Given n processes with their burst times, the task is to find average waiting time and average turn around time using FCFS scheduling algorithm.
First in, first out (FIFO), also known as first come, first served (FCFS), is the simplest scheduling algorithm. FIFO simply queues processes in the order that they arrive in the ready queue.
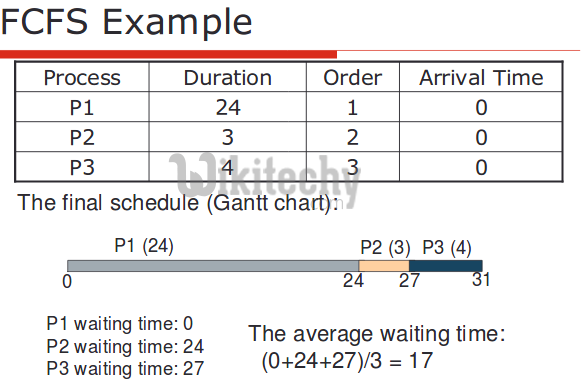
In this, the process that comes first will be executed first and next process starts only after the previous gets fully executed.
Here we are considering that arrival time for all processes is 0.
How to compute below times in Round Robin using a program?
- Completion Time: Time at which process completes its execution.
- Turn Around Time: Time Difference between completion time and arrival time. Turn Around Time = Completion Time – Arrival Time
- Waiting Time(W.T): Time Difference between turn around time and burst time.
Waiting Time = Turn Around Time – Burst Time
In this post, we have assumed arrival times as 0, so turn around and completion times are same.
Implementation:
1- Input the processes along with their burst time (bt).
2- Find waiting time (wt) for all processes.
3- As first process that comes need not to wait so
waiting time for process 1 will be 0 i.e. wt[0] = 0.
4- Find waiting time for all other processes i.e. for
process i ->
wt[i] = bt[i-1] + wt[i-1] .
5- Find turnaround time = waiting_time + burst_time
for all processes.
6- Find average waiting time =
total_waiting_time / no_of_processes.
7- Similarly, find average turnaround time =
total_turn_around_time / no_of_processes.
[ad type=”banner”]
C++ Programming:
[ad type=”banner”]Output:
Processes Burst time Waiting time Turn around time 1 10 0 10 2 5 10 15 3 8 15 23 Average waiting time = 8.33333 Average turn around time = 16 [ad type="banner"]
Important Points:
- Non-preemptive
- Average Waiting Time is not optimal
- Cannot utilize resources in parallel : Results in Convoy effect (Consider a situation when many IO bound processes are there and one CPU bound process. The IO bound processes have to wait for CPU bound process when CPU bound process acquires CPU. The IO bound process could have better taken CPU for some time, then used IO devices).