What is Router - What are Routers in Computer Network
What is a Router?
- The router is a physical or virtual internetworking device that is designed to receive, analyze, and forward data packets between computer networks.
- A router examines a destination IP address of a given data packet, and it uses the headers and forwarding tables to decide the best way to transfer the packets.
- There are some popular companies that develop routers; such are Cisco, 3Com, HP, Juniper, D-Link, Nortel, etc. Some important points of routers are given below:
- A router is used in LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network) environments. For example, it is used in offices for connectivity, and you can also establish the connection between distant networks such as from Bhopal to other cities or regions.
- It shares information with other routers in networking.
- It uses the routing protocol to transfer the data across a network.
- Furthermore, it is more expensive than other networking devices like switches and hubs.

- A router works on the third layer of the OSI model, and it is based on the IP address of a computer. It uses protocols such as ICMP to communicate between two or more networks. It is also known as an intelligent device as it can calculate the best route to pass the network packets from source to the destination automatically.
- A virtual router is a software function or software-based framework that performs the same functions as a physical router.
- It may be used to increase the reliability of the network by virtual router redundancy protocol, which is done by configuring a virtual router as a default gateway.
- A virtual router runs on commodity servers, and it is packaged with alone or other network functions, like load balancing, firewall packet filtering, and wide area network optimization capabilities.
Why Routers?
- A router is more capable as compared to other network devices, such as a hub, switch, etc., as these devices are only able to execute the basic functions of the network.
- For example, a hub is a basic networking device that is mainly used to forward the data between connected devices, but it cannot analyze or change anything with the transferring data. On the other hand, the router has the capability to analyze and modify the data while transferring it over a network, and it can send it to another network. For example, generally, routers allow sharing a single network connection between multiple devices.
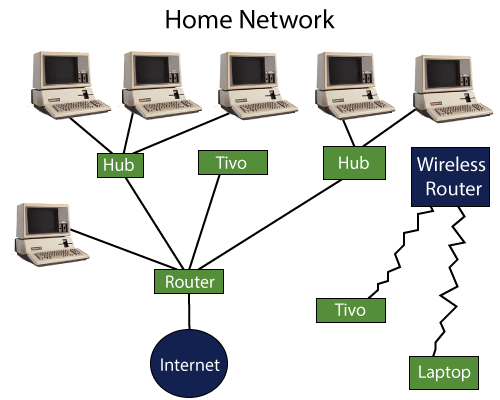
How does Router work?
- A router analyzes a destination IP address of a given packet header and compares it with the routing table to decide the packet's next path. The list of routing tables provides directions to transfer the data to a particular network destination. They have a set of rules that compute the best path to forward the data to the given IP address.
- Routers use a modem such as a cable, fiber, or DSL modem to allow communication between other devices and the internet. Most of the routers have several ports to connect different devices to the internet at the same time. It uses the routing tables to determine where to send data and from where the traffic is coming.
- A routing table mainly defines the default path used by the router. So, it may fail to find the best way to forward the data for a given packet. For example, the office router along a single default path instructs all networks to its internet services provider.
- There are two types of tables in the router that are static and dynamic. The static routing tables are configured manually, and the dynamic routing tables are updated automatically by dynamic routers based on network activity.
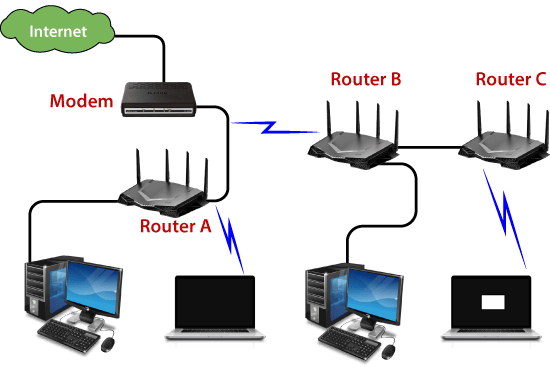
Types of Router
There are several types of routers available in the market. Some of them are mentioned below:
1. Broadband Routers:
- These are one of the important kinds of routers. It is used to do different types of things. it is used to connect computers or it is also used to connect to the internet.
2. Wireless routers:
- These routers are used to create a wireless signal in your office or home. Wireless routers receive data packets over wired broadband, convert the packets written in binary code into radio signals that are picked up by electronic devices, and then convert them back into previous packets.
3. Edge Routers:
- As the name indicates, these are located at the edges usually connected to an Internet Service Provider, and distribute packets across multiple packets.
