Phases of NLP
Phases of NLP
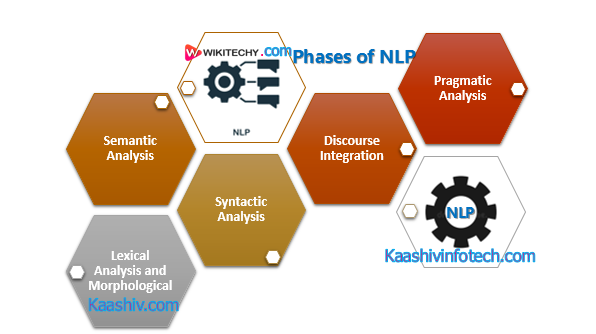
Phases of NLP
1. Lexical Analysis and Morphological
- This phase scans the source code as a stream of characters and converts it into meaningful lexemes. It divides the whole text.
2. Syntactic Analysis (Parsing)
- Syntactic Analysis is used to check grammar, word arrangements, and shows relationship among the words.
- Example:
- Madurai goes to the chennai, does not make any sense, so this sentence is rejected by the Syntactic analyzer.
Read Also
3. Semantic Analysis
- Semantic analysis is concerned with the meaning representation. It mainly focuses on the literal meaning of words.
4. Discourse Integration
- Discourse Integration depends upon the sentences that proceeds it.
5. Pragmatic Analysis
- It helps you to discover the intended effect by applying a set of rules that characterize cooperative dialogues.
- For Example:
- "Open the book" is interpreted as a request instead of an order.
Why NLP is difficult ?
- NLP is difficult because Ambiguity and Uncertainty exist in the language.
Ambiguity
- There are the following three ambiguity -
- Lexical Ambiguity
- Syntactic Ambiguity
- Referential Ambiguity
Lexical Ambiguity
- Lexical Ambiguity exists in the presence of two or more possible meanings of the sentence within a single word.
- Example:
- Venkat is looking for a match.
- The word match refers to that either Venkat is looking for a partner or Venkat is looking for a match(any games).
Syntactic Ambiguity
- Syntactic Ambiguity exists in the presence of two or more possible meanings within the sentence.
- Example:
- I saw the lion with the binocular.
- In the above example, did I have the binoculars? Or did the lion have the binoculars?
Referential Ambiguity
- Referential Ambiguity exists when you are referring to something using the pronoun.
- Example:
- Kavitha went to Vinitha. She said, "I am hungry."
- In the above sentence, you do not know that who is hungry, either Kavitha or Vinita.
