ASP.NET MVC Tutorial for Beginners - .Net Tutorial
ASP.NET MVC Tutorial
- MVC otherwise known as Model-View-Controller design pattern or an application development pattern which separates an application into three main components.
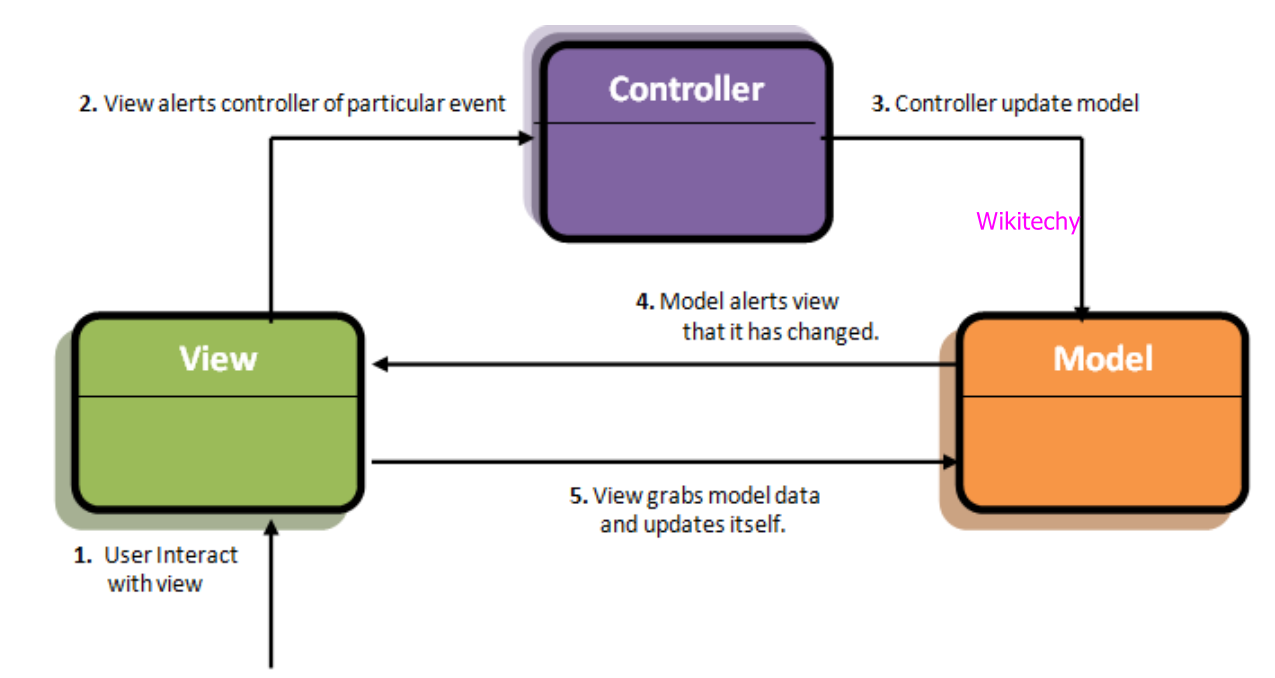
Model
- It is a part of application that implements the logic for the data domain of the application.
- It is used to store and retrieve model state in a database such as SQL Server database.
- It also used business logic separation from the data.
View
- It is a component that forms the application's user interface and uses to create web pages for the application.
- It would be an edit view of a Products table that displays text boxes, drop-down lists and check boxes based on the current state of a Product object.
Controller
- It is the component which handles user interaction then it works with the model and selects the view to render the web page.
- The view only displays the information whereas the controller handles and responds to the user input and requests, in MVC application.
Advantages of MVC Framework
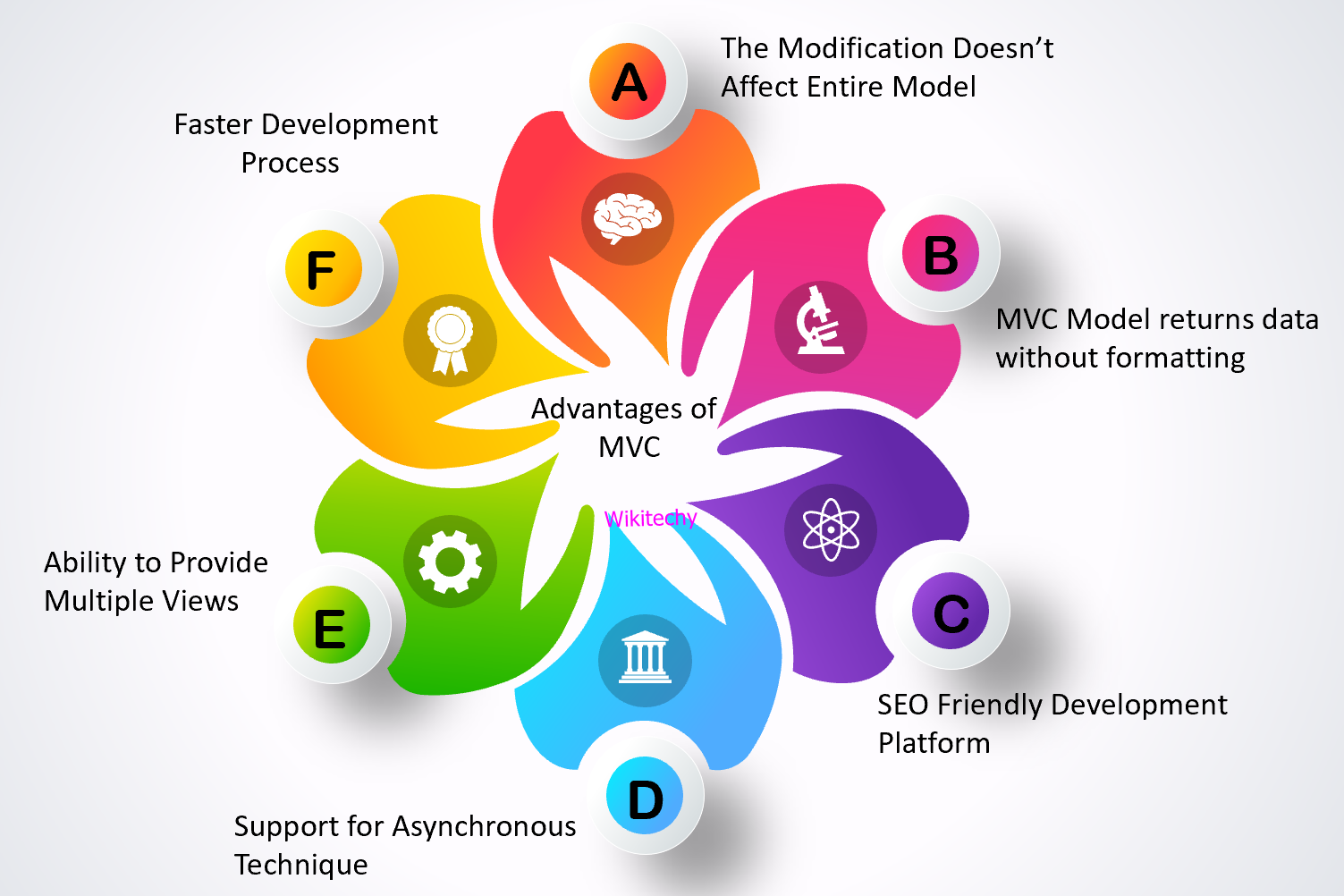
Faster Development Process
- MVC architecture could be put to better use, while developing any specific web application.
- Unlike others, this further makes the development process faster.
Ability to Provide Multiple Views
- Using MVC model multiple views could be created then, furthermore code duplication is limited in it.
