Find the node with minimum value in a Binary Search Tree
This is quite simple. Just traverse the node from root to left recursively until left is NULL. The node whose left is NULL is the node with minimum value.
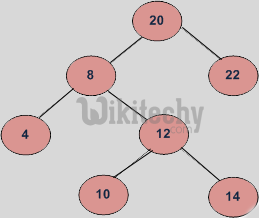
For the above tree, we start with 20, then we move left 8, we keep on moving to left until we see NULL. Since left of 4 is NULL, 4 is the node with minimum value.
Implementation of Python Programming:
Python Programming
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
""" Give a binary search tree and a number,
inserts a new node with the given number in
the correct place in the tree. Returns the new
root pointer which the caller should then use
(the standard trick to avoid using reference
parameters). """
def insert(node, data):
if node is None:
return (Node(data))
else:
if data <= node.data:
node.left = insert(node.left, data)
else:
node.right = insert(node.right, data)
return node
""" Given a non-empty binary search tree,
return the minimum data value found in that
tree. Note that the entire tree does not need
to be searched. """
def minValue(node):
current = node
while(current.left is not None):
current = current.left
return current.data
root = None
root = insert(root,4)
insert(root,2)
insert(root,1)
insert(root,3)
insert(root,6)
insert(root,5)
print "\nMinimum value in BST is %d" %(minValue(root))
Output:
Minimum value in BST is 1
Time Complexity: O(n) Worst case happens for left skewed trees.
Similarly we can get the maximum value by recursively traversing the right node of a binary search tree.
[ad type=”banner”]

