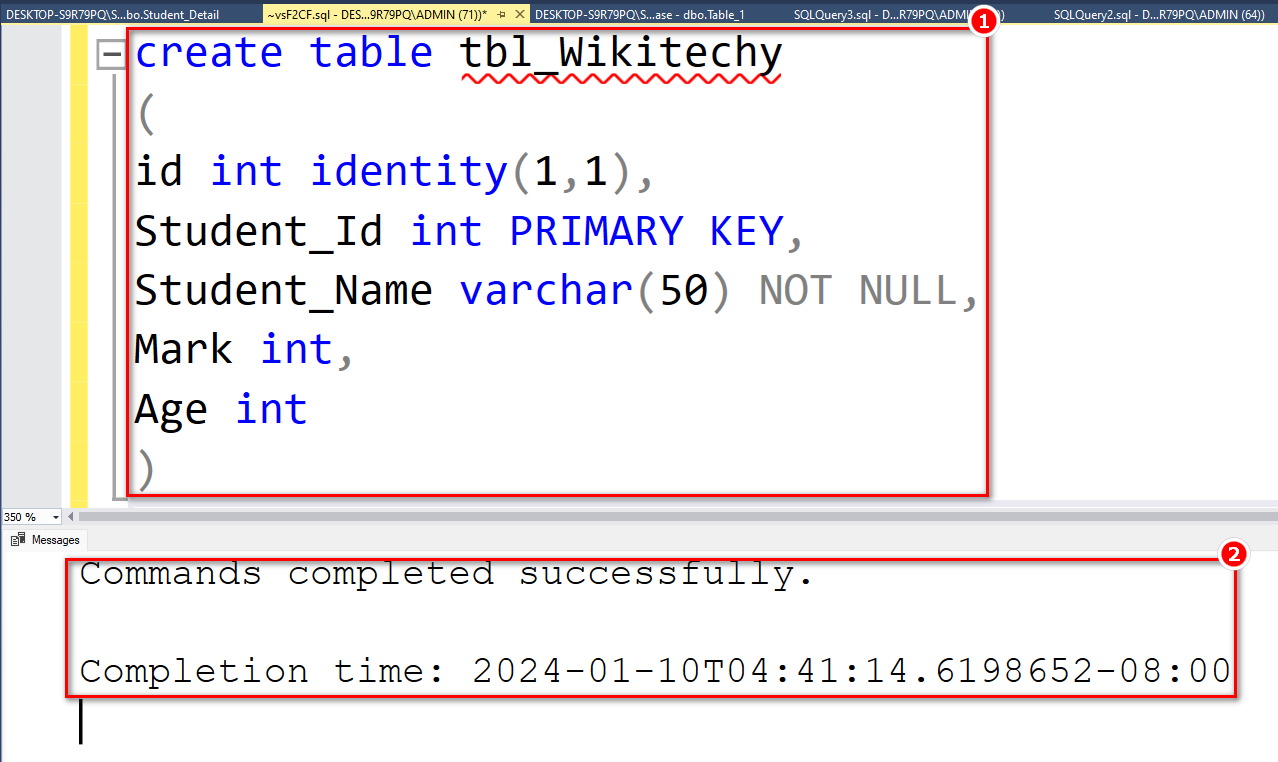
CREATE TABLE tbl_Wikitechy ( ID INT IDENTITY(1,1), Student_Id INT PRIMARY KEY, Student_Name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, Mark INT, Age INT )
Output
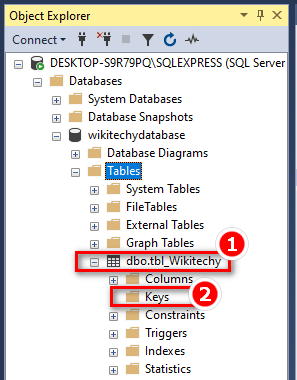
Step 1
Step 2
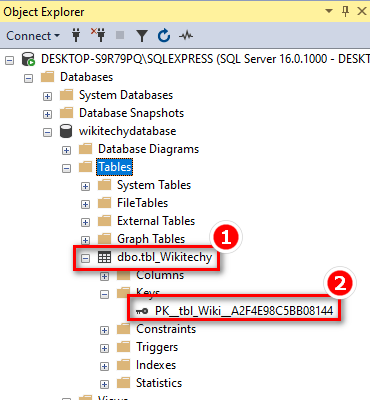
PRIMARY KEY on ALTER TABLE
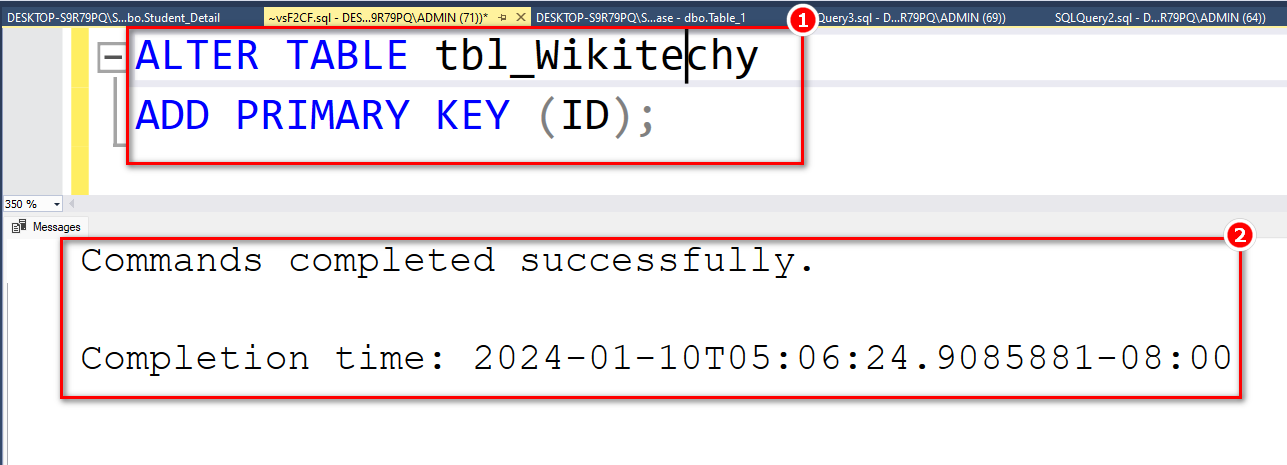
