Find Length of a Linked List both Iterative and Recursive:
Write a Python function to count number of nodes in a given singly linked list.
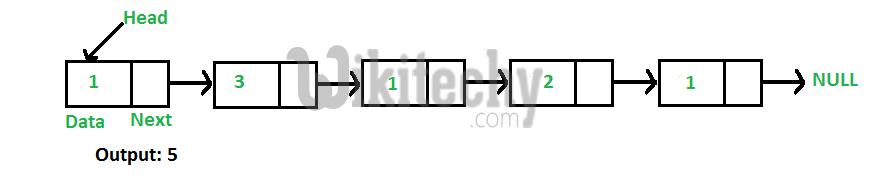
For example, the function should return 5 for linked list 1->3->1->2->1.
Singly Linked List:
Singly Linked List is a collection of ordered set of elements. A Node in singly linked list has two parts – data part and link part. Data part of the node contains the actual information which is represented as node. Link part of the node contains address of next node linked to it.
It can be traversed in only one direction because the node stores only next pointer. So, it can’t reverse linked list.
Iterative Solution
1) Initialize count as 0
2) Initialize a node pointer, current = head.
3) Do following while current is not NULL
a) current = current -> next
b) count++;
4) Return count
Python Programming:
[ad type=”banner”]Output:
count of nodes is 5
Recursive Solution
int getCount(head) 1) If head is NULL, return 0. 2) Else return 1 + getCount(head->next)
Python Programming:
[ad type=”banner”]Output:
count of nodes is 5
