 1.Definition
1.Definition
| Aspect | Process | Thread |
|---|---|---|
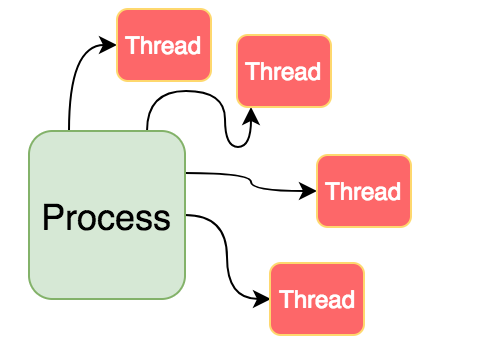
| Definition | A process is an independent program in execution, with its own memory space, resources, and environment. In Java running a Java application creates a process. | A thread is the smallest unit of execution within a process. Threads within the same process share the same memory space and can communicate directly by accessing shared variables. |
| Weight | Heavy-weight | Light-weight |
2.Example
| Scenario | Process Example | Thread Example |
|---|---|---|
| Web Browser | Each tab in Google Chrome runs as a process | Downloading files, playing video, and scrolling within the same tab are separate threads |
| Operating System | Running Microsoft Word, Excel, and Outlook | Spell check, auto-save, and formatting in Word happen on different threads within the same process |
3.Feature Comparison
| Feature | Process | Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | Has its own separate memory space | Shares memory space with other threads in the process |
| Creation Time | Slower due to the allocation of resources | Faster and more efficient |
| Communication | Slower (Inter-Process Communication needed) | Faster (Shared memory space) |
| Crash Impact | Crashing one process doesn’t affect others | Crashing a thread can affect the entire process |
| Context Switching | Slower due to separate memory spaces | Faster due to shared memory |
| Isolation | Strong isolation, preventing interference | Weaker isolation, threads can interfere with each other |
| Execution | Can run on separate machines | Runs on multiple cores within the same machine |
4.Advantages
| Aspect | Advantages of Processes | Advantages of Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Stability | Fault isolation: one process crash doesn’t affect others | Efficient resource sharing within the same process |
| Efficiency | Suitable for distributed systems | Faster for tasks within the same application |
| Scalability | Good for tasks that require full isolation | Optimized for multi-core CPUs for concurrency |
| Resource Sharing | Better security and isolation | Faster communication due to shared memory |
| Overhead | Higher due to independent memory and resources | Lower overhead; lighter and quicker to create |