Java Algorithm – Write a program function to detect loop in a linked list
Given a linked list, check if the the linked list has loop or not. Below diagram shows a linked list with a loop.
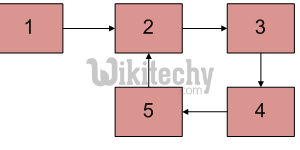
Following are different ways of doing this
Use Hashing:
Traverse the list one by one and keep putting the node addresses in a Hash Table. At any point, if NULL is reached then return false and if next of current node points to any of the previously stored nodes in Hash then return true.
Mark Visited Nodes:
This solution requires modifications to basic linked list data structure. Have a visited flag with each node. Traverse the linked list and keep marking visited nodes. If you see a visited node again then there is a loop. This solution works in O(n) but requires additional information with each node.
A variation of this solution that doesn’t require modification to basic data structure can be implemented using hash. Just store the addresses of visited nodes in a hash and if you see an address that already exists in hash then there is a loop.
Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm:
This is the fastest method. Traverse linked list using two pointers. Move one pointer by one and other pointer by two. If these pointers meet at some node then there is a loop. If pointers do not meet then linked list doesn’t have loop.
Java Programming:
Output:
Found loop
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)