Methods to Protect Your Cloud Data from Hackers
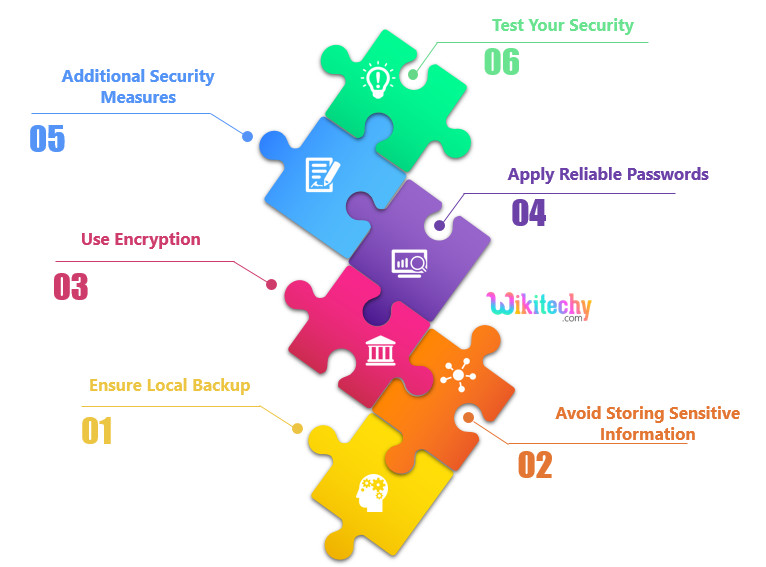
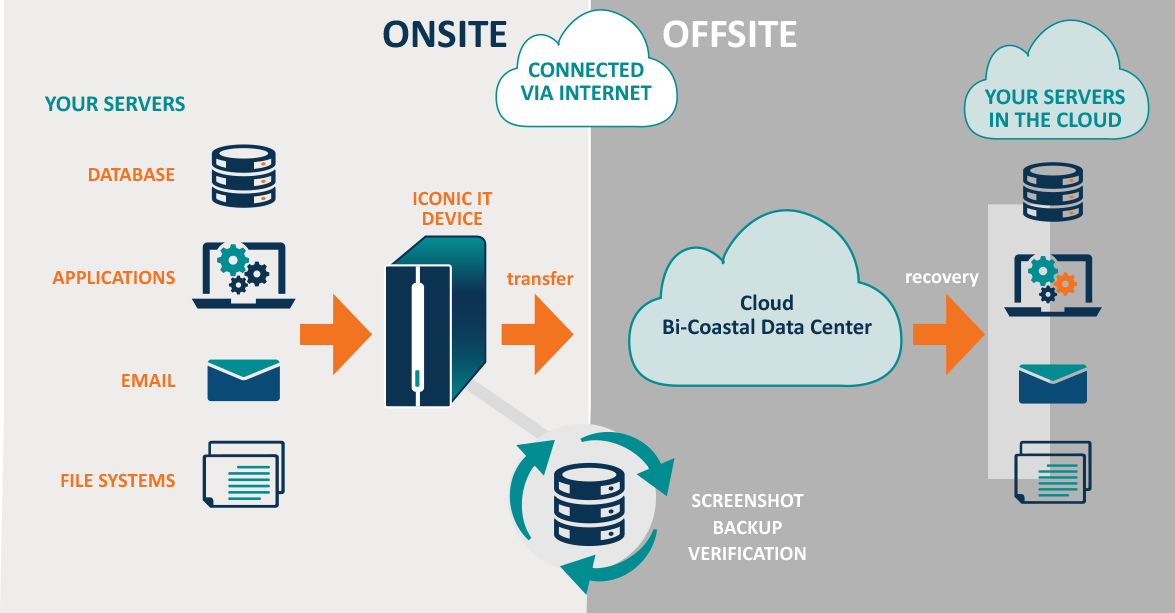
Ensure Local Backup
It is the important protection that one can take to cloud data security. Misuse of data is one thing, but losing possible data from your end may result in terrible values. Specially in the IT world, where information is everything organizations depend upon; losing data files could not only lead to a important financial loss but may also attract legal action.
