Robotics Tutorial - Robotic Tutorial for Beginners - Robotic Tutorials
What is Robotics ?
- In artificial intelligence robotics is the term that deals with a study of creating intelligent and efficient robots.
- It is mainly composed of mechanical engineering, computer science engineering for construction, electrical engineering and application of robots.
- Robotics is science of designing or building an application of robots and main aim of robotics is to design an efficient robot.
Robotics
What are Robots ?
- Robots are re-programmable, multifunctional, automatic industrial machine which is designed for replacing human in hazardous work.
- They can be work as an automatic machine sweeper, machine removing mines in a war field, an automatic car for a child to play with, in military, etc.
Robots
Aspects of Robotics
- They have electrical components for providing power and control the machinery.
- To accomplish a particular task, robots have mechanical construction.
- It contains some type of computer program that determines when, how and what a robot does something.
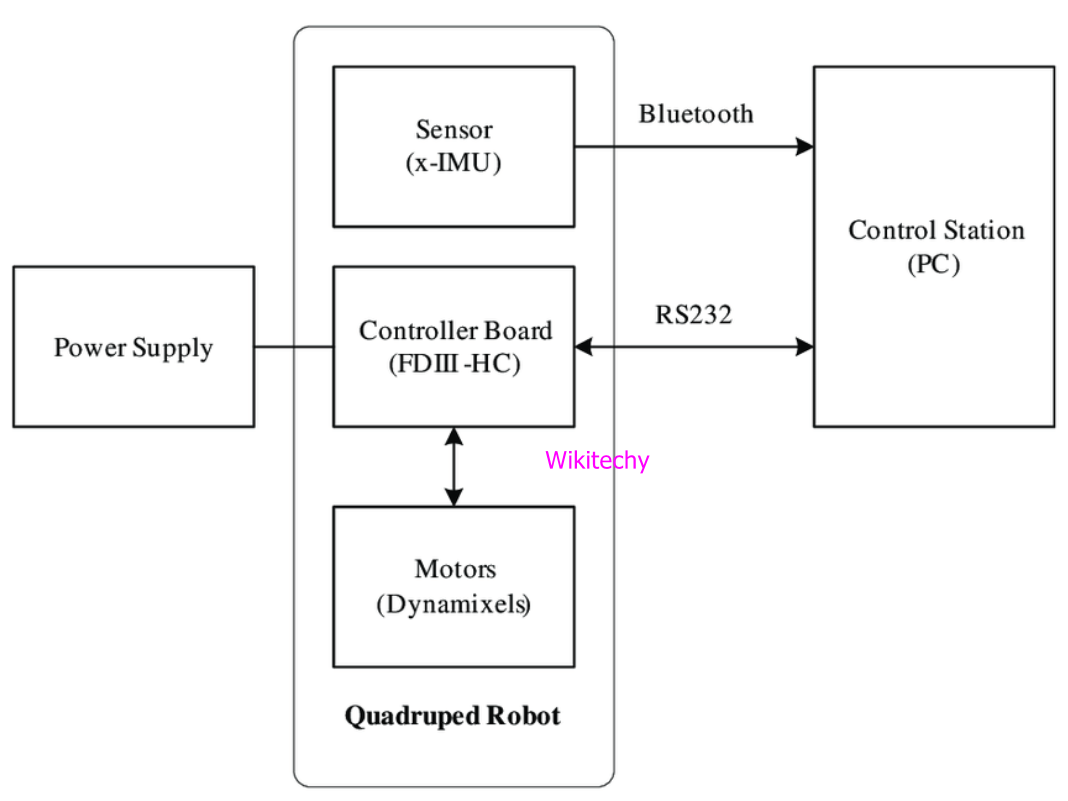
Key Components of Robot
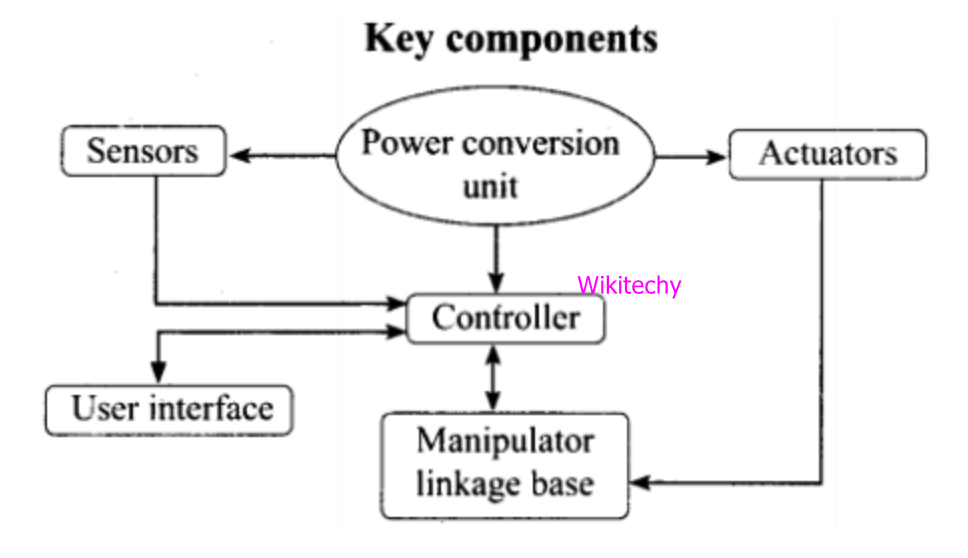
Key Components of Robot
Power Supply
- The working power to the robot is provided by hydraulic, pneumatic power, batteries or solar power resources.
Actuators
- The major function of actuators is to convert energy into movement and they are the energy conversion device used inside a robot.
Electric motors (DC/AC)
- Motors are the electromechanical component which is used for converting electrical energy into its equivalent mechanical energy.
- Motors are used for providing rotational movement in robots.
Sensors
- Sensors provide real time information on the task environment.
- At environment robots are equipped with tactile sensor it imitates the mechanical properties of touch receptors of human fingerprints and a vision sensor is used for computing the depth.
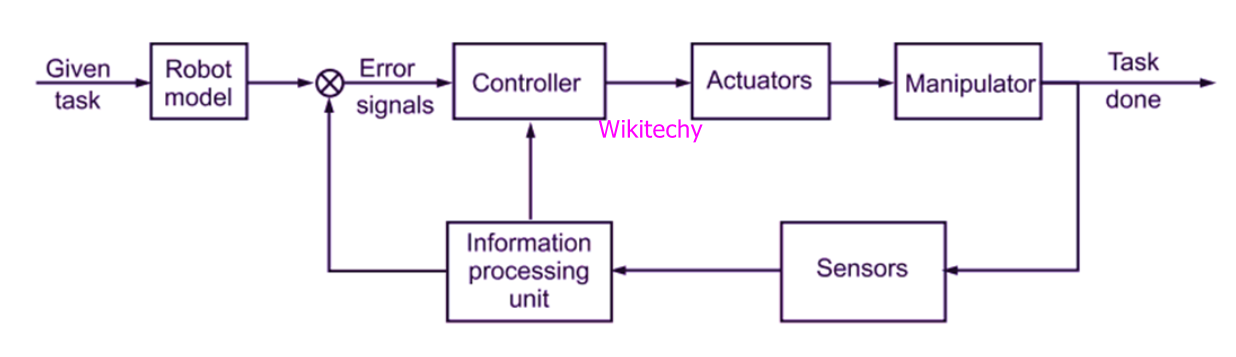
Controller
- It is a part of robot that coordinates all motion of the mechanical system and also receives an input from immediate environment through various sensors.
