A computer network is a group of interconnected computers that communicate over a shared channel to exchange resources and data. These resources are either hosted on or provided by the network’s nodes. In this discussion, we will explore computer networks and their various types.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a system where multiple devices (computers, printers, servers, etc.) are connected to communicate and share resources like data, files, and hardware. These connections can use wired (Ethernet cables) or wireless (Wi-Fi) technologies, enabling devices to interact efficiently.
Types of Computer Networks
- Personal Area Network (PAN): A small network for personal devices, like smartphones and laptops, often connected via Bluetooth or USB.
- Local Area Network (LAN): Covers a limited area like homes or offices, typically using Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Connects multiple LANs within a city or campus using high-speed links.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Covers large geographical areas, connecting countries or continents (e.g., the Internet).
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Offers secure access over public networks by encrypting data.

Advantages of Computer Networks
- Resource Sharing: Easy access to printers, files, and applications.
- Communication: Facilitates instant messaging, emails, and video calls.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces hardware duplication through shared devices.
- Scalability: Supports growth by connecting more devices.
- Centralized Management: Simplifies updates, backups, and security.
Uses of Computer Networks
- Business Operations: Share resources and manage data centrally.
- Education: Online learning platforms and research collaboration.
- Healthcare: Real-time data exchange between hospitals and devices.
- Government Services: Secure communication and data management.
- Entertainment: Streaming services, gaming, and social media.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a short-range network intended for personal use, connecting devices that belong to a single individual. It is primarily used for communication between devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, printers, and wearable devices (e.g., smartwatches and fitness trackers). PANs operate in a small area, typically within 10 meters of the user, and are ideal for applications that require direct device-to-device interaction.

Types of PANs:
- Wired PAN: Devices are connected using cables, such as USB or Thunderbolt. For example, a smartphone connected to a computer via USB for charging or file transfer.
- Wireless PAN: Uses wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Infrared (IR), or Zigbee for connectivity. For example, connecting Bluetooth headphones to a smartphone.
Advantages of PAN:
- Convenience: Easy to set up and use for personal device connectivity.
- Mobility: Enables devices to communicate wirelessly while on the move.
- Cost-effective: No need for expensive infrastructure.
- Low Power Consumption: Designed for energy-efficient operation.
- Privacy: Typically supports personal devices within a secure and controlled area.
Applications of PAN:
- File Sharing: Transferring data between a laptop and smartphone.
- Device Synchronization: Syncing calendars, contacts, and media between personal devices.
- Peripheral Connectivity: Connecting wireless printers, keyboards, or headphones.
- Health Monitoring: Linking fitness trackers to smartphones for real-time data.
- Internet Tethering: Using a smartphone as a hotspot for internet access.
Technologies Used in PAN:
- Bluetooth: Commonly used for short-range communication between devices like headphones and phones.
- Infrared (IR): Rarely used today but was popular for remote controls and older devices.
- Zigbee: Often used for smart home devices due to its low power consumption.
- USB: A wired method for faster and more reliable data transfer.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): Used for very short-range communication, like mobile payment systems.
Local Area Network (LAN):
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school. It allows connected devices to share resources like files, printers, and internet access. LANs are typically confined to a single building or campus and use technologies such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi for communication.
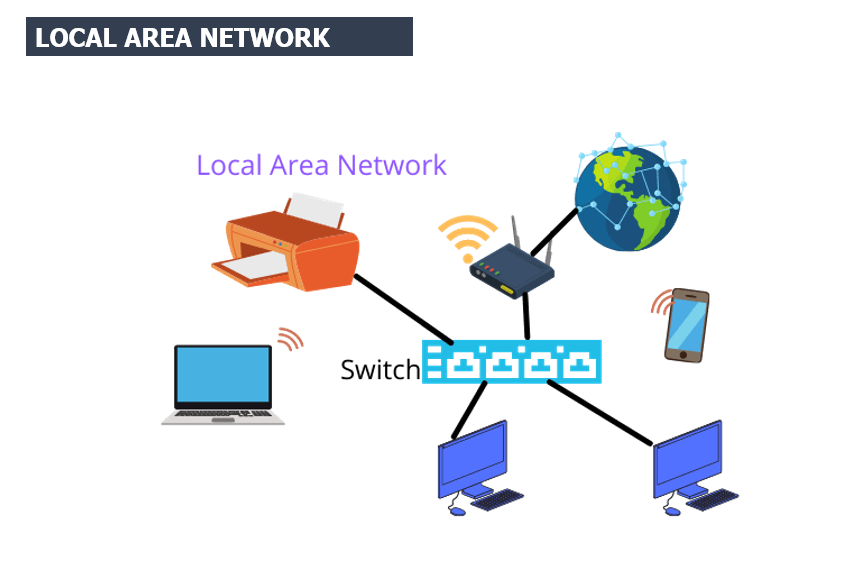
Components of LAN:
- Switches: Central devices that connect multiple computers and manage data flow.
- Routers: Devices that connect LANs to other networks, such as the internet.
- Cables or Wireless Access Points: Mediums for connecting devices, either through Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
- End Devices: Computers, printers, or servers that are part of the network.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Hardware in devices enabling network communication.