Use Encryption
Encrypting data before uploading it to the cloud is an excellent protection against threats from unwanted hackers. Use local encryption as an extra layer of security. It is Known as zero-knowledge proof in cryptography , This method will even secure your data against service providers and administrators themselves. Therefore, choose a service provider who provides a precondition data encryption . Also if you’re already choosing for an encrypted cloud service, having a initial round of encryption for your files will give you a extra security.

Avoid Storing Sensitive Information
Many corporations refrain from storing private data on their servers, and there may be sensibility in the back of the decision — saving sensitive will become a responsibility of the association. Cooperation with such data can result in gruesome issues for the firm. Giants which includes Facebook had been dragged to court under such troubles in the past. Moreover, importing sensitive data is faulty from the customer’s perspective too. Simply keep away from storing such sensitive data at the cloud.
Apply Reliable Passwords
Use discretion and don’t make your passwords predictable. Also, introduce a two-step verification technique to enhance the security level of your data. Even if there may be a breach in a single security step, the alternative protects the data. Use updated patch ranges in order that hackers can’t break-in easily. There are many hints at the Internet to make a very good password. Use your creativity to strengthen the password similarly and keep converting it at everyday intervals.
Additional Security Measures
Although passwords are accurate for maintaining data encrypted, applying extra measures also are important. Encryption stops illegal get entry to data, however it doesn’t secure its existence. There are probabilities that your data might get corrupted over the time or that many humans may have access on your data and password security seems unreliable. Your cloud should be secured with antivirus programs, admin controls, and different functions that assist protect data. A secure cloud system and its committed servers should use the proper security tools and should function according to privilege controls to move data.
Test Your Security
Testing may include examining your cloud to see how well it is performing in association with its security setup. You can also hire ethical hackers to test your system’s security level and check if it has decayed over time; this may also provide a window to the possible loopholes that may allow hacking from unidentified sources. Never assume that your cloud system is always safe. Keeping cloud data safe requires constant action.