- Microprocessor is the heart of robot's controller that is linked with the input/output and monitoring device.
- The command issued by the controller activates the motion control mechanism, consisting of various controller, amplifier and actuators.
Read Also
Robot Locomotion
- Locomotion is the method of moving from one place to another and mechanism that makes a robot capable of moving in its environment is known as robot locomotion.
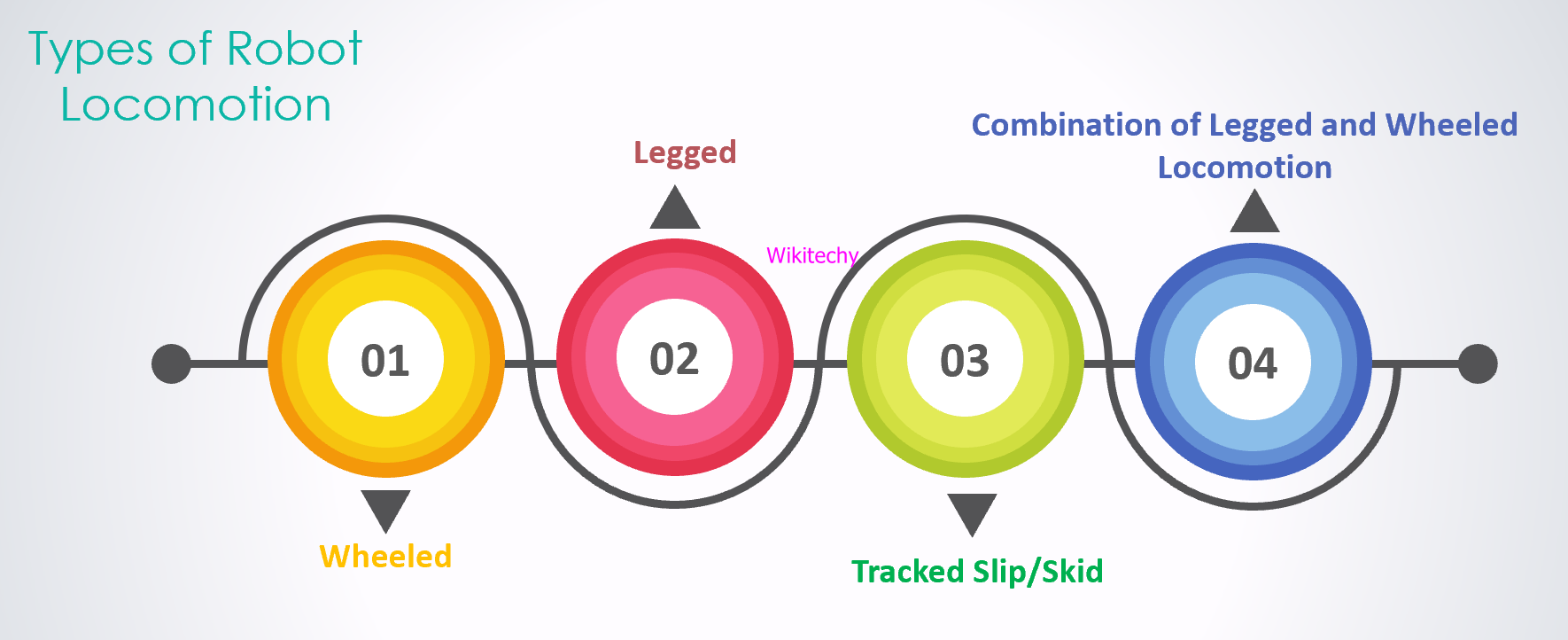
Robot LocomotionInterpreter
- Here, there are four types of robot locomotion.
Wheeled Locomotion
- Wheeled locomotion is little easy to implement as there are lesser stability issues in case of more number of wheels and it requires less number of motors for accomplishing a movement.
- While compared to legged locomotion it is more power efficient.
- Castor wheel rotates around the offset steering joint and wheel axle.
- Standard wheel rotates around the contact and the wheel axle.
- Ball or spherical wheel is technically difficult to implement due to architectural complexity and it is an Omni directional wheel with only one directional movement is allowed.
- Swedish 45 and Swedish 90 wheels is an Omni-wheel, which rotates around the contact point, around the wheel axle, and around the rollers.
Legged locomotion
- It comes up with the variety of one, two, four, and six legs then if has multiple legs then leg coordination is required for locomotion.
- Legged locomotion consumes more power while demonstrating trot, hop, jump, walk, climb up or down etc.
- Legged locomotion is suited for rough as well as smooth terrain where irregular or too smooth surface makes it consume more operational power and it requires more number of motors for accomplish a movement.
Slip/Skid Locomotion
- In Slip/Skid locomotion the vehicles use tracks as available in a tank and it offers stability because of large contact area of ground and track.
- In the same or opposite direction robot is steered by moving tracks with different speeds.
Artificial Intelligence in Robotics
- The capability to perform different tasks went on increasing exponentially, with the invention of machines or computers.
- John McCarthy is the founder of Artificial Intelligence which is "The engineering and science developed intelligent machine, especially an intelligent computer program".
- In similar manner the intelligent humans think, it is a way of developing a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or software that think intelligently.
- It is implemented by studying how humans decide and how human brain thinks, learn, and work while trying to solve a problem, and then using the result of this study as a basis of developing intelligent systems and software.
