Write a function to delete a given node in a doubly linked list
(a) Original Doubly Linked List
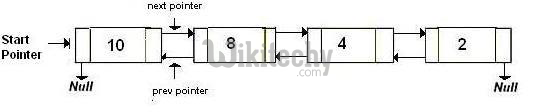
(a) After deletion of head node
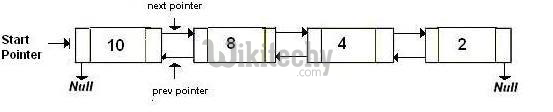
(a) After deletion of middle node

(a) After deletion of last node
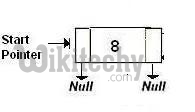
Algorithm
Let the node to be deleted is del.
1) If node to be deleted is head node, then change the head pointer to next current head.
2) Set next of previous to del, if previous to del exixts.
3) Set prev of next to del, if next to del exixts.
[ad type=”banner”]
Java Programming:
// Java program to delete a node from doubly linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head = null;
class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/*Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */
void deleteNode(Node head_ref, Node del) {
/* base case */
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
/* If node to be deleted is head node */
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
/* Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT the last node */
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
/* Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT the first node */
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
/* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/
return;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(Node head_ref, int new_data) {
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the begining,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = (head);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if ((head) != null) {
(head).prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(head) = new_node;
}
/*Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked lsit */
void printList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */
list.push(head, 2);
list.push(head, 4);
list.push(head, 8);
list.push(head, 10);
System.out.println("Original Linked list ");
list.printList(head);
/* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */
list.deleteNode(head, head); /*delete first node*/
list.deleteNode(head, head.next); /*delete middle node*/
list.deleteNode(head, head.next); /*delete last node*/
System.out.println("");
/* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */
System.out.println("Modified Linked List");
list.printList(head);
}
}
Time Complexity: O(1)
Time Complexity: O(1)
[ad type=”banner”]