- MVC architecture aims to provide the best solution for the same, with the increasing demand for accessing the application in new ways.
Support for Asynchronous Technique
- MVC architecture works greatly in tune with the JS frameworks and implies that we can run MVC apps easily on either PDF files, site-specific browsers or desktop widgets.
The Modification does not Affect the Entire Model
- The frequent updates of any web application change the User Interface of the same.
- In entire MVC architecture a change in any one component will not lead to a change and all three components work independently.
MVC Model Returns the Data without Formatting
- The MVC pattern returns the data, without any type of formatting.
- It is similar to the one used in HTML codes, as they can be further put to use using other interfaces like Dream viewer.
SEO Friendly Development Platform
- The development of SEO-friendly web pages or web applications is supported by the MVC platform.
- When using this platform, developing SEO-friendly URLs becomes very easy and thus, helping in the generation of more visits from a particular application.
Disadvantages of MVC Framework
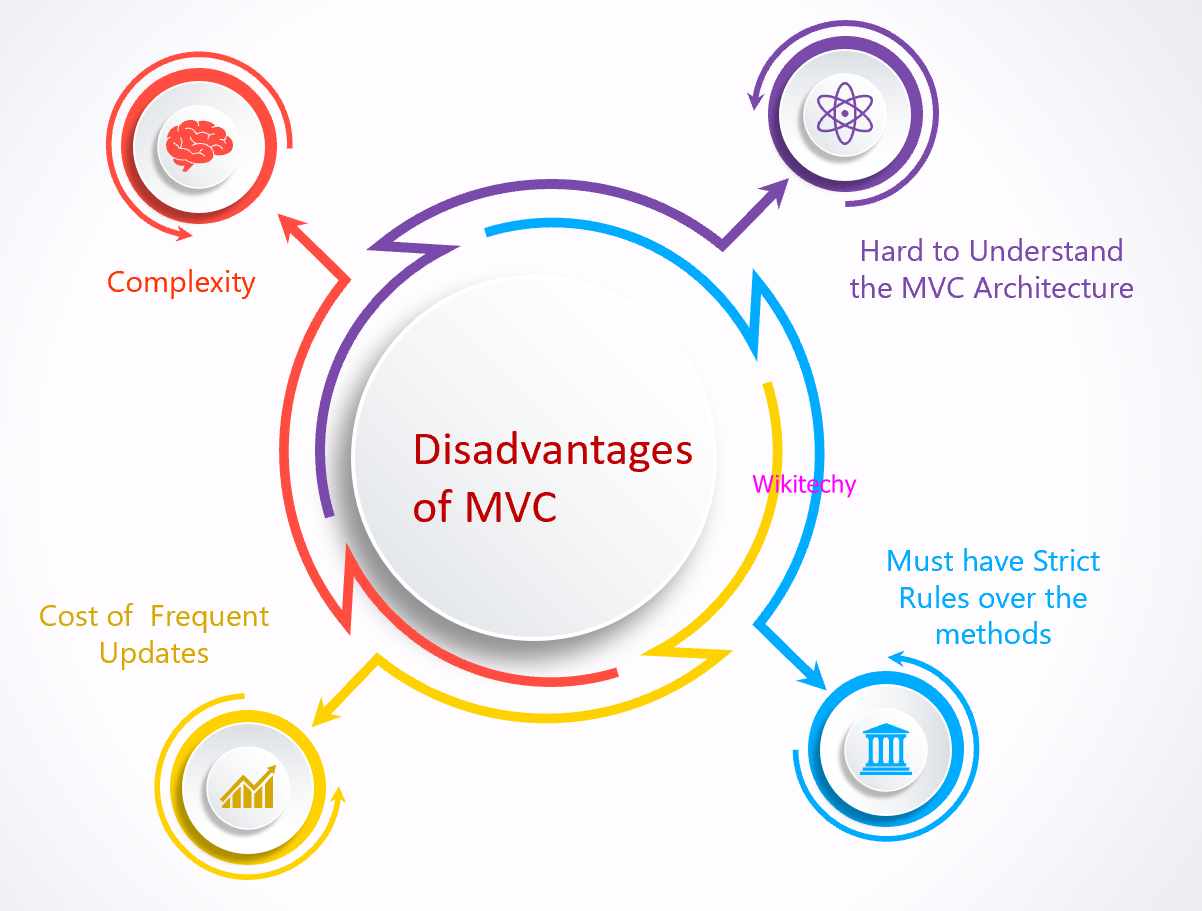
Complexity
- MVC architecture pattern updates with a new extent of indirection through its updates, with time.
Cost of Frequent Updates
- In the MVC pattern, the model keeps on going with frequent changes, views could be overburdened with update requests.
Hard to Understand the MVC Architecture
- MVC architecture is actually not that easy to understand and learn.
- Due to its frequent updates and complex structure, we might find it a bit tricky to keep up with all the components and the UI code for the same.
Must have Strict Rules Over the Methods
- The third component of the MVC architecture, controller keeps an eye over the events that are triggered by the View component.
- These methods do not have strict access, which in turn becomes one of the major drawbacks of the MVC.
How to create MVC Project
- In this topic, we are using visual studio 2017 IDE to create MVC web application and includes the various steps that are given below.
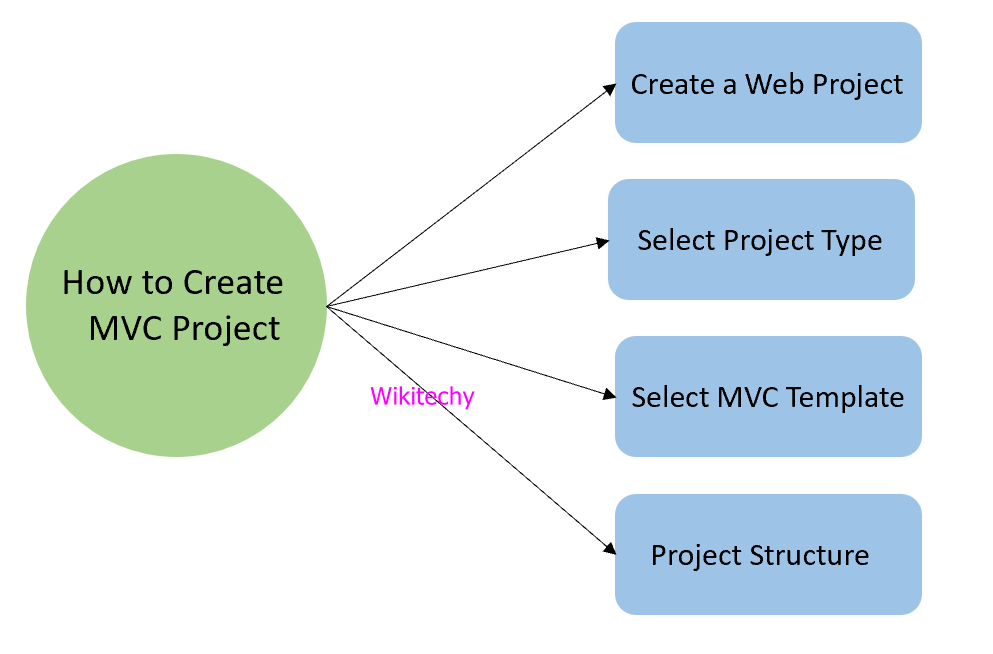
Create a Web Project
- Click on file menu from the menu bar and then select new submenu to create a new project.