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
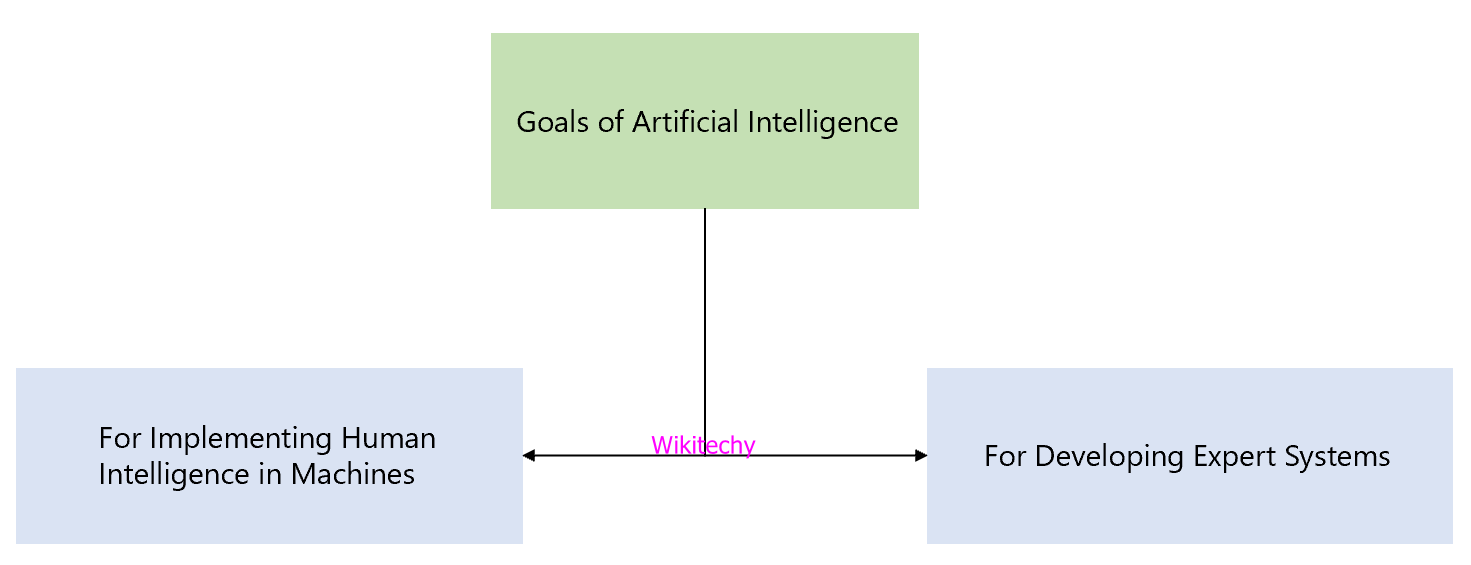
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
For Implementing Human Intelligence in Machines
- Creating systems that understand, learn, behave and think like humans.
For Developing Expert Systems
- The systems which exhibit intelligent learn, behavior, demonstrate, explain and advice its users.
Contributes to Artificial Intelligence
Contributes to Artificial Intelligence
Pygame Example
Expert Systems
- There are various applications which integrate machine, special information and software to impart reasoning and advising, those systems provide explanation and advice to the users.
Gaming
- In strategic games Artificial Intelligence plays major role such as chess, tic-tac-toe, poker, etc.
- Using AI, the machine can think of large number of possible moves based on general knowledge.
Natural Language Processing
- It is possible to interact using natural language processing with a computer that can understand natural language spoken by humans.
Vision Systems
- On computer these systems understand, comprehend and interpret a visual input.
Intelligent Robots
- Robots have sensors embedded to detect physical data from the outside environment such as light, pressure, heat, sound, etc.
- They are designed for performing the tasks given by a human.
- They have efficient processors, large memory and multiple sensors to exhibit intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence Research Areas
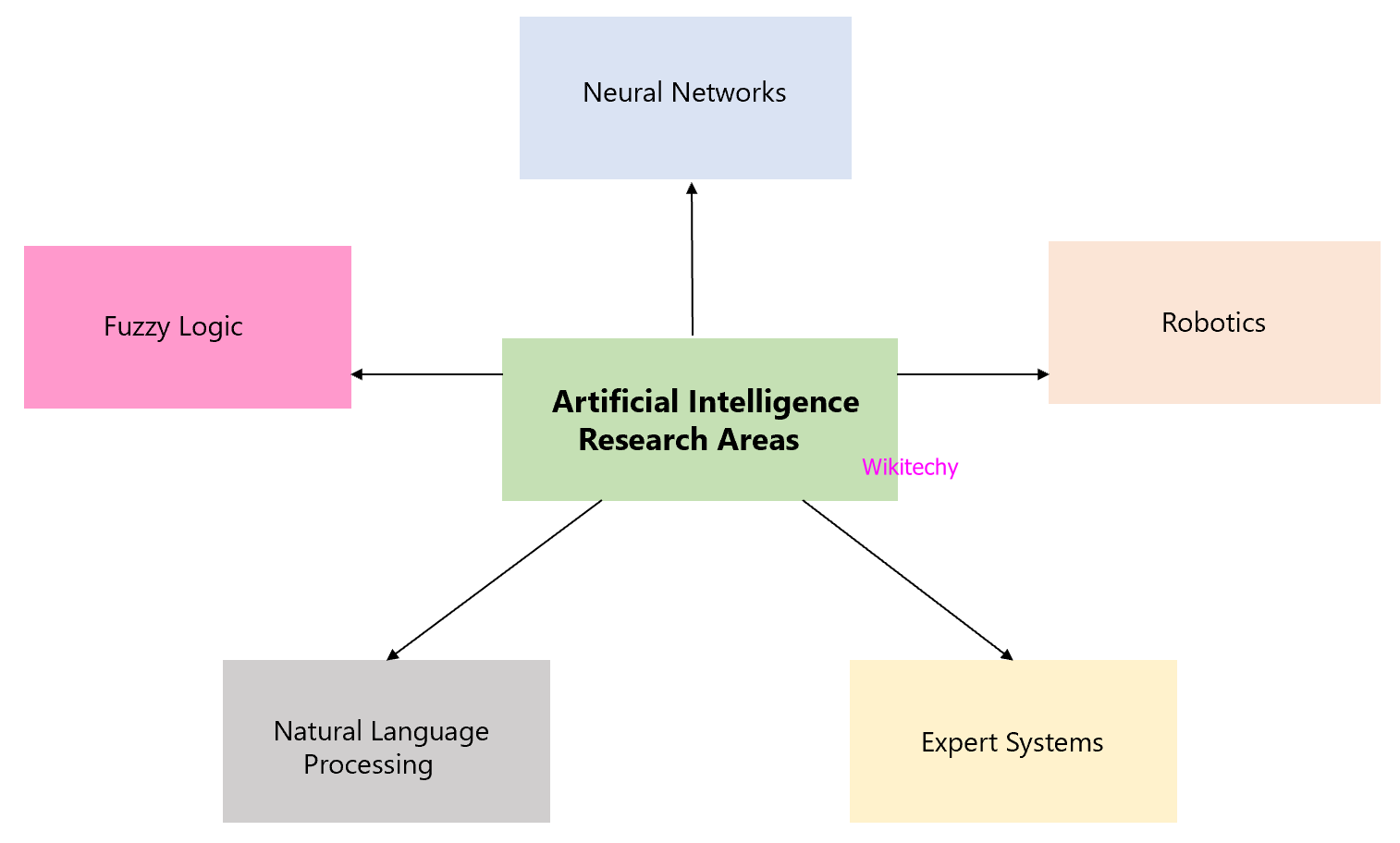
Artificial Intelligence Research Areas
Expert System
- An expert system is used for solving complex problems by reasoning about knowledge, represented primarily by if-then rules rather than by conventional procedural code, in artificial intelligence.