- To establish a PRIMARY KEY constraint on the 'ID' column after the table is already created, use the following SQL:
Syntax
ALTER TABLE tbl_Wikitechy ADD PRIMARY KEY (ID);
Output
Step 1
Step 2
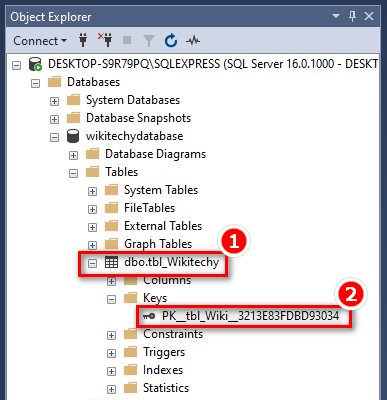
- To enable the naming of a PRIMARY KEY constraint and to define a PRIMARY KEY constraint on multiple columns, utilize the following SQL syntax:
Syntax
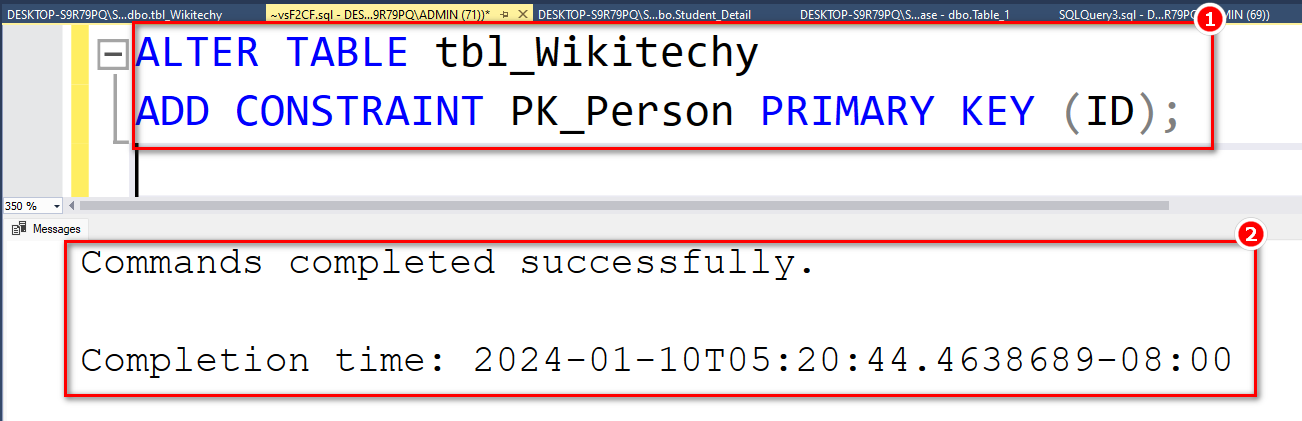