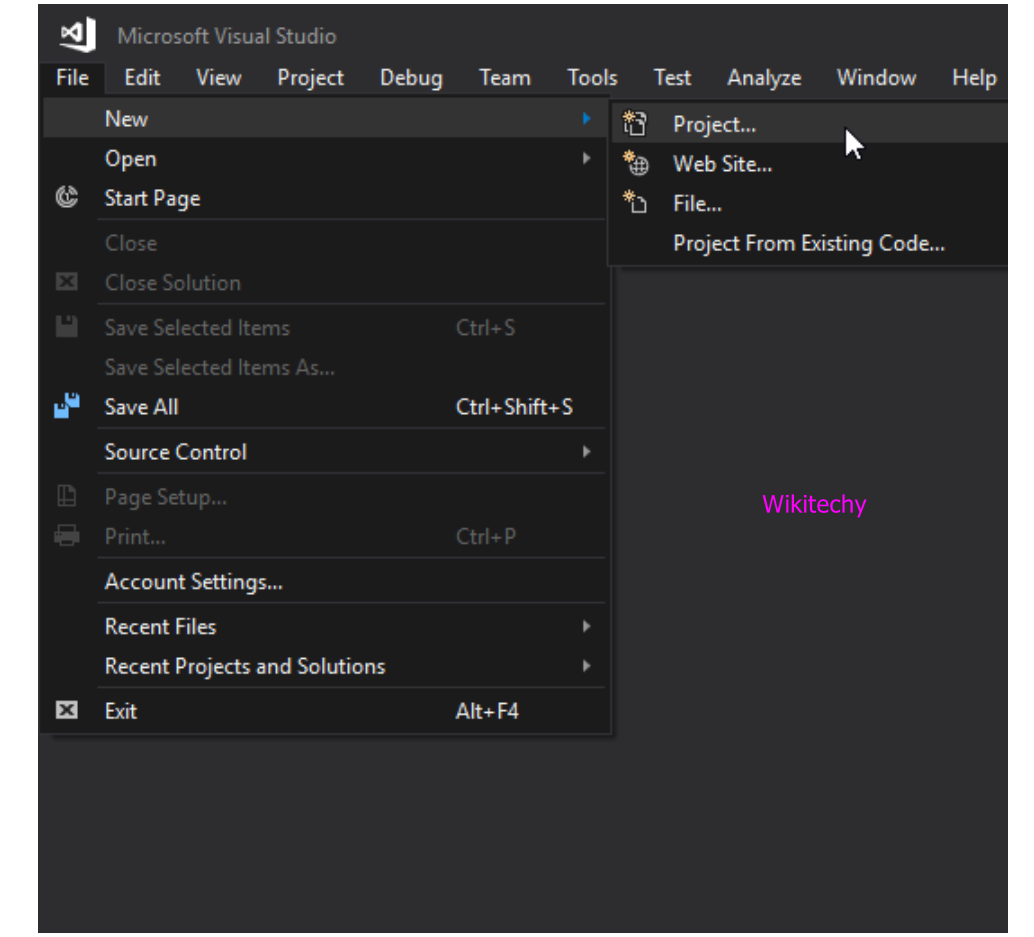
Select Project Type
- Then select type of project as a web project and provide name of the project.
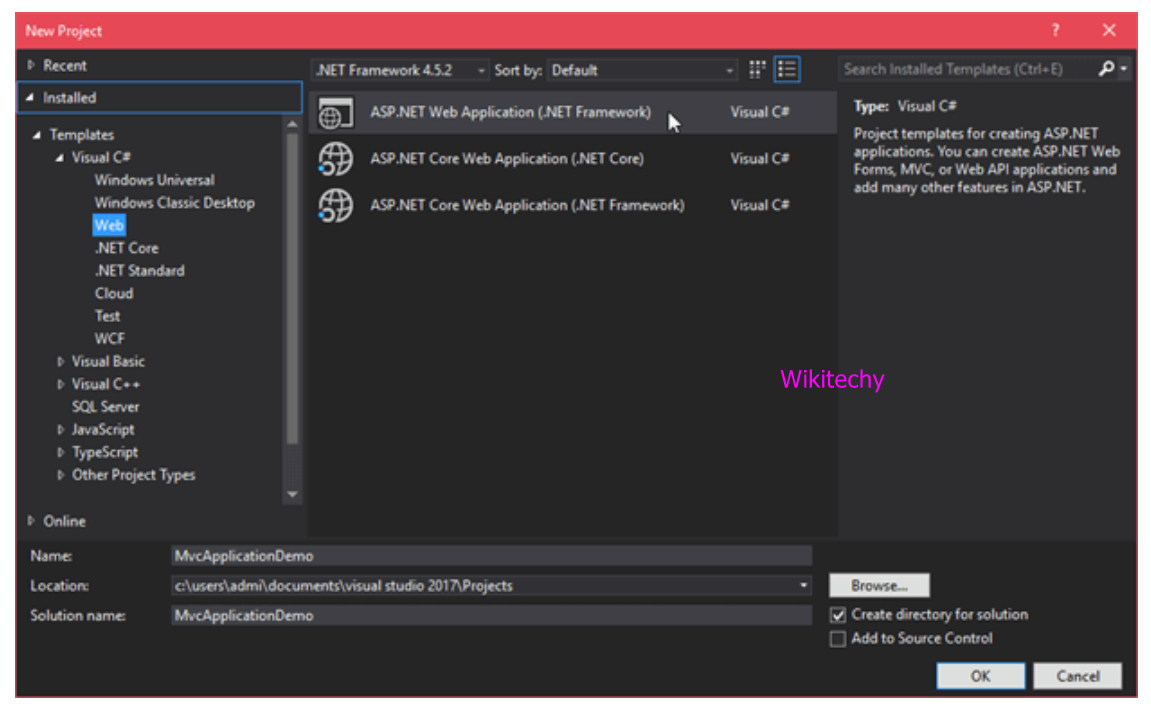
Select MVC Template
- Now select the web template that we want to implement, after selecting project type.
- Since we are working on MVC then select MVC template from the list of available templates then provide the authentication type to the application.
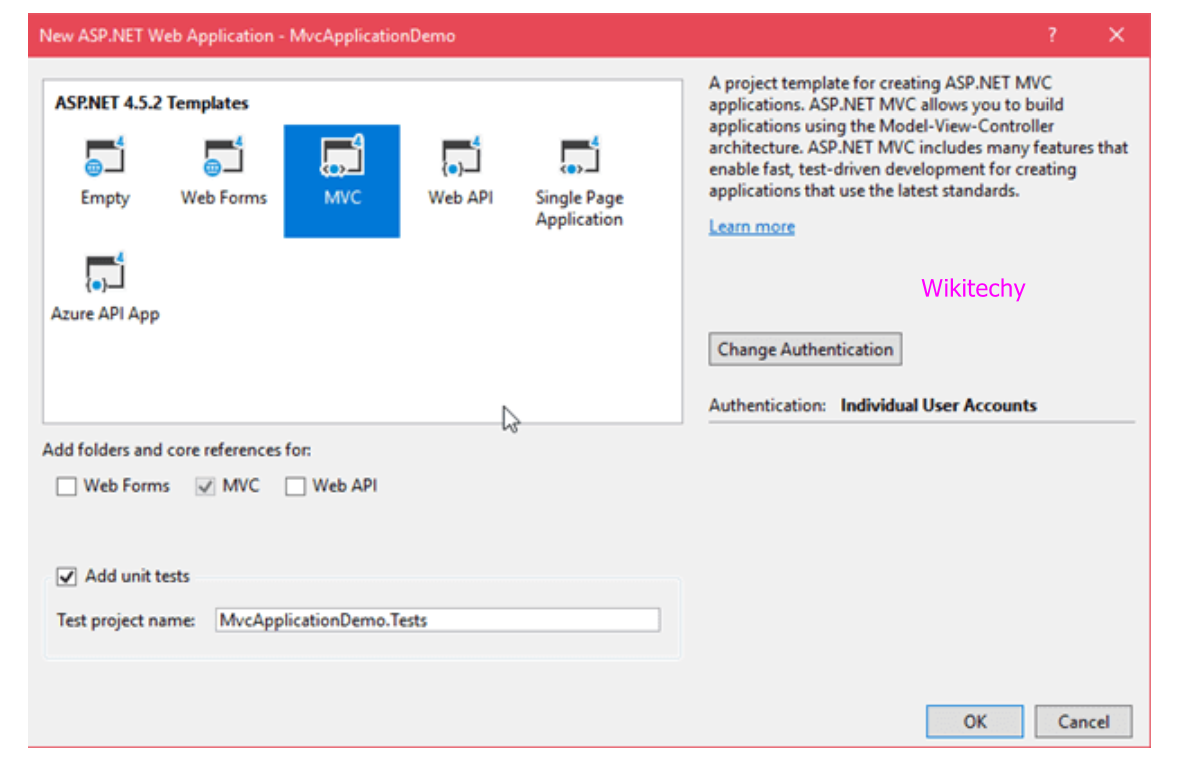
- It creates a project that has following structure, after clicking ok.
