We have discussed Circular Linked List Introduction and Applications, in the previous post on Circular Linked List. In this post, traversal operation is discussed.
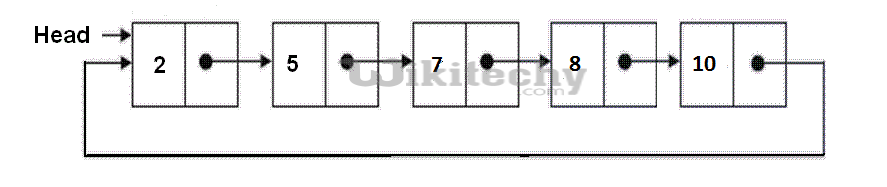
In a conventional linked list, we traverse the list from the head node and stop the traversal when we reach NULL. In a circular linked list, we stop traversal when we reach the first node again. Following is C code for linked list traversal.
void printList(struct node *first)
{
struct node *temp = first;
if (first != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != first);
}
}
Python Programming:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, data):
ptr1 = Node(data)
temp = self.head
ptr1.next = self.head
if self.head is not None:
while(temp.next != self.head):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = ptr1
else:
ptr1.next = ptr1
self.head = ptr1
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
if self.head is not None:
while(True):
print "%d" %(temp.data),
temp = temp.next
if (temp == self.head):
break
cllist = CircularLinkedList()
cllist.push(12)
cllist.push(56)
cllist.push(2)
cllist.push(11)
print "Contents of circular Linked List"
cllist.printList()
[ad type=”banner”]
Output:
Contents of Circular Linked List
11 2 56 12