ALTER TABLE tbl_Wikitechy ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Person PRIMARY KEY (ID);
Output
Step 1
Step 2
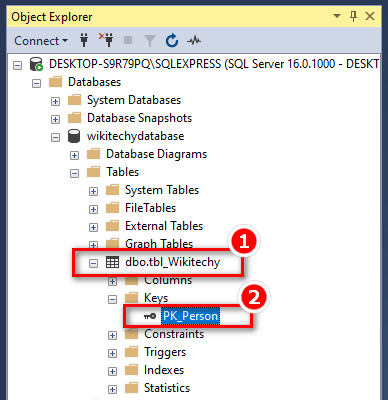
DROP a PRIMARY KEY Constraint
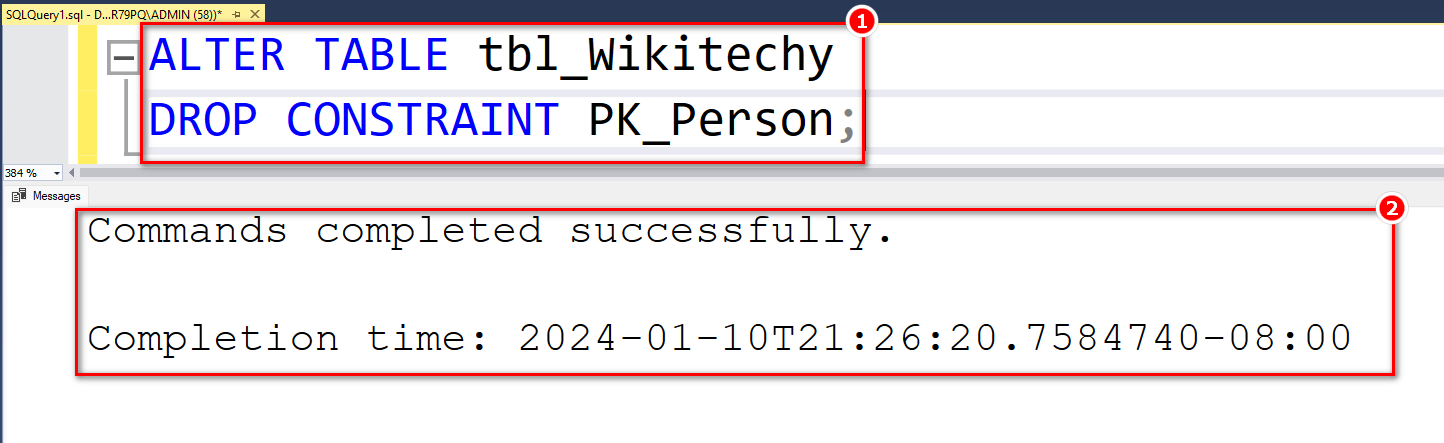
- To remove a PRIMARY KEY constraint, utilize the following SQL::
Syntax
ALTER TABLE tbl_Wikitechy DROP CONSTRAINT PK_Person;
Output
Step 1
Step 2