MVC Web Application Project Structure
- We just created the project structure by following.
- In this project contains three folders named Model, View and Controller.
- The home controller is default controller for the application and it contains the following codes.
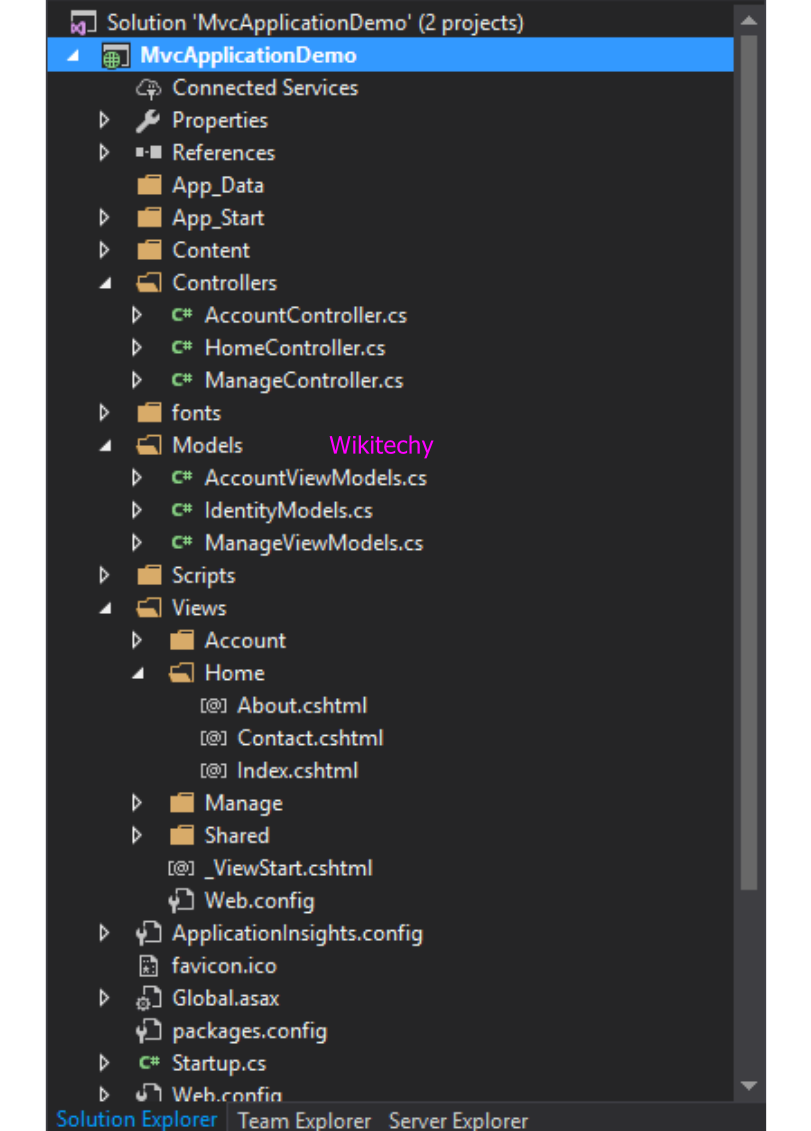
ASP.NET MVC Controller
- Controller is a class that handles user requests then retrieves data from the Model and renders view as response.
- The ASP.NET MVC framework maps requested URLs to the classes that referred as controller.
- Controller handle user input, processes incoming requests, interactions and executes appropriate business logic.
- The Controller Base is a base class for all controller classes and provides general MVC handling.
- It gets the values to use as the action method's arguments and locates for the appropriate action method to call and validate.
- It handles all errors that might occur during execution of the action and uses WebFormViewEngine class for rendering ASP.NET page.
Sample Code
MusicStoreController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Controllers
{
public class MusicStoreController : Controller
{
// GET: MusicStrore
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
index. Cshtml
<div class="jumbotron">
<h2>Welcome to the music store.</h2>
</div>
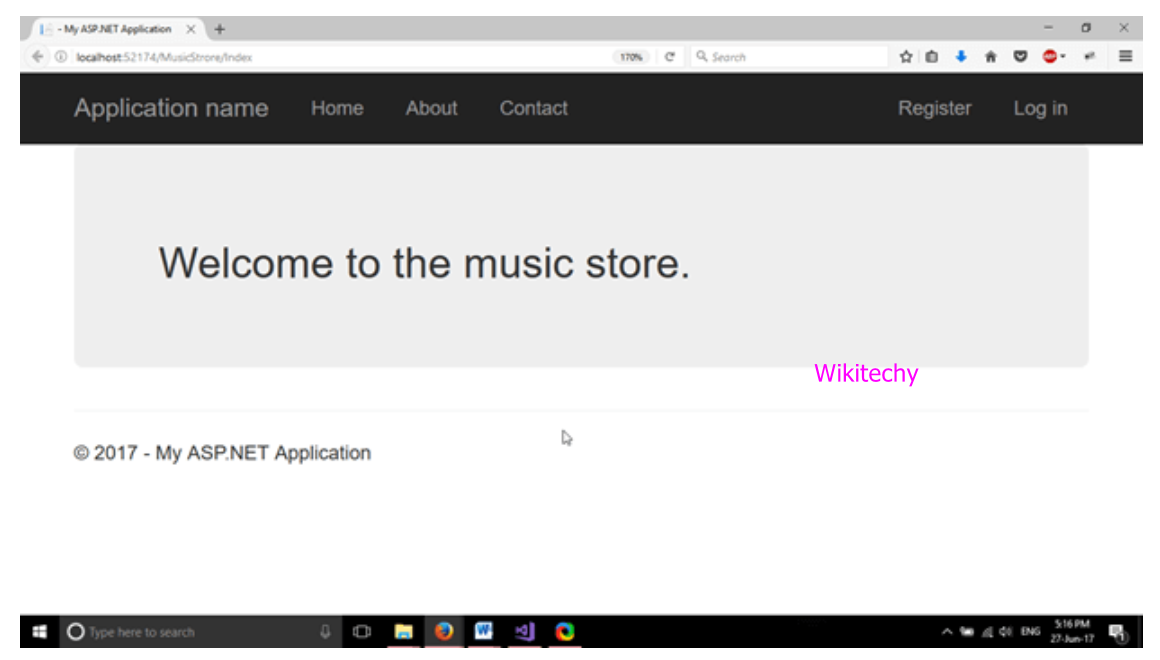
Output
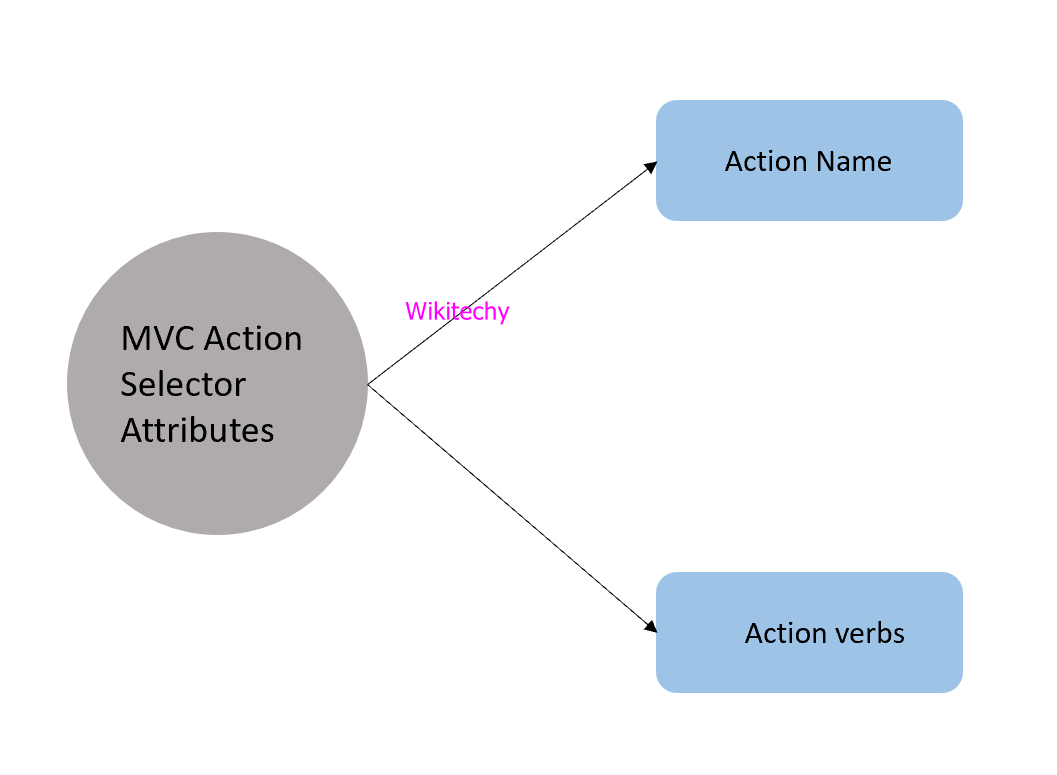
ASP.NET MVC Action Selectors
- Action selectors are attributes that are applied on action methods of a controller and it is used to select correct action method to call as per the request.