Neutral Networks
- Neural networks are system of interconnected neurons which exchange messages between each other and they are used for approximate functions or estimate a large number of inputs which are generally unknown.
- Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) belongs to a family of model inspired by biological neural networks in machine learning.
Robotics
- It is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is mainly composed to mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science engineering for designing, construction and application of robots.
- Robotics is science of designing or building an application of robots and aim of robotics is to design an efficient robot.
Natural Language Processing
- NLP is a method of communicating with an intelligent system by using a natural language such as English and their input and output system is speech and written text.
Fuzzy Logic
- In 1965 Fuzzy logic was introduced as a proposal of fuzzy set theory.
- Fuzzy logic is applied to various fields, from artificial intelligence to control theory and it is a form of many-valued logic in which truth table values of variable may be real number between 0 and 1.
Read Also
Types of Robots
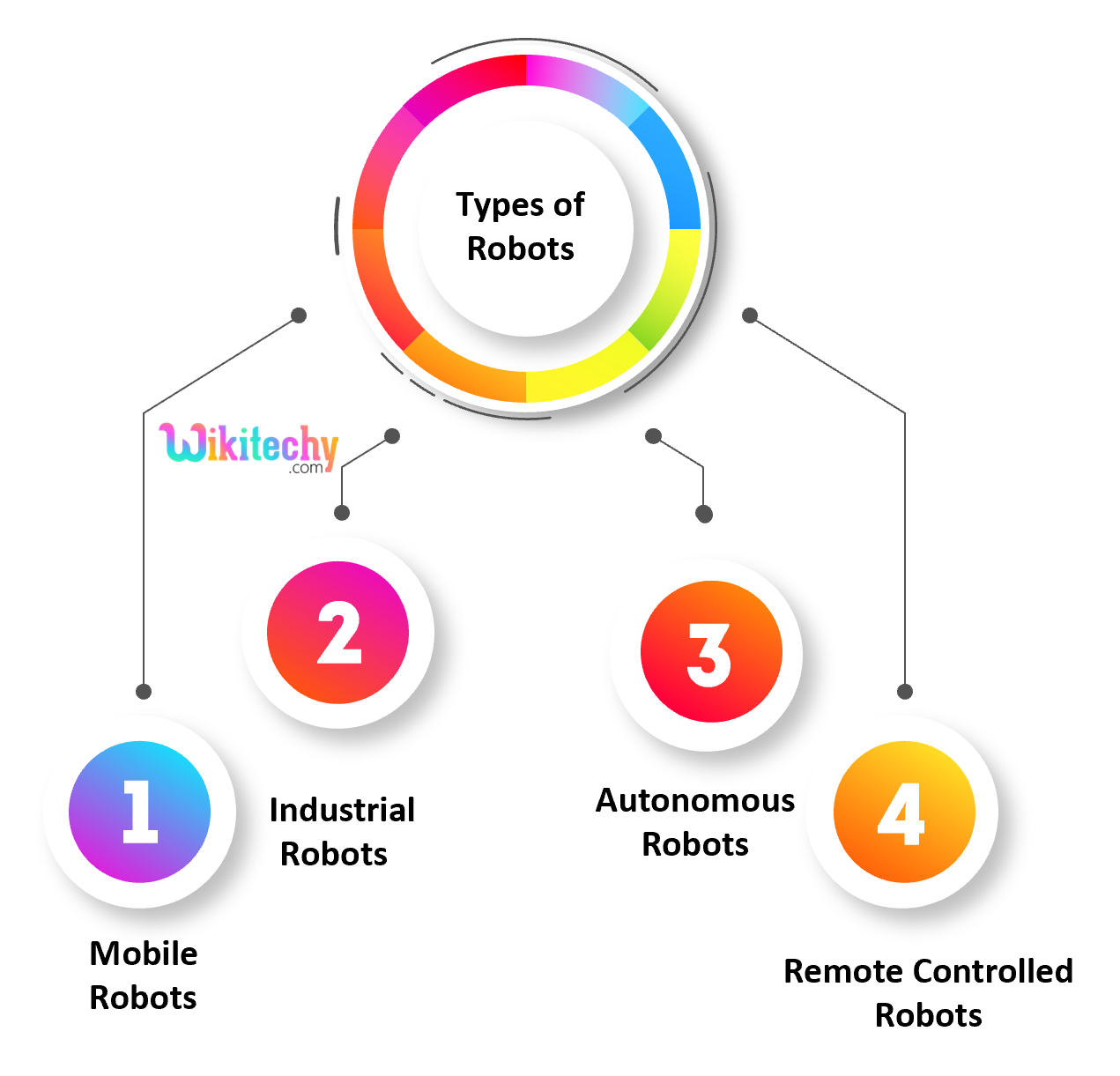
Types of Robots
Mobile Robots
- Using locomotion mobile robots are able to move from one location to another location.
- Robots is an automatic machine that is capable of navigating an uncontrolled environment without any requirement of physical and electromechanical guidance devices.
- Here, there are two types of mobile robots, they are rolling robots and walking robots.
- Rolling robots require wheels to move around and it can easily and quicky search.
- Walking robots have at least 4 legs and with legs are usually used in condition where the terrain is rocky.
Industrial Robots
- Industrial robots perform same tasks repeatedly without ever moving and in industries they are working in which there is requirement of performing dull and repeated tasks suitable for robot.
- An industrial robot never tired, whether it will perform their works day and night without ever complaining.
Autonomous Robots
- Autonomous robots are self-supported and it uses a program that provides them the opportunity to decide the action to perform depending on their surroundings.
- These robots often learn new behavior using artificial intelligence.
Remote Controlled Robots
- Remote controlled robot used for performing undetermined and complicated tasks that autonomous robot cannot perform due to uncertainty of operation.
- With real brainpower complicated tasks are best performed by human beings.
- Human can perform dangerous tasks without being at the spot where the tasks are performed by using remote controlled operation.