Advantages of LAN:
- High Speed: Facilitates fast data sharing and communication.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces hardware duplication through shared resources.
- Enhanced Security: Offers better control over access and data protection within the network.
- Easy Setup: Can be quickly deployed in small-scale environments.
- Centralized Backup: Enables efficient data backup and management.
Uses of LAN:
- Educational Institutions: Connecting computers in classrooms and libraries.
- Businesses: Sharing files, printers, and internet connections in offices.
- Gaming: Facilitating multiplayer gaming in close proximity.
- Home Networks: Connecting devices like laptops, smart TVs, and printers.
- Healthcare: Linking computers and medical devices within a hospital.
Technologies Used in LAN:
- Ethernet: Most common wired technology for LANs.
- Wi-Fi: Enables wireless communication between devices in the network.
- Fiber Optics: Used in high-speed LANs for efficient data transfer.
- Powerline Networking: Utilizes electrical wiring for data transmission.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a type of computer network that spans a large geographical area, often connecting multiple smaller networks such as LANs or MANs. It is used to link systems located in different cities, countries, or even continents. WANs typically rely on technologies like fiber optics, satellite links, or leased lines and are often owned and operated by telecom companies.
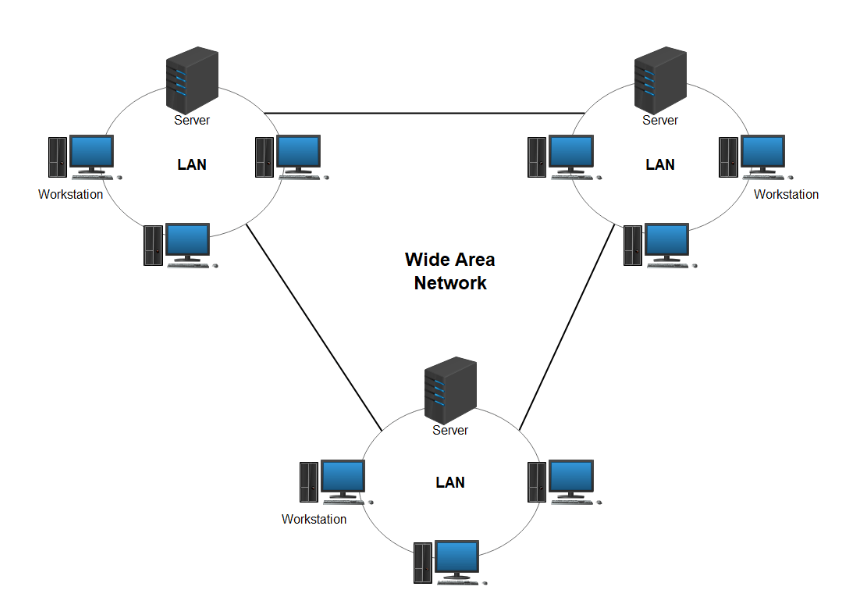
Components of WAN:
- Routers: Direct data traffic between networks.
- Modems: Convert digital signals into formats suitable for transmission over telephone or cable lines.
- Transmission Media: Fiber optics, satellite links, or wireless technologies.
- Gateways: Facilitate communication between different types of networks.
- Cloud Services: Modern WANs increasingly rely on cloud-based solutions for scalability.
Advantages of WAN:
- Global Connectivity: Links offices, organizations, and individuals worldwide.
- Resource Sharing: Enables centralized management and resource access across locations.
- Business Expansion: Supports remote branches and international operations.
- Data Collaboration: Allows seamless sharing of information between geographically separated teams.
- Disaster Recovery: Facilitates data backup and recovery over wide areas.
Uses of WAN:
- Multinational Companies: Connects offices and systems across different countries.
- Banking: Links ATMs and branch networks globally.
- Education: Provides remote access to libraries, resources, and online classes.
- E-commerce: Facilitates online transactions and inventory management.
- Healthcare: Enables telemedicine and secure sharing of medical records.
Technologies Used in WAN:
- Fiber Optic Cables: High-speed, long-distance data transmission.
- Satellite Links: Used in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Leased Lines: Dedicated lines for consistent performance.
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching): Efficient data routing for business networks.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Securely extends private networks over public infrastructure.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a network that spans a city, town, or campus. It is larger than a Local Area Network (LAN) but smaller than a Wide Area Network (WAN). MANs interconnect multiple LANs within a defined region, providing fast and efficient data transfer. Commonly, they use technologies like fiber optics and are often operated by a single organization, municipality, or telecom provider.