- MVC action selector attributes consist of two types, they are
- ActionName
- ActionVerbs
Action Name
- This attribute allows us to specify a different name for the action method and it is useful when we want to call action by different name.
Sample Code
MusicStoreController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Controllers
{
public class MusicStoreController : Controller
{
[ActionName("store")]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
store.cshtml
@{
ViewBag.Title = "store";
}
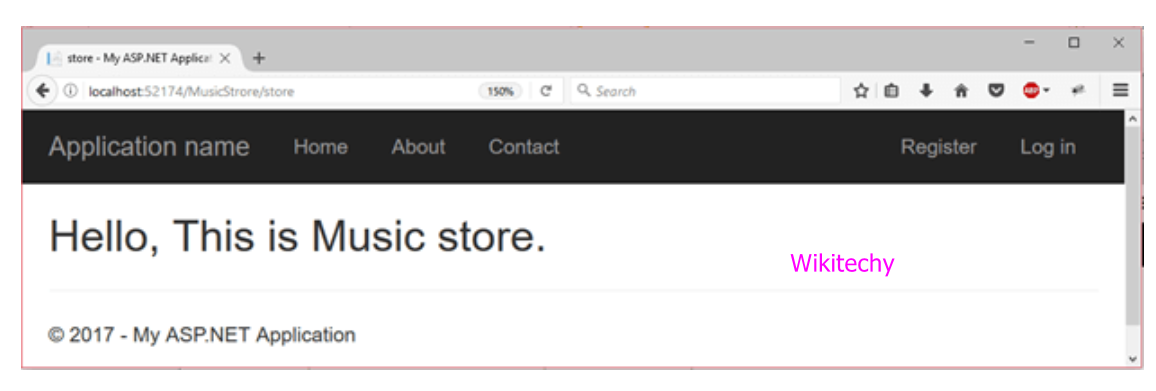
<h2>Hello, This is Music store.</h2>
Output
ActionVerbs
- ASP.NET MVC works for HTTP Request methods and provides action verbs that are applied on the action methods.
- There are various ActionVerbs, they are:
- HttpPost
- HttpGet
- HttpPut
- HttpDelete
- HttpOptions
- HttpPatch
- ActionVerbs are name of the http requests that a controller handle and we can use for selection among the action methods.
Sample Code
MusicStoreController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Controllers
{
public class MusicStoreController : Controller
{
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Welcome()
{
return View();
}
}
}
index.cshtml
<div class="jumbotron">
<h2>Welcome to the music store.</h2>
</div>
Output
- When the index action is called, it produces the following output.
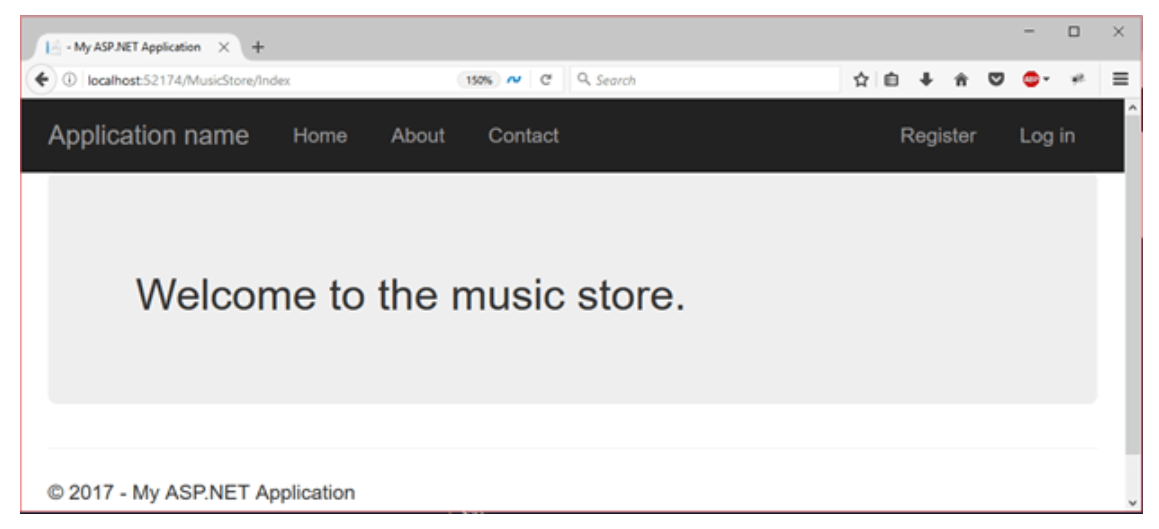
- When we make a get request for the store action method, it produces the error message.