Types of Robot Sensors
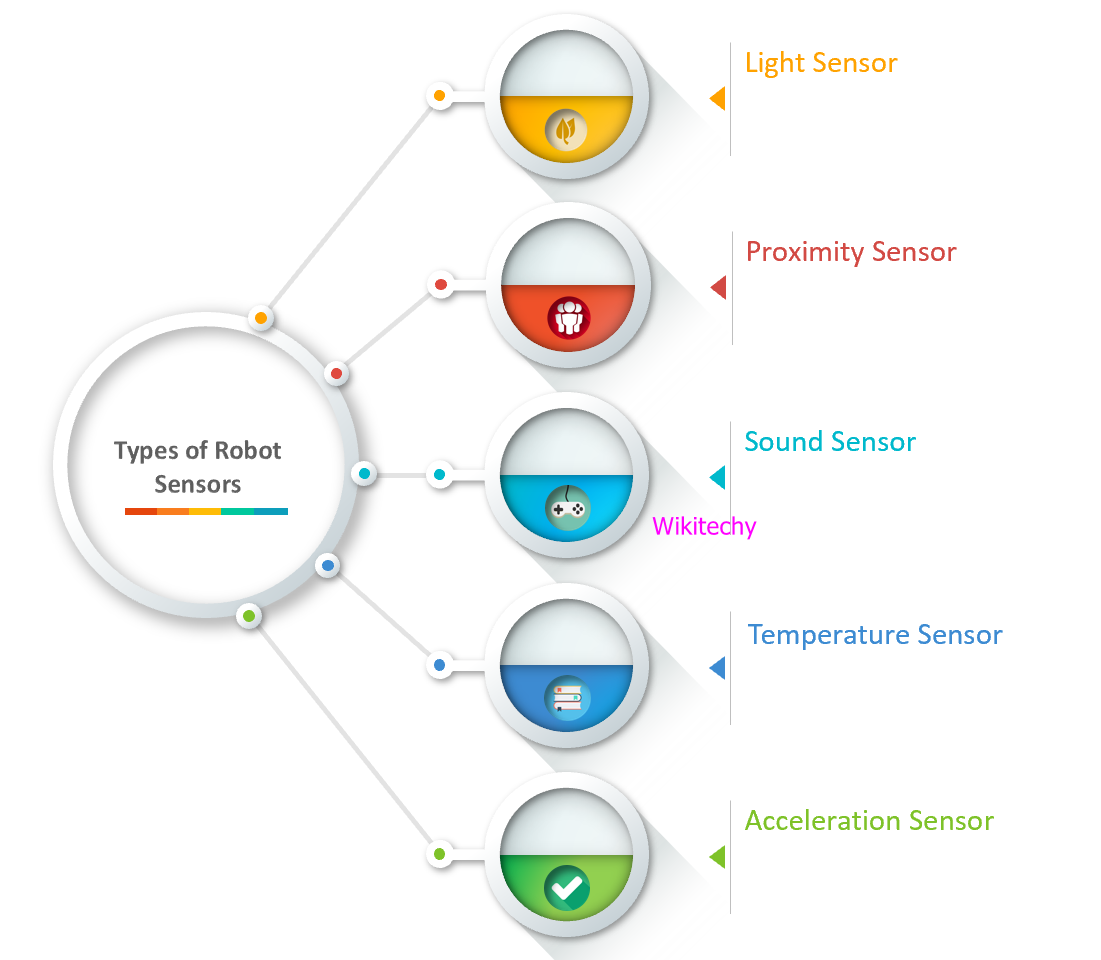
Types of Robot Sensors
Light Sensor
- Light sensor is a transducer creates a voltage difference equivalent to the light intensity fall on a light sensor.
- Photo resistor and Photovoltaic cells are the two main light sensors used in robots.
- Photo resistor is used for detecting the light and varies with change in light intensity.
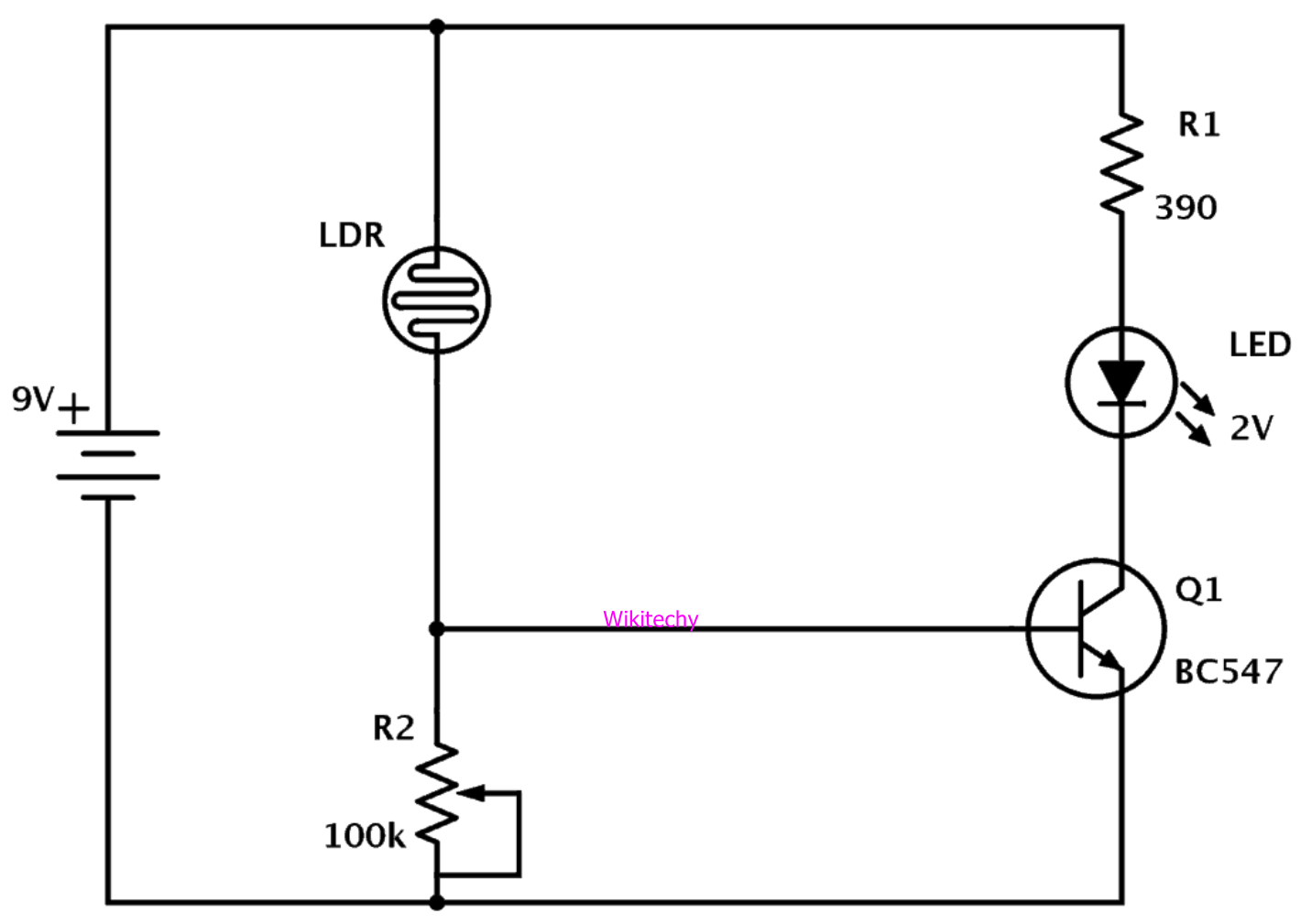
Photo resistor
- Photovoltaic cells are energy conversion device used to convert solar radiation into electrical electric energy and used to build a solar robot.
