Hacking Web Applications are as follows :
XSS
- XSS is one of the hacking web applications vulnearability. It is cross side scripting. It permits a malicious actor to embed a malicious script on a site generally in a comment section or in some place where user can add some data. When somebody visits that page, they are sent in the background with a malicious script.
Information Leakage
- It can be understood like if we do not turn the debug mode off when we take the web application from the development into production. At the time of error full error message is disclosed to the user which may contain secure information. It makes the web application vulnerable to hijacking.
Weak Authentication
- Weakly set usernames and passwords make the application easily vulnerable to hacking .
CSRF
- Cross site request forgery is almost same as XSS but is on server side.
Predictability of Secure Interfaces
- The security interfaces must be less expectable to be safer.
SQL Injection
- It is a web hacking technique used to place malicious code in SQL statements.
Insecure Session Handling
- Ensure that the session stake between the user and the server is secured and encrypted.
Poor Development Practices
- At the time of web application development security issues should be handled properly.
Not Validating Untrusted Data
- If there is any way through which user will input information, that data should always be seen and untrusted and must be validated.
Hacking Web Applications – Attack Techniques
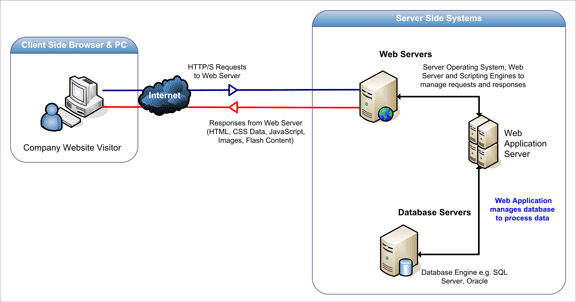
Denial of Service
- It is the interruption in a legal user’s access to a computer network, typically one caused with malicious intent.
SQL Injection
- It is the use of invalidated data that then runs a SQL script which presents data back to the user in the browser.
Brute Force Login
- It is basically guess usernames and passwords.
XSS
- In this malicious scripting is used to redirect users to another malicious site.
CSRF
- It is same as XSS but that it is a server side attack.
Form Tampering
- It is when people put untrusted data in the forms and manipulate them.
Buffer Overflow
- It is making use of poor memory use in the application to make the application act unpredictably.
Poor Error Handling
- It is moving for e.g. leaving the debug mode on during development and allowing the attacker to get information.
Session Hijacking
- Session Hijacking is the misuse of a valid computer session to gain illegal access to information or services in a computer system.
Impact of Hacking Web Applications Attacks
- Reputational Harm
- Defacement
- Data Theft
- Malware Servicing
- Web Server Compromise
What are the countermeasures ?
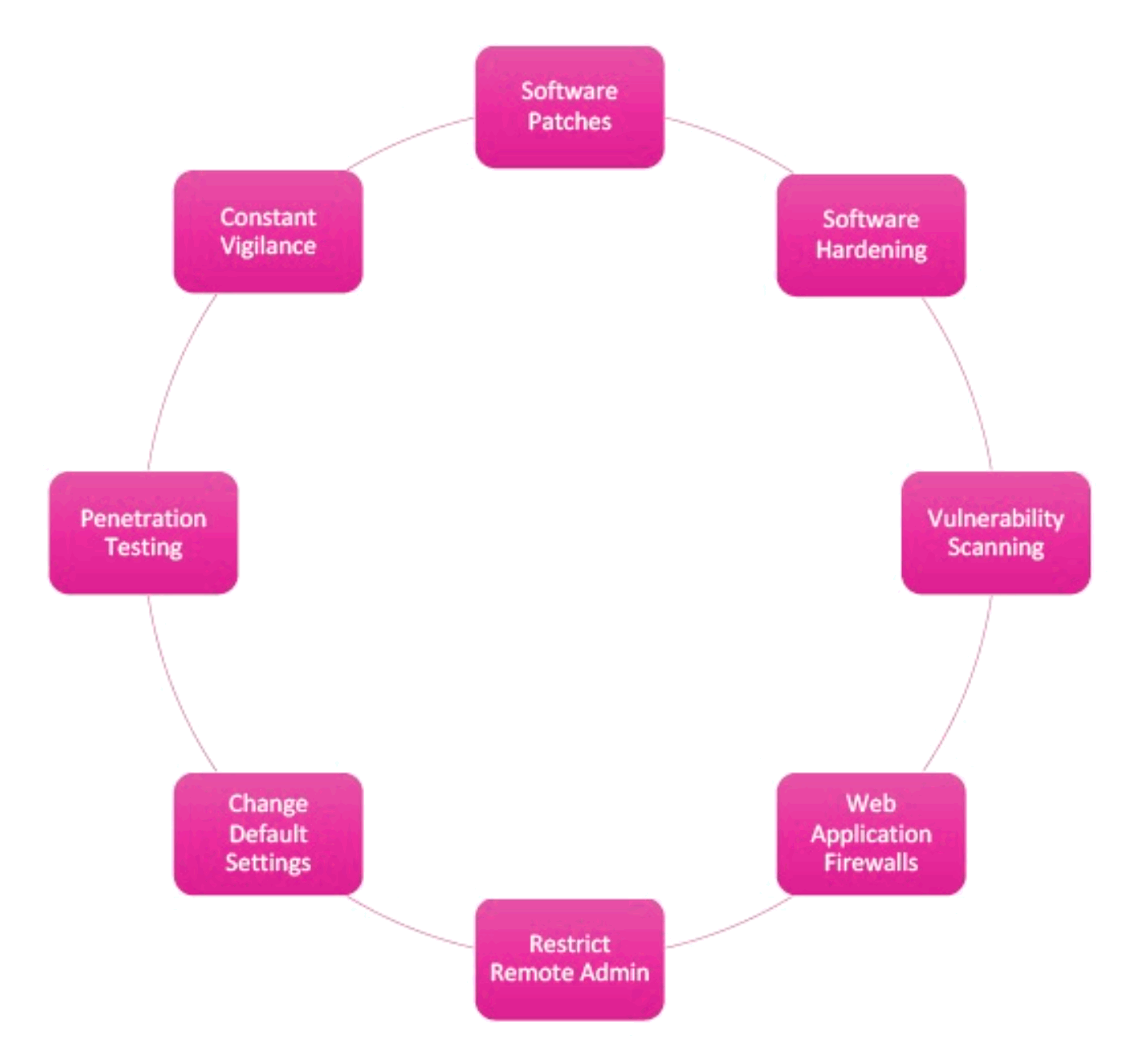
Software Patches – One must cover the software from time to time.
Software Hardening – Both server and software should perform the task they had to do.
Vulnerability Scanning – Look for vulnerabilities on the web server.
Web Application Firewalls – There must be a firewall to protect the web application from unwanted attacks.
Restrict Remote Admin – One must try and complicate and hide the URL.
Change Default Settings – If the application has a default admin username and password it must be changed on time.
Penetration Testing – It must be done to look for weaknesses across all applications.
Constant Vigilance – Web applications should be monitored regularly to ensure that they are entirely secured.