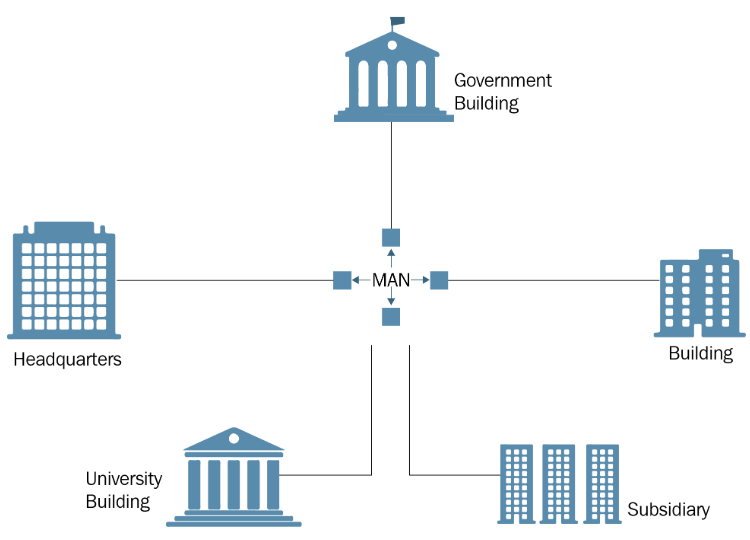
Components of MAN:
- Routers: Direct data flow between interconnected LANs.
- Switches: Manage data within each segment of the MAN.
- Transmission Media: Uses high-speed mediums like fiber optics, coaxial cables, or wireless links.
- Access Points: Allow wireless devices to connect to the network.
- Servers: Provide centralized services like data storage and applications.
Advantages of MAN:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Links multiple networks within a city or region.
- High-Speed Communication: Facilitates quick data exchange across interconnected systems.
- Cost Efficiency: More affordable than a WAN for city-wide connectivity.
- Supports Local Services: Enables centralized management of city-wide operations like public transport and utilities.
- Scalable: Easily integrates new users or networks.
Uses of MAN:
- City-Wide Internet Access: Provides broadband connections for urban areas.
- Educational Campuses: Connects departments, libraries, and laboratories.
- Healthcare Systems: Links hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers.
- Public Services: Supports municipal services like traffic management and surveillance.
- Corporate Networks: Connects branch offices within the same metropolitan area.
Technologies Used in MAN:
- Fiber Optics: High-speed backbone for MANs.
- Microwave Links: Used for wireless MANs.
- Ethernet: Common for linking smaller LANs within the MAN.
- SONET/SDH: Synchronous data transfer technology.
- WiMAX: Wireless broadband access over long distances.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure communication technology that creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server, ensuring privacy and security. VPNs allow users to access the internet or private networks safely by masking their IP address and encrypting data, even when connected through public networks like Wi-Fi.
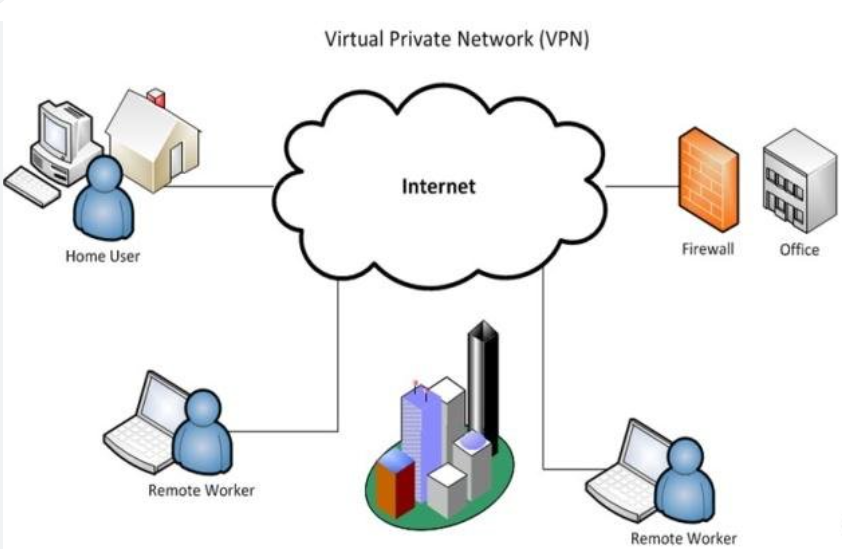
How VPN Works:
- Encryption: Converts data into a secure format that only the recipient can decrypt.
- Tunneling Protocols: Establish secure connections using technologies like OpenVPN, IPSec, or WireGuard.
- Server Location: Redirects internet traffic through servers in different locations, altering the user’s apparent location.
- Authentication: Ensures only authorized users can access the VPN.
Advantages of VPN:
- Enhanced Security: Protects data on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Privacy Protection: Hides your IP address and browsing activities.
- Remote Work Enablement: Securely connects employees to company networks.
- Bypass Censorship: Access restricted websites or services.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive leased lines in corporate networks.
Uses of VPN:
- Remote Work: Allows employees to access company resources securely.
- Streaming: Bypasses geographic restrictions on streaming platforms.
- Online Privacy: Prevents tracking by websites and advertisers.
- Gaming: Reduces latency and provides access to geo-blocked games.
- Secure Transactions: Protects financial data during online banking or shopping.
Types of VPN:
- Remote Access VPN: Allows individuals to connect securely to a private network.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connects multiple networks, often used by businesses.
- Personal VPN: Used by individuals to secure their internet connection.
- Mobile VPN: Optimized for devices that switch networks frequently.
- Cloud VPN: Provides secure access to cloud-based resources.