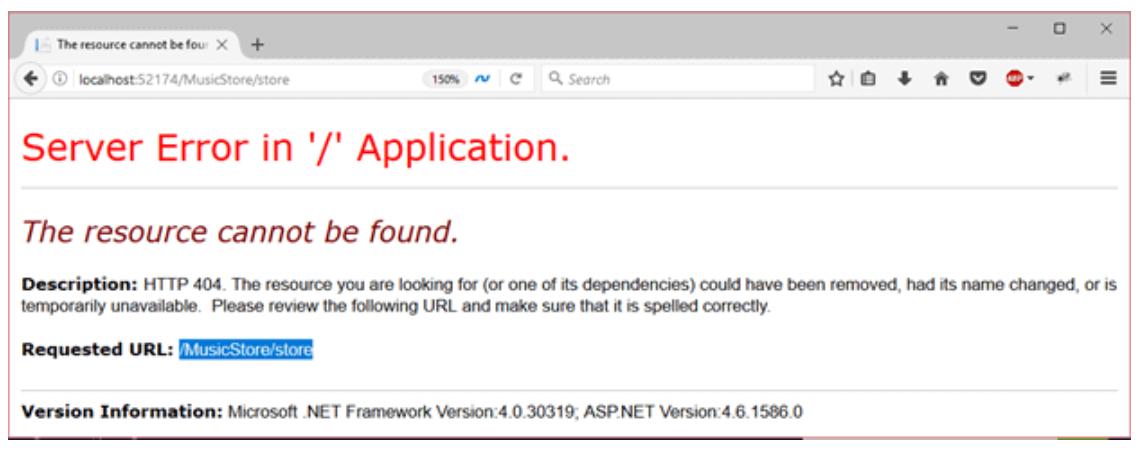
ASP.NET MVC Model
- Model is a class which is used for accessing data from the data base and contains the business logic of the application.
- The model class does not contain any HTML code as well and does not handle directly input from the browser.
- They are also referring as objects that are used to implement conceptual logic for the application.
- A controller interacts with the model, perform the logic, access the data and pass that data to the view.
Creating a Model
- Model contains getter and setter for its properties
- Right click on the model folder of the project and then follow this sequence Model->Add->New Item->Visual C#->Code->Class, to add the model.
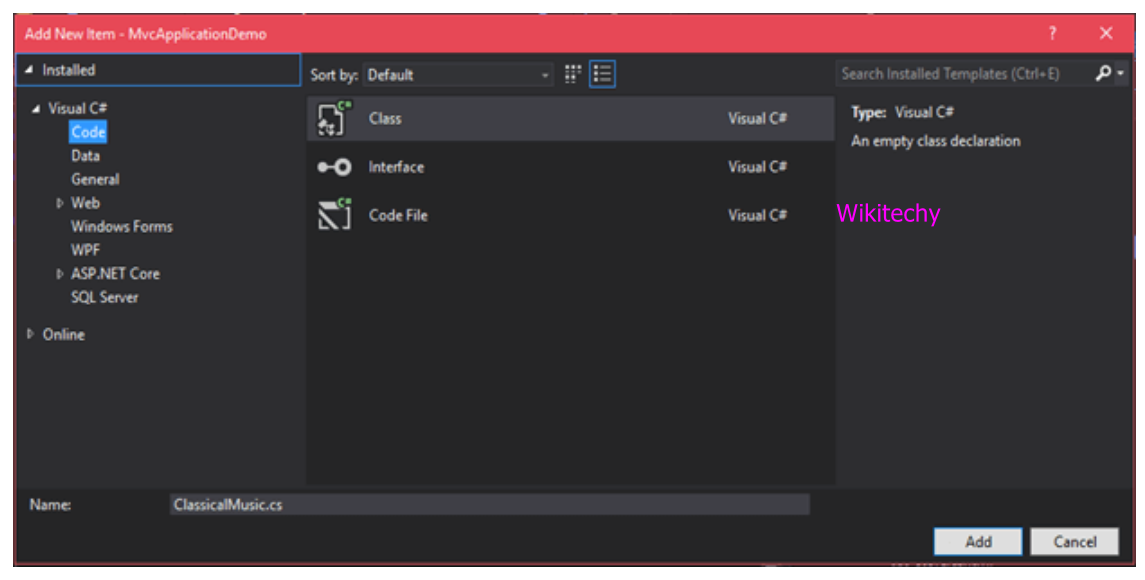
Sample Code
Student.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Models
{
public class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Contact { get; set; }
}
}
ASP.NET MVC Model Binding
- It is a process in which we bind a model to controller and view then, it is a simple way to map posted form values to a .NET Framework type and pass the type to an action method as a parameter.
- It can convert HTTP requests into objects that are passed to an action method so it acts as a converter.
Create a Model
- Right click on the Model folder and add a class to create new model.
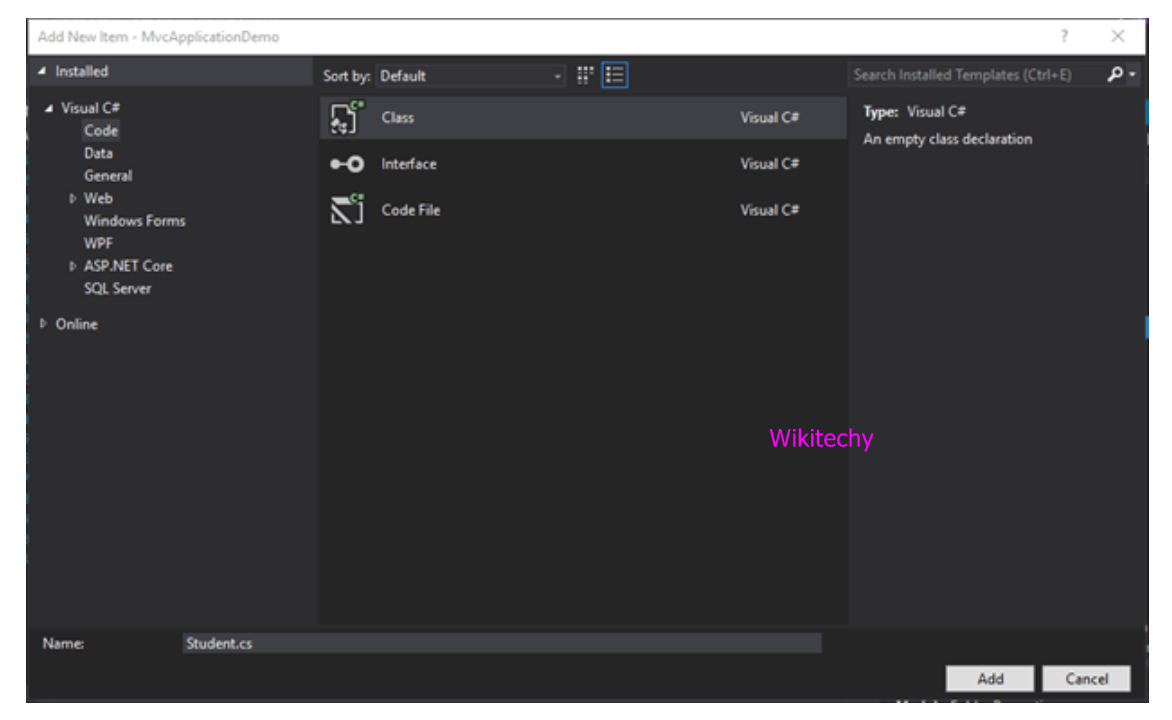
Sample Code
Student.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Models
{
public class Student
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Contact { get; set; }
}
}
Create a Controller
- Let's create a controller for this class, after creating a model.
- Right click on the Controller folder and add the controller class.