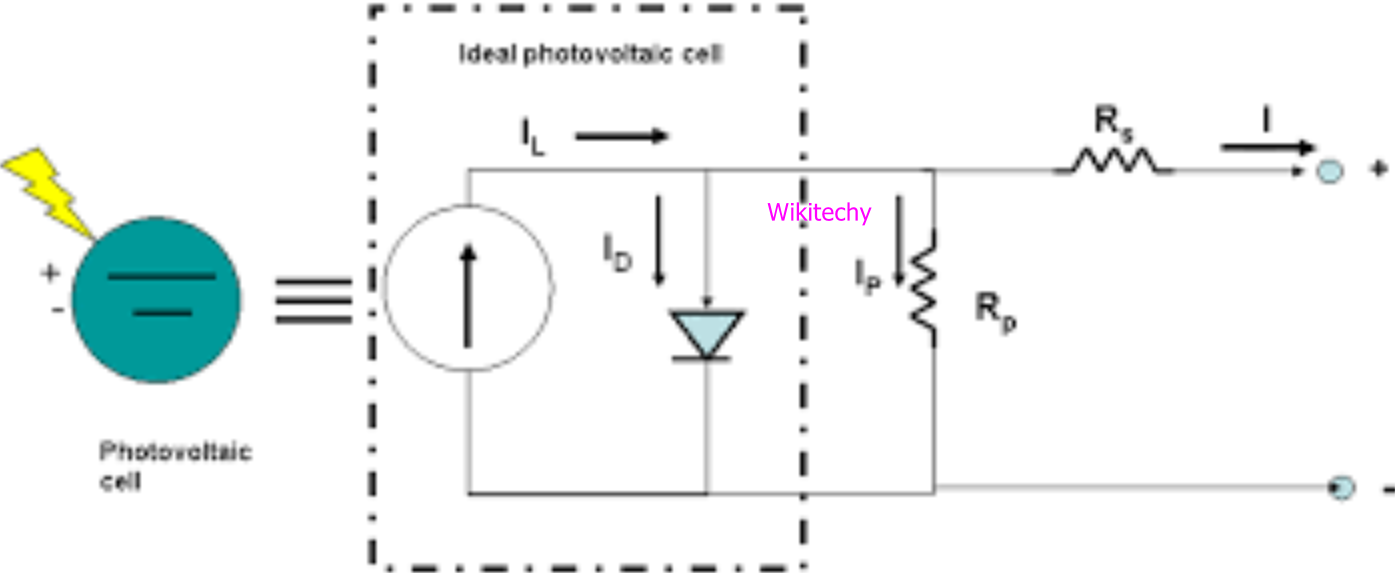
Photovoltaic cells
Proximity Sensor
- This sensor can detect the presence of nearby object without any physical contact.
- In proximity sensor transmitter transmits an electromagnetic radiation and receiver receives and analyzes the return signal for interruptions and the working of this sensor is simple.
- In robotics there are two types of proximity sensor they are Infrared (IR) Transceivers and Ultrasonic Sensor.
- At IR sensor LED transmit the beam of IR light and if it finds an obstacle then the light is reflected back which is captured by an IR receiver.
- At ultrasonic sensors transmitter generates high frequency sound waves, the received echo pulse suggests an object interruption.
- In robotics system general ultrasonic sensors are used for distance measurement.
Sound Sensor
- Sound sensors are a microphone used to detect sound and return a voltage equivalent to the sound level.
- A simple robot can be designed to navigate based on the sound receives by using sound sensor.
- Implementation of sound sensors is difficult compare to light sensor because it generates a small voltage difference which will be amplified to generate measurable voltage change.
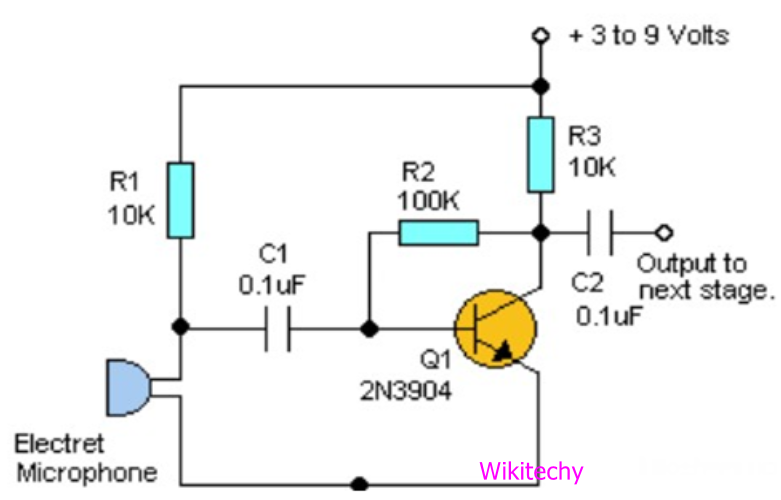
Sound Sensor
Temperature Sensor
- Temperature sensors are used for sensing the change in temperature of the surrounding.
- This sensor is based on principle of change in voltage difference for a change in temperature this change in voltage will provide the equivalent temperature value of the surrounding.
Acceleration Sensor
- This sensor is used for measuring tilt and acceleration.
- There are two kinds of forces which affect an accelerometer is Static force and Dynamic force.
- Static force is the frictional force between any two objects and Dynamic force is the amount of acceleration required to move an object.
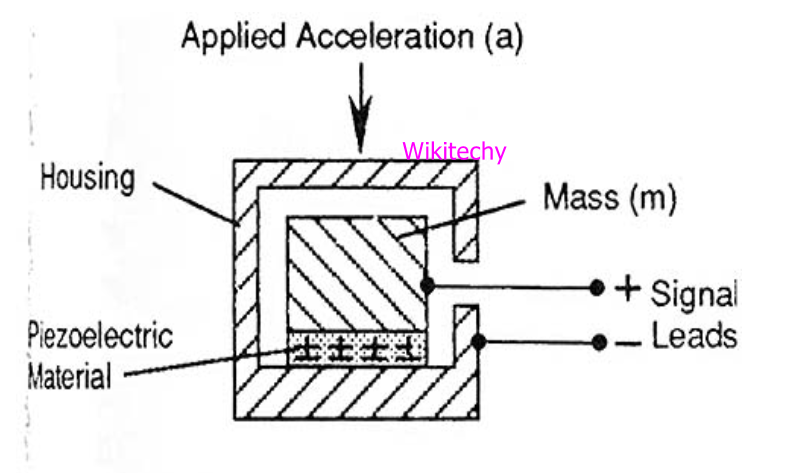
Acceleration Sensor
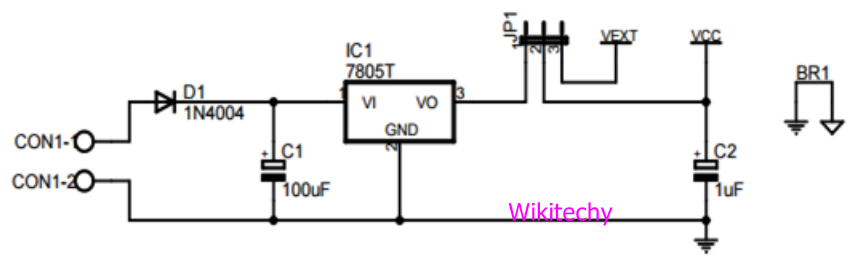
Power Supply
- It is the circuit used for converting 220V AC signal to 5V or 10V DC signal required for operation of robot electronic circuit.
