Definition:
In Java , a String is a sequence of characters. Strings are objects in Java, and the String class is part of the java.lang package. Strings in Java are immutable, meaning once a String object is created, its value cannot be changed. However, it is possible to create new strings based on transformations of the original.
Example:
Overall Output:
Features of String in Java:
- Once a string is created, its value cannot be changed. Any modification to the string creates a new string object, leaving the original string unchanged.
- Java uses a special memory area called the String Constant Pool to store string literals. If a string literal already exists in the pool, a reference to the existing literal is returned instead of creating a new object.
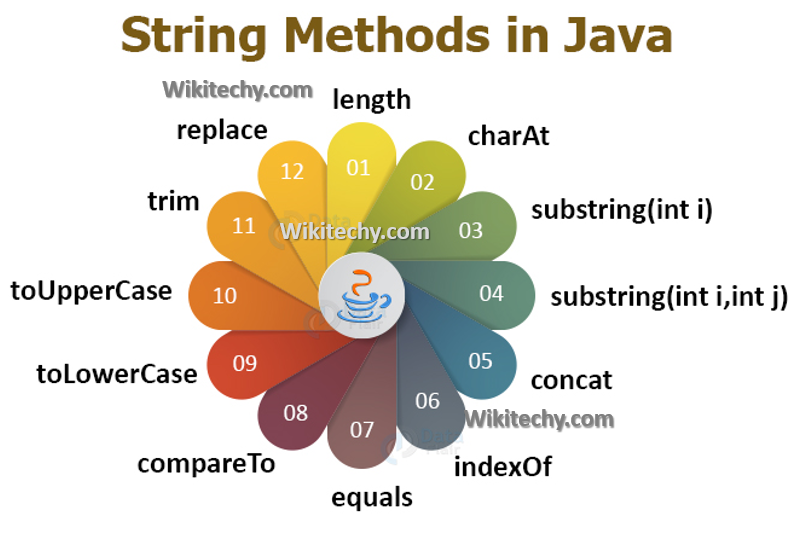
- The String class provides a variety of methods for operations like concatenation (+ or concat()), substring (substring()), searching (indexOf()), comparison (equals() and compareTo()), and more.
- The length() method returns the number of characters in a string.
- Java Strings support Unicode, making them capable of storing text from multiple languages and symbols.
- The String class allows the manipulation of string data through methods like replace(), toLowerCase(), toUpperCase(), trim(), and more.
- While String objects are immutable, StringBuilder and StringBuffer are mutable versions of strings that allow efficient modifications without creating new objects.
Advantages of String in Java:
- Strings can be created and manipulated easily using built-in operators (+) and methods (e.g., substring(), replace()).
- Memory Due to the string pool, Java optimizes memory usage by reusing string literals, which prevents the creation of duplicate string objects.
- Immutability makes strings thread-safe, meaning that they can be shared across threads without concerns about data inconsistency.
- Java’s String class fully supports Unicode, making it useful for developing international applications.
- Java provides a wide variety of methods for string manipulation, making it convenient to perform operations like searching, comparing, and transforming strings.
Uses of Strings in Java:
- Strings are used extensively in applications for manipulating text, such as handling user input, displaying information, and creating dynamic messages.
- Strings are often used to process data, such as extracting information from text files, network protocols, or web APIs.
- Strings are used to create dynamic text by combining different pieces of data or messages.
- When reading or writing data to files, strings are commonly used to handle the content, such as storing the contents of a file or breaking down the data into individual lines or tokens.
- Strings are used to store configuration settings, such as URLs, usernames, and other parameters in applications.