4. Core Routers:
- Core routers distribute packets within the same network. The main task is to carry heavy data transfers.
Architecture of a Router
A Generic router consists of the following components:
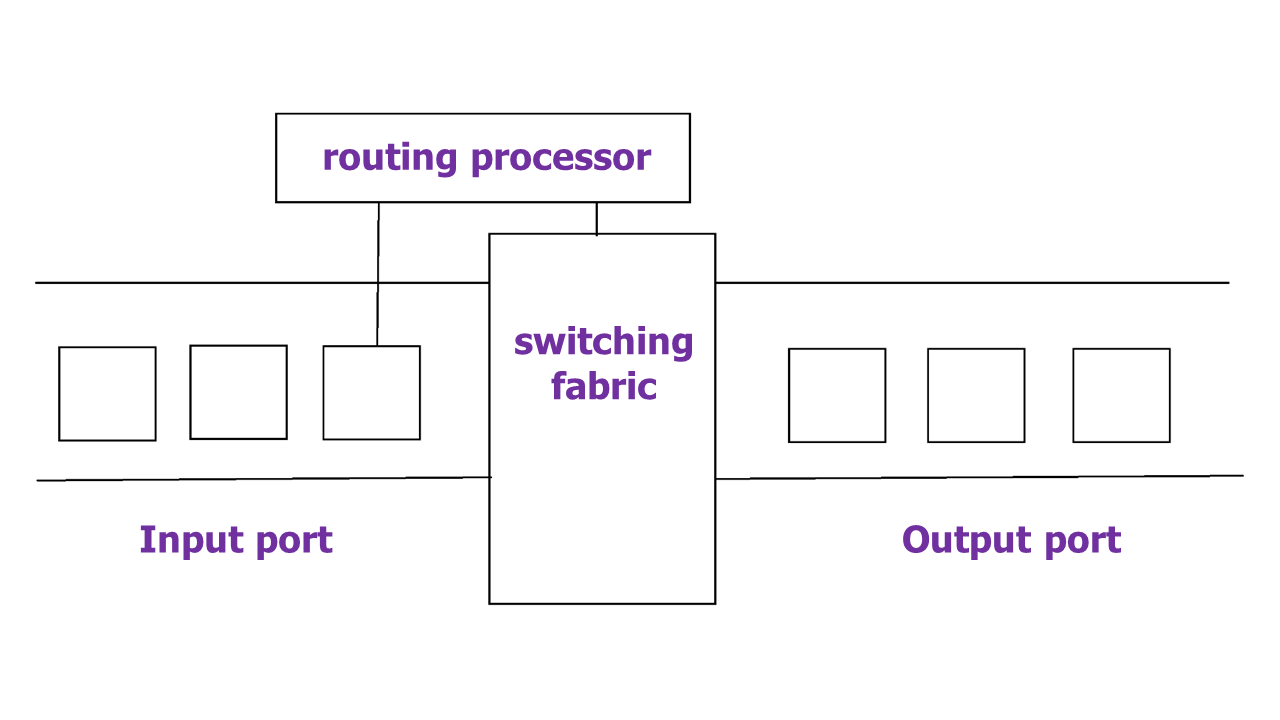
1. Input Port:
- This is the interface by which packets are admitted into the router, it performs several key functions as terminating the physical link at the router, this is done by the leftmost part in the below diagram, and the middle part does the work of interoperating with the link-layer like decapsulation, in the last part of the input port the forwarding table is looked up and is used to determine the appropriate output port based on the destination address.
2. Switching Fabric:
- This is the heart of the Router, It connects the input ports with the output ports. It is kind of a network inside a networking device. The switching fabric can be implemented in several ways some of the prominent ones are:
- In this, we have a processor which copies the packet from input ports and sends it to the appropriate output port. It works as a traditional CPU with input and output ports acting as input and output devices
- In this implementation, we have a bus that connects all the input ports to all the output ports. On receiving a packet and determining which output port it must be delivered to, the input port puts a particular token on the packet and transfers it to the bus. All output ports can see the packets but they will be delivered to the output port whose token has been put in, the token is then scraped off by that output port and the packet is forwarded
- This is a more sophisticated network, here instead of a single bus we use a 2N bus to connect n input ports to n output ports.
