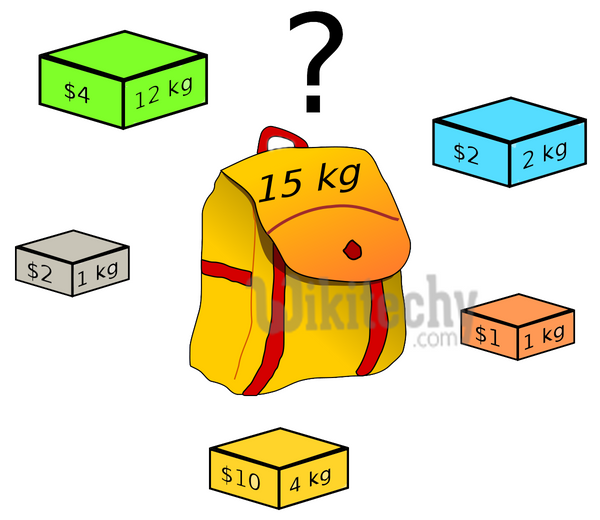
0-1 Knapsack Problem:
Given weights and values of n items, put these items in a knapsack of capacity W to get the maximum total value in the knapsack. In other words, given two integer arrays val[0..n-1] and wt[0..n-1] which represent values and weights associated with n items respectively. Also given an integer W which represents knapsack capacity, find out the maximum value subset of val[] such that sum of the weights of this subset is smaller than or equal to W. You cannot break an item, either pick the complete item, or don’t pick it (0-1 property).
A simple solution is to consider all subsets of items and calculate the total weight and value of all subsets. Consider the only subsets whose total weight is smaller than W. From all such subsets, pick the maximum value subset.
Optimal Substructure:
To consider all subsets of items, there can be two cases for every item: (1) the item is included in the optimal subset, (2) not included in the optimal set.
Therefore, the maximum value that can be obtained from n items is max of following two values.
- Maximum value obtained by n-1 items and W weight (excluding nth item).
- Value of nth item plus maximum value obtained by n-1 items and W minus weight of the nth item (including nth item).
If weight of nth item is greater than W, then the nth item cannot be included and case 1 is the only possibility.
Overlapping Subproblems:
Following is recursive implementation that simply follows the recursive structure mentioned above.
Implementation of Python:
Output:
220
It should be noted that the above function computes the same subproblems again and again. See the following recursion tree, K(1, 1) is being evaluated twice. Time complexity of this naive recursive solution is exponential (2^n).
[ad type=”banner”]In the following recursion tree, K() refers to knapSack(). The two
parameters indicated in the following recursion tree are n and W.
The recursion tree is for following sample inputs.
wt[] = {1, 1, 1}, W = 2, val[] = {10, 20, 30}
K(3, 2) ---------> K(n, W)
/ \
/ \
K(2,2) K(2,1)
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
K(1,2) K(1,1) K(1,1) K(1,0)
/ \ / \ / \
/ \ / \ / \
K(0,2) K(0,1) K(0,1) K(0,0) K(0,1) K(0,0)
Recursion tree for Knapsack capacity 2 units and 3 items of 1 unit weight.
Since subproblems are evaluated again, this problem has Overlapping Subprolems property. So the 0-1 Knapsack problem has both properties of a dynamic programming problem. Like other typical Dynamic Programming(DP) problems, recomputations of same subproblems can be avoided by constructing a temporary array K[][] in bottom up manner. Following is Dynamic Programming based implementation based python.
Implementation of Python:
Output:
220
Time Complexity: O(nW) where n is the number of items and W is the capacity of knapsack.
[ad type=”banner”]