Given pointer to the head node of a linked list, the task is to reverse the linked list.
Examples:
Input : Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->NULL
Output : Linked list should be changed to,
4->3->2->1->NULL
Input : Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output : Linked list should be changed to,
5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Input : NULL
Output : NULL
Input : 1->NULL
Output : 1->NULL
[ad type=”banner”]
Iterative Method
Iterate trough the linked list. In loop, change next to prev, prev to current and current to next
Java Programming:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
static void reverse(struct node** head_ref)
{
struct node* prev = NULL;
struct node* current = *head_ref;
struct node* next;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head_ref = prev;
}
void push(struct node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct node* new_node =
(struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void printList(struct node *head)
{
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 85);
printf("Given linked list\n");
printList(head);
reverse(&head);
printf("\nReversed Linked list \n");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
Given linked list
85 15 4 20
Reversed Linked list
20 4 15 85
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
[ad type=”banner”]
Recursive Method:
1) Divide the list in two parts - first node and rest of the linked list.
2) Call reverse for the rest of the linked list.
3) Link rest to first.
4) Fix head pointer
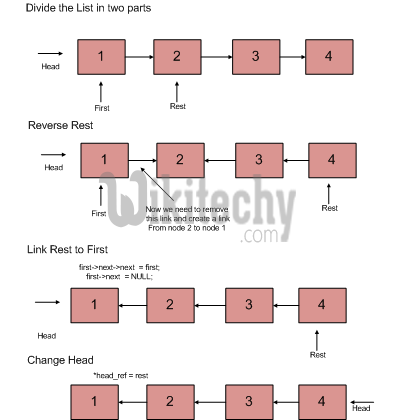
C Programming:
void recursiveReverse(struct node** head_ref)
{
struct node* first;
struct node* rest;
if (*head_ref == NULL)
return;
first = *head_ref;
rest = first->next;
if (rest == NULL)
return;
recursiveReverse(&rest);
first->next->next = first;
first->next = NULL;
*head_ref = rest;
}
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
[ad type=”banner”]
Java Programming:
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node reverseUtil(Node curr, Node prev) {
if (curr.next == null) {
head = curr;
curr.next = prev;
return null;
}
Node next1 = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
reverseUtil(next1, curr);
return head;
}
void printList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(2);
list.head.next.next = new Node(3);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(8);
System.out.println("Original Linked list ");
list.printList(head);
Node res = list.reverseUtil(head, null);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Reversed linked list ");
list.printList(res);
}
}
[ad type=”banner”]
Output:
Given linked list
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Reversed linked list
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