What is Cloud Data Security and why is it important ?
- Cloud Data Security covers critical things including data integrity, intellectual property, and customer data — All of which, in case of a breach, can cause important harm to any business.
- If we dig deeper into the subject, we’ll find that the most chilling data breaches that make it to news headlines are usually caused by an outsider attack.
- Such attacks are typically carried out by competitors or hackers looking for economic gain.
- While such breaches can cost up to millions of dollars, the good news is, linked to insider attacks, they’re much easier to detect and address using the right cloud security tools.
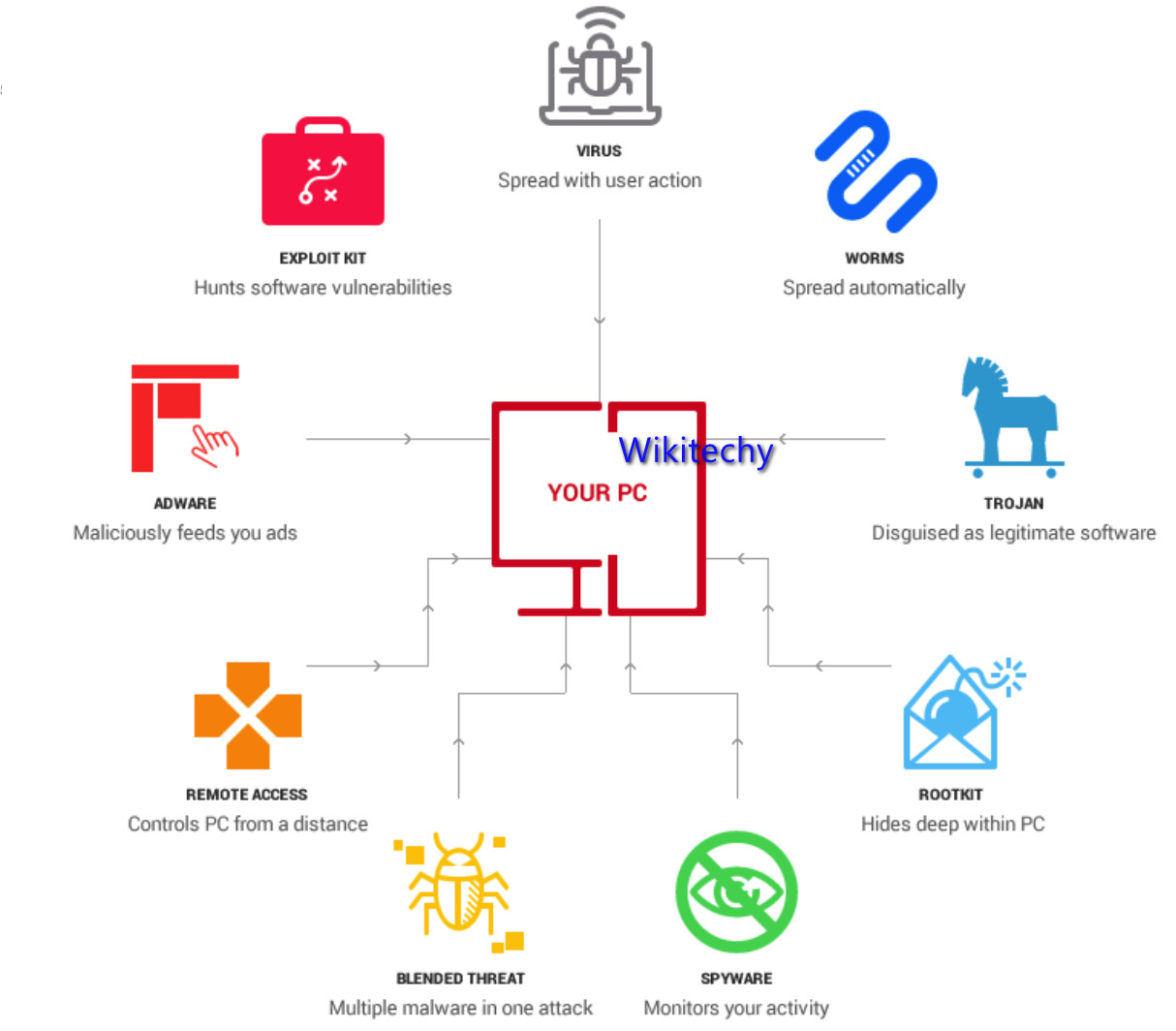
6 Outsider Cloud Data Security Attacks
Password Hacking :
- ‘A weak password is a criminal’s favourite house lock’
- Basic old-fashioned password hacking remains one of the most common outsider attacks in cloud environments.
- Things like crackable passwords, weak access security systems and insider vulnerabilities ALL make your cloud environment rip for outsider attacks.
- In specific, remains very common as users continue to use the same username and password on doubtful websites without even realising that they’re sharing these details with 3rd parties.
Ransomware spreading into the Cloud

- Ransomware is a type of unknown attack that works on the well-known concept of extortion — ‘Digital extortion’.
- And just like any extortion scheme, here the attacker steals your data and holds it until a certain ransom is paid.
- Ransomware attacks generally target organizations that are more likely to pay higher ransoms.
- In fact, the Finance, Insurance, Hospitals and Energy sectors are at the top of the list for Ransomware targeted sectors. In the meantime, Shared files in the cloud are a top ransomware target.
- Ransomware results in operational paralysis, the inability to recover backed-up data, and reputational damage, which can be disturbing for any organisation.
Cloud Account Hijacking:
- Cloud hijacking is another type of outsider attack in which an individual cloud account or domain is stolen or hijacked by an attacker.
- The Cloud Security Union rated service traffic hijacking as the third-greatest cloud computing security risk.
- Account hijackers prey on cooperated credentials to access and hijack cloud accounts. That’s another reason why multifactor authentication is important.
- Cloud account hijacking incidents can result in data leakage, the use of false information and loss of reputation.