A. Switching via memory:
B. Switching via bus:
C. Switching via interconnection network:
3. Output Port:
- This is the segment from which packets are transmitted out of the router. The output port looks at its queuing buffers (when more than one packets have to be transmitted through the same output port queuing buffers are formed) and takes packets, does link layer functions, and finally transmits the packets to an outgoing link
4. Routing Processor:
- It executes the routing protocols, and it works like a traditional CPU. It employs various routing algorithms like the link-state algorithm, distance-vector algorithm, etc. to prepare the forwarding table, which is looked up to determine the route and the output port.
Advantages of Router
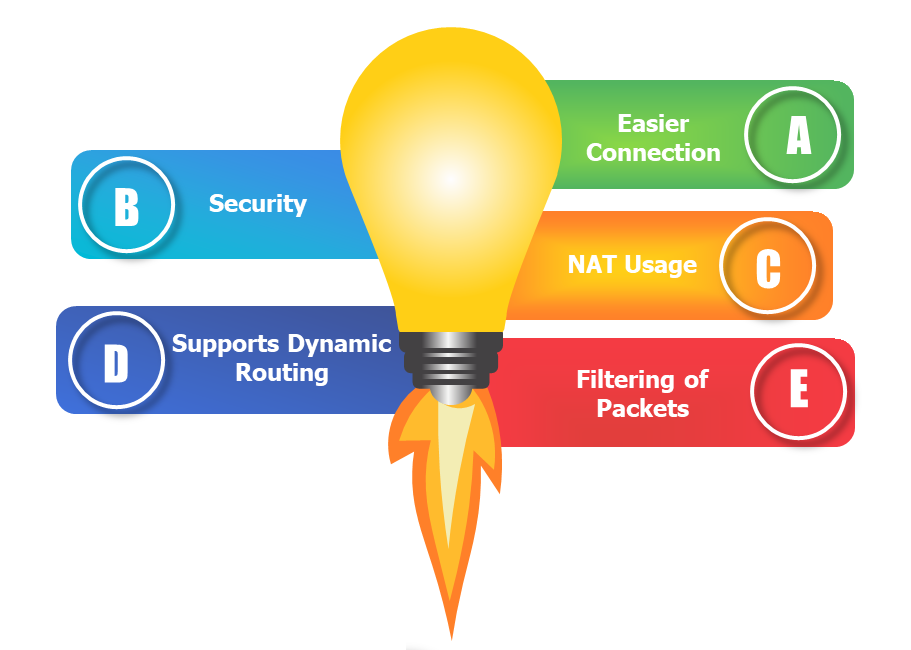
1. Easier Connection:
- Sharing a single network connection among numerous machines is the router’s main job. This enables numerous people to connect to the internet, boosting total productivity. In addition, routers have connections between various media and network designs.
2. Security:
- Undoubtedly, installing a router is the first step in securing a network connection. Because using a modem to connect directly to the internet exposes your PC to several security risks. So that the environment is somewhat secure, routers can be utilized as an intermediary between two networks. While not a firewall or antivirus replacement.
3. NAT Usage:
- Routers use Network Address Translation (NAT) to map multiple private IP addresses into one public IP address. This allows for a better Internet connection and information flow between all devices connected to the network.
4. Supports Dynamic Routing:
- The router employs dynamic routing strategies to aid in network communication. The internet work’s optimum path is chosen through dynamic routing. Additionally, it creates collision and broadcast domains. Overall, this can lessen network traffic.
5. Filtering of Packets:
- Switching between packets and filtering packets are two more router services. A collection of filtering rules are used by routers to filter the network. The packets are either allowed or passed through.
Disadvantages of Router
1. Slower:
- Routers analyze multiple layers of information, from the physical layer to the network layer, which slows down connections. The same issue can also be encountered when multiple devices are connected to these network devices, causing “connection waiting”.
2. High Cost:
- They are more expensive than some other tools for systems administration. This includes security, extension, and the focal point. As a result, routers are typically not the greatest option for issues.
3. Need for configuration:
- The router must be properly configured to work properly. In general, the more complex the intended use, the more configuration is required. This requires professional installation, which can add to the cost of buying a router.
4. Quality Issues:
- The time transitions are not always accurate. Even yet, some modern devices use the 2.4GHz band, which is frequently deactivated. These kinds of separations are frequently possible for those who live in apartments and condominiums.
5. Bandwidth shortages:
- Dynamic routing techniques used by routers to support connections tend to cause network overhead, consuming a lot of bandwidth. This leads to a bandwidth shortage that significantly slows down the internet connection between connected devices.