- Here use add-command to add the components and use the net-command to draw the connections.
Microcontroller in Robotics
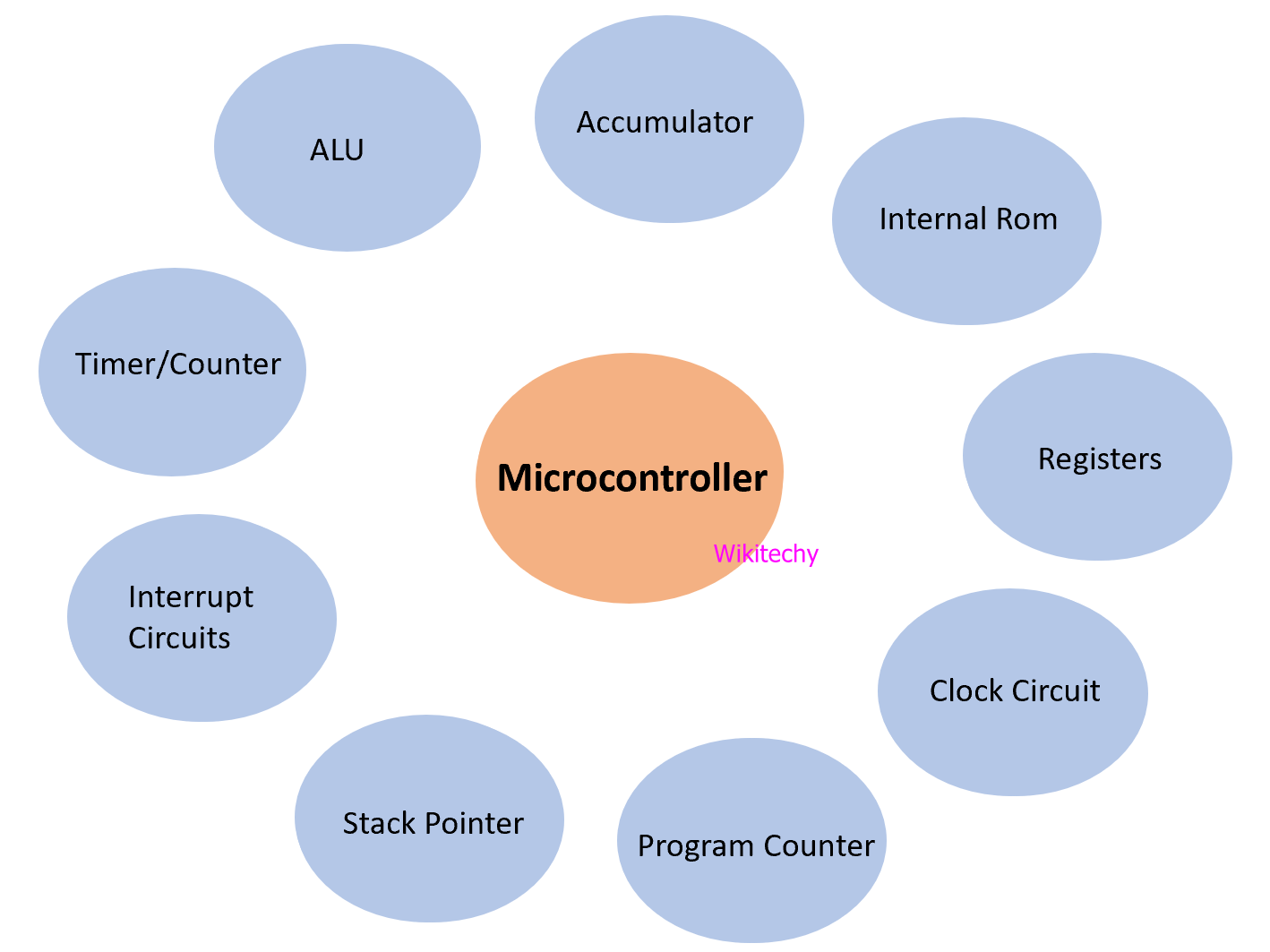
- It is the advanced version of microprocessors and contain on chip central processing unit (CPU), Read only memory (ROM), Random access memory (RAM), input/output unit, interrupts controller etc.
- Microprocessor is mainly used for highspeed signal processing operation inside an embedded system.
- Microprocessor acts as a major component used in designing of an embedded system.
Designing of PCB (Printed Circuit Board):
- Using etched copper pathways printed circuit board connects electrical components and it also provides mechanical strength to the robotic circuit.
- Printed Circuit Board are composed of organic and inorganic dielectric materials with many layers.
- The eagle software is used for generating the layout of the circuit and copper tracks are used on a conducting sheet in PCB.
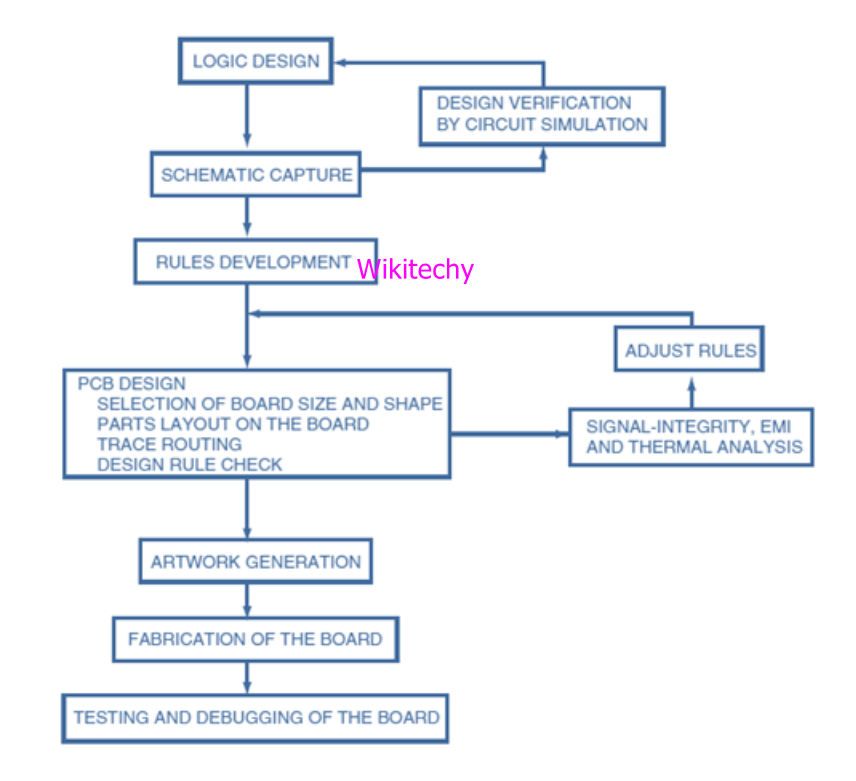
Designing of PCB
Materials required in PCB designing
- Laser Printer
- Electric Iron
- Two Plastic Trays
- Over Head Projector (OHP) sheets or a wax paper.