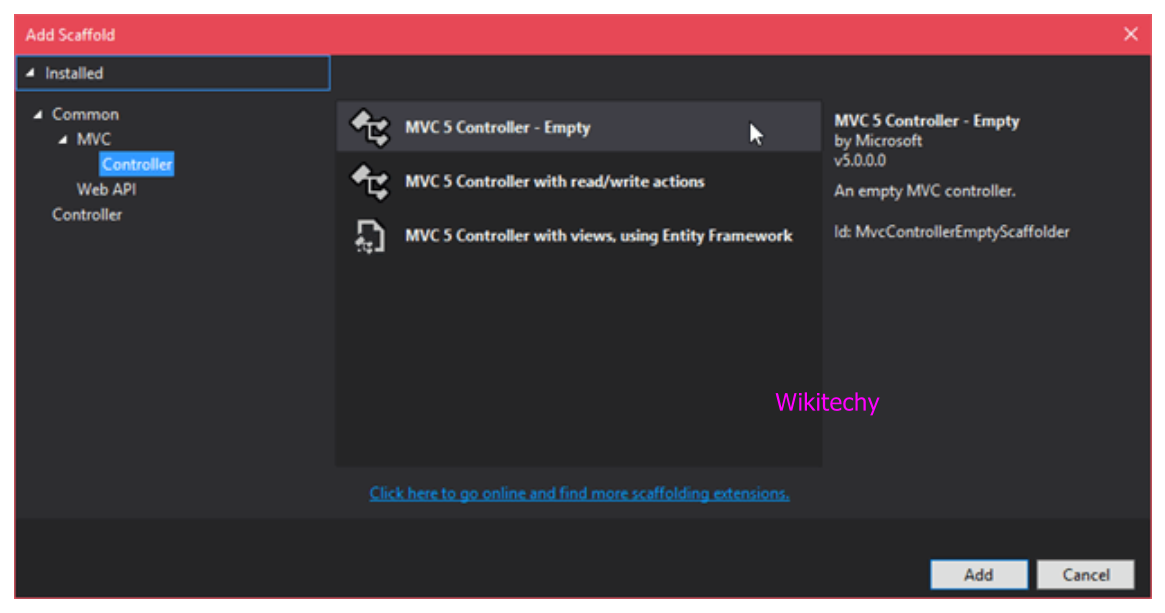
Sample Code
StudentsController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Controllers
{
public class StudentsController : Controller
{
// GET: Students
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
Creating a View
- To create view right click within the body of Index action method and select Add View option.
- It will pop up for the name of the view and Model to attach with the view.
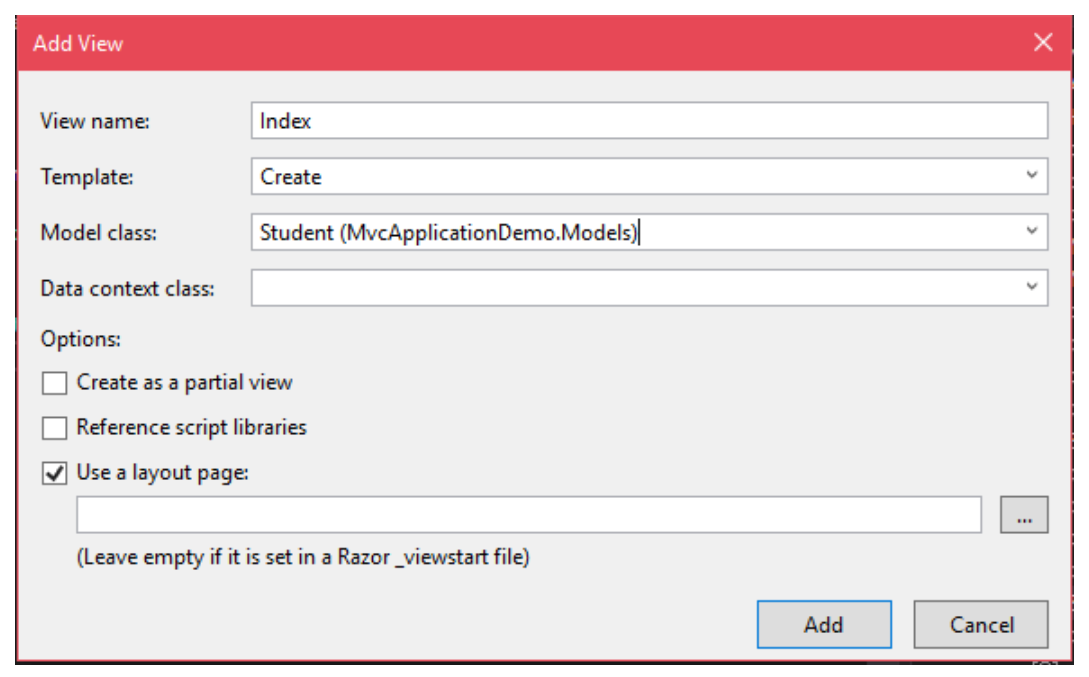
Sample Code
Index.cshtml
@model MvcApplicationDemo.Models.Student
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<h4>Student</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Email, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Email, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Contact, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Contact, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Contact, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
Final Output
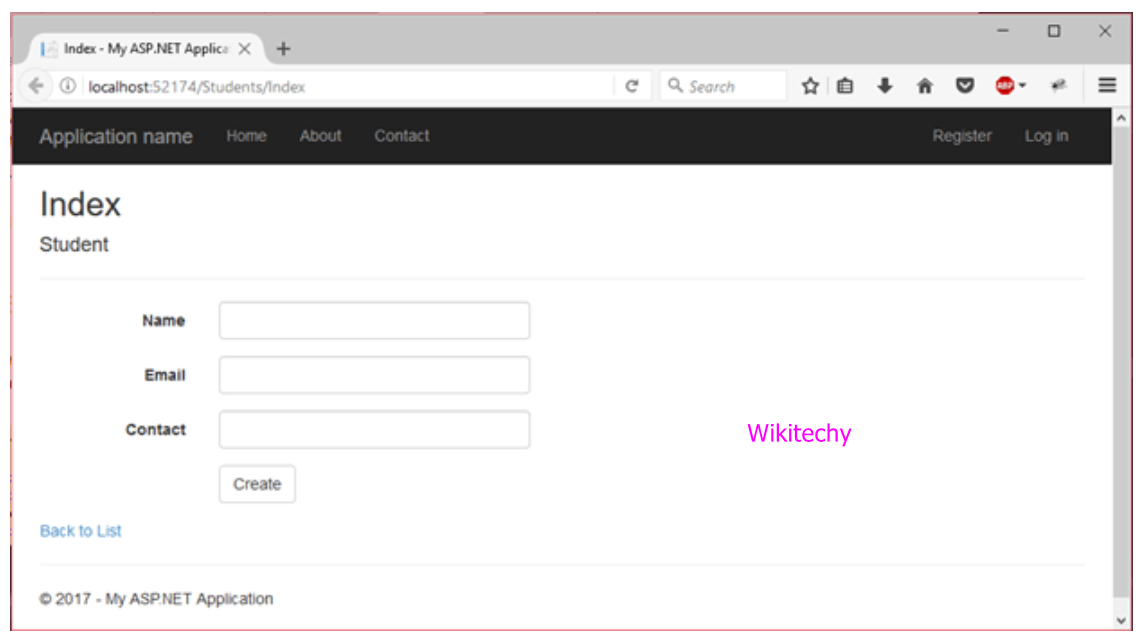
ASP.NET MVC View
- It is used to create web pages for the application and View is a standard HTML page that may contain script.
- MVC Views are mapped to the action and then controller renders the view to the browser, unlike ASP.NET Web Pages.
