Definition:
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of “objects“, which can contain data (in the form of fields or attributes) and methods (functions) that act on the data. Java is a pure object-oriented language where everything is modeled as an object. OOP allows the creation of reusable and modular code that models real-world entities.
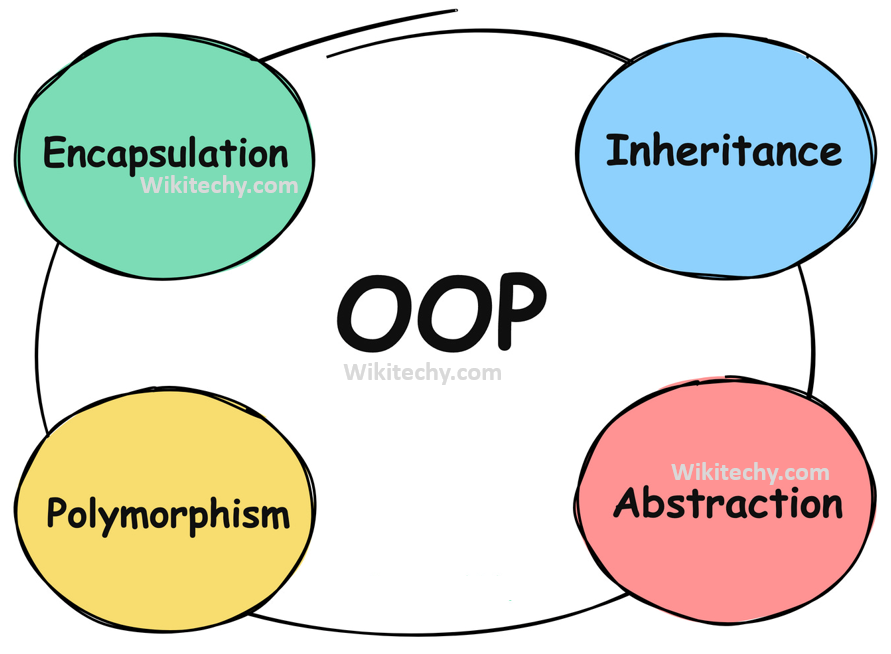
In Java, the four main principles of OOP are:
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
Example:
Output:
Features of OOP in Java:
1.Encapsulation:
- Bundling the data (fields) and methods (functions) that operate on the data into a single unit, i.e., a class. It also hides the internal state of objects from outside interference.
2.Inheritance:
- Mechanism where one class (child class) inherits properties and behaviors from another class (parent class), allowing code reuse.
3.Polymorphism:
- The ability of a method to behave differently based on the object calling it. There are two types: compile-time (method overloading) and runtime (method overriding).
4.Abstraction:
- Hiding implementation details and only exposing the essential features of an object. This is achieved in Java through abstract classes and interfaces.
Advantages of OOP in Java:
- Each object is self-contained, which makes it easy to troubleshoot and manage complex systems.
- Through inheritance, objects can be reused across different programs or parts of a program.
- OOP makes it easier to update or extend systems as it isolates changes within specific objects.
- The modular approach and code reusability lead to faster development cycles and easier debugging.
- OOP allows developers to model real-world entities and interactions in a natural and intuitive way, improving the clarity and intuitiveness of code.
Uses of OOP in Java:
- Java’s Swing and JavaFX libraries use OOP concepts to create interactive, event-driven interfaces.
- OOP is widely used in large-scale systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and other business applications due to its modular structure.
- Game entities like characters, weapons, and environments can be modeled as objects with behaviors, making OOP ideal for game development.
- OOP concepts are used in Android development (Java or Kotlin) to create reusable components like activities, fragments, and services.
- Java-based web frameworks like Spring and JavaServer Faces (JSF) heavily utilize OOP to build scalable and maintainable web applications.