- Drill machine
- Steel wool
- PCB/ Copper board
- Etching solution (Ferric Chloride)
Line Follower Robot
- Line follower robot is an autonomous machine that can follow a path and it can be seen like a white line on a black surface (or vice-versa) or it can be invisible as magnetic field.
- Line follower robot is guidance system for industrial robots moving on shop floor and automated cars running on road with embedded magnet.
Hardware Required
- Analog IR Sensor-3 piece
- AVR Microcontroller Board-1 piece
- 12V, 1A DC Adapter-1 piece
- AVR USB Programmer-1 piece
- 1 to 1 Connector-15 piece
- DC Motor Driver-1 piece
- Robot-1 piece
- 10 to 10 FRC Female Connector-2 piece
Software Required
- WinAVR-2010
- AVRDUDE-GUI
- BASCOM-AVR Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- USBasp Driver
Block Diagram
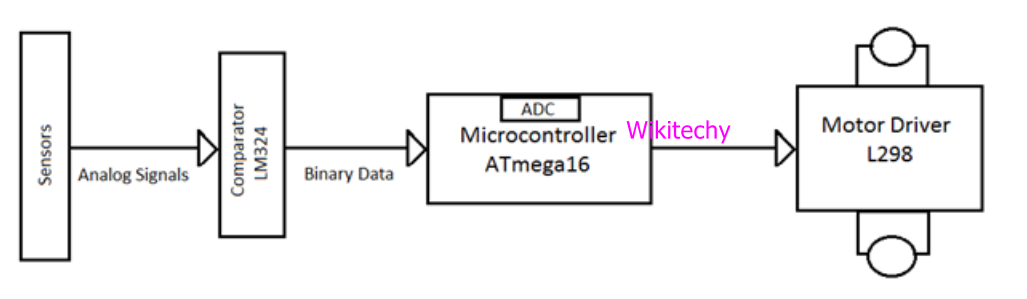
Line Follower Block Diagram
Sample Code
$regfile = "m16def.dat".
$crystal = 1000000
Config Lcd = 16 * 2
Config Lcdpin = Pin , Rs = Portb.2 , E = Portb.3 , Db4 = Portb.4 , Db5 = Portb.5 , Db6 = Portb.6 , Db7 = Portb.7
Config Adc = Single , Prescaler = Auto , Reference = Avcc
Start Adc
Config Timer1 = Pwm , Pwm = 8 , Prescale = 1 , Compare A Pwm = Clear Down , Compare B Pwm = Clear Down
Start Timer1
Dim Lb As Integer , Lw As Integer , Lm As Integer , L As Integer
Dim Rb As Integer , Rw As Integer , Rm As Integer , R As Integer
Cls
Lcd "sense black"
Wait 5
Lb = Getadc(1)
Rb = Getadc(0)
Lowerline
Lcd Lb ; "_" ; Rb
Wait 1
Cls
Lcd "sense white"
Wait 5
Lw = Getadc(1)
Rw = Getadc(0)
Lowerline
Lcd Lw ; "_" ; Rw
Wait 1
Cls
Lm = Lw + Lb
LmLm = Lm / 2
Rm = Rw + Rb
RmRm = Rm / 2
Do
Cls
L = Getadc(1)
R = Getadc(0)
If L < Lm And R < Rm Then
Lcd "fwd"
Pwm1a = 100
Portd.6 = 0
Pwm1b = 100
Portd.3 = 0
Elseif L > Lm And R < Rm Then
Lcd "left"
Pwm1a = 100
Portd.6 = 0
Pwm1b = 0
Portd.3 = 0
Elseif L < Lm And R > Rm Then
Lcd "right"
Pwm1a = 0
Portd.6 = 0
Pwm1b = 100
Portd.3 = 0
Elseif L > Lm And R > Rm Then
Lcd "stop"
Pwm1a = 0
Portd.6 = 0
Pwm1b = 0
Portd.3 = 0
End If
Loop
End
Circuit Diagram
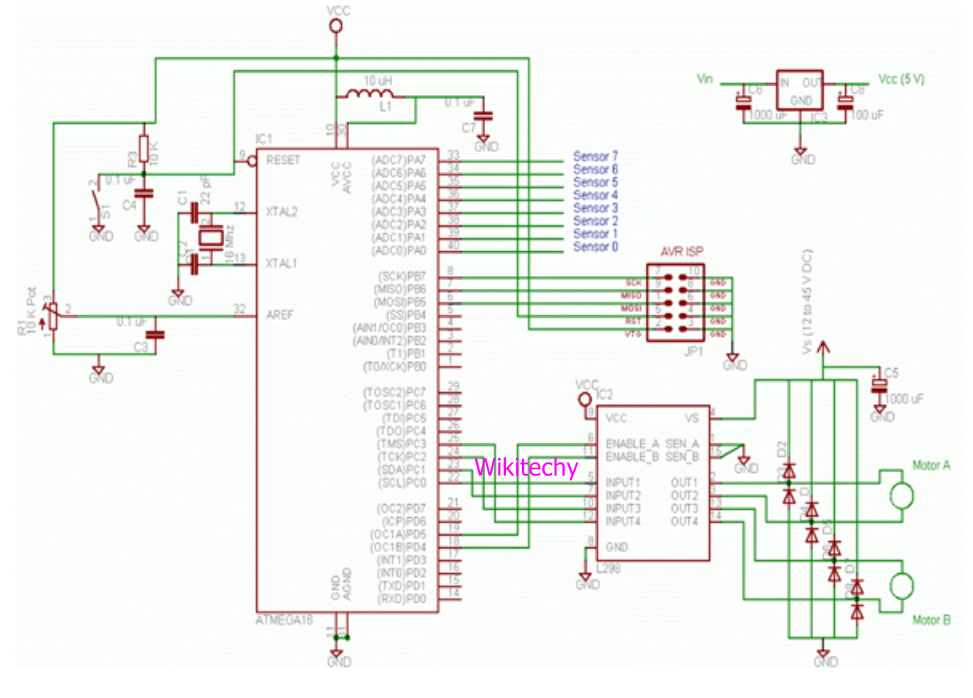
Line Follower Circuit Diagram