- MVC has certain conventions for project structure and uses Razor view engine so that we can write server-side code in HTML as well.
- The view file should be located in the subdirectory of View folder.
Creating View to the Application
- Right click on the subfolder inside the View folder and select Add-> Add View, to add view.
- It will pop up for the view name etc.
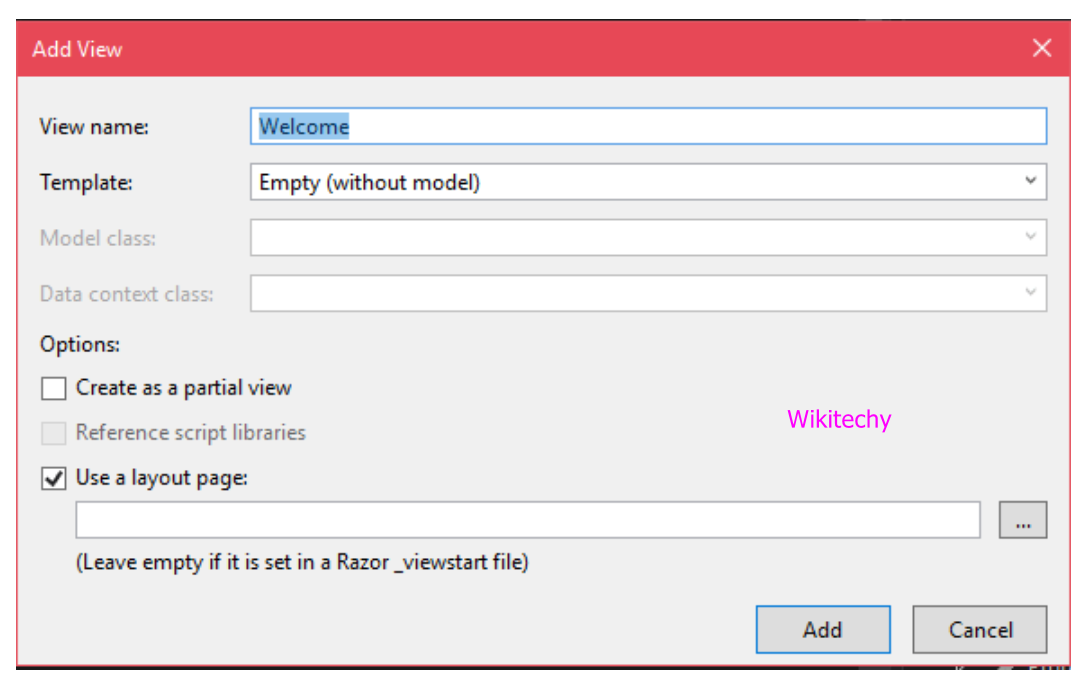
Sample Code
Welcome.cshtml
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Welcome";
}
<h2>Welcome</h2>
We have a controller like this, if we want to execute it
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcApplicationDemo.Controllers
{
public class StudentsController : Controller
{
// GET: Students
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Welcome()
{
return View();
}
}
}
- Controller has Welcome action method that will render Welcome view file to the browser.
- Right click on the Welcome.cshtml file and select view in browser.
Output
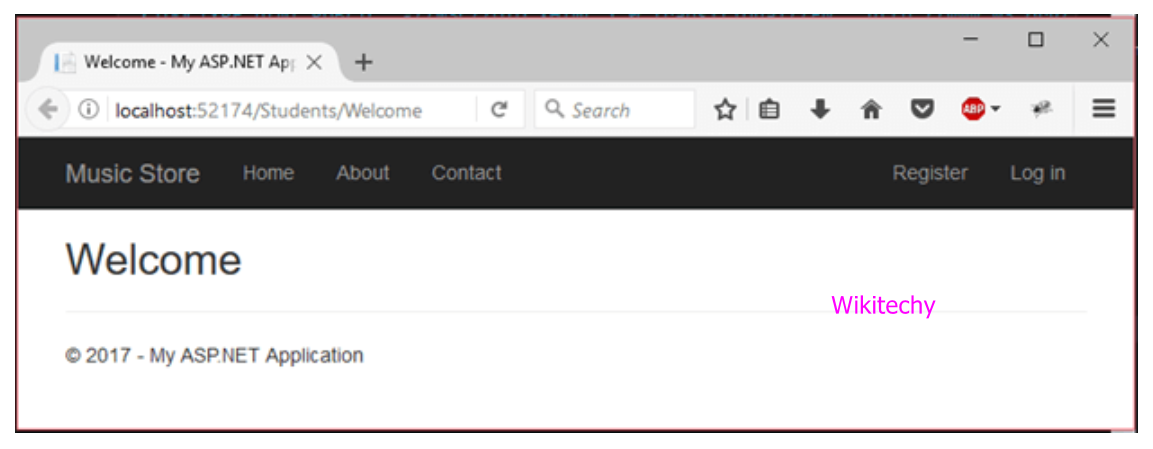
MVC Project – Login Code
Table => Model cs code
namespace ProductLogin.Models
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Data.Entity.Spatial;
public partial class tbl_user
{
public int id { get; set; }
[StringLength(100)]
public string uname { get; set; }
[StringLength(100)]
public string pwd { get; set; }
}
}
Model Code => Data Context -> DB Context Code
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
namespace ProductLogin.Models
{
public partial class Model1 : DbContext
{
public Model1()
: base("name=Model1")
{
}
public virtual DbSet tbl_user { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity()
.Property(e => e.uname)
.IsUnicode(false);
modelBuilder.Entity()
.Property(e => e.pwd)
.IsUnicode(false);
}
}
}
Login => Controller Code
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using ProductLogin.Models;
namespace ProductLogin.Controllers
{
public class tbl_userController : Controller
{
private Model1 db = new Model1();
// GET: tbl_user/Create
public ActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
// POST: tbl_user/Create
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Login([Bind(Include = "id,uname,pwd")] tbl_user tbl_user)
{
using (Model1 db = new Model1())
{
var obj = db.tbl_user.Where(a=>a.uname.Equals(tbl_user.uname) &&
a.pwd.Equals(tbl_user.pwd)).FirstOrDefault(); ;
if (obj!=null)
{
return RedirectToAction("Index");
//ModelState.AddModelError("", "Error 1" + tbl_user.uname);
}
else
{
ModelState.AddModelError("", "Error" + tbl_user.uname);
}
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// GET: tbl_user
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(db.tbl_user.ToList());
}
// GET: tbl_user/Details/5
public ActionResult Details(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
tbl_user tbl_user = db.tbl_user.Find(id);
if (tbl_user == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// GET: tbl_user/Create
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
// POST: tbl_user/Create
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "id,uname,pwd")] tbl_user tbl_user)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.tbl_user.Add(tbl_user);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// GET: tbl_user/Edit/5
public ActionResult Edit(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
tbl_user tbl_user = db.tbl_user.Find(id);
if (tbl_user == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// POST: tbl_user/Edit/5
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Edit([Bind(Include = "id,uname,pwd")] tbl_user tbl_user)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.Entry(tbl_user).State = EntityState.Modified;
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// GET: tbl_user/Delete/5
public ActionResult Delete(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
tbl_user tbl_user = db.tbl_user.Find(id);
if (tbl_user == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(tbl_user);
}
// POST: tbl_user/Delete/5
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
tbl_user tbl_user = db.tbl_user.Find(id);
db.tbl_user.Remove(tbl_user);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
db.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
}
}
Login.cshtml => View Code
@model ProductLogin.Models.tbl_user
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Login";
}
<h2>Create</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<h4>tbl_user</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.uname, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.uname, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.uname, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.pwd, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.pwd, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.pwd, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Login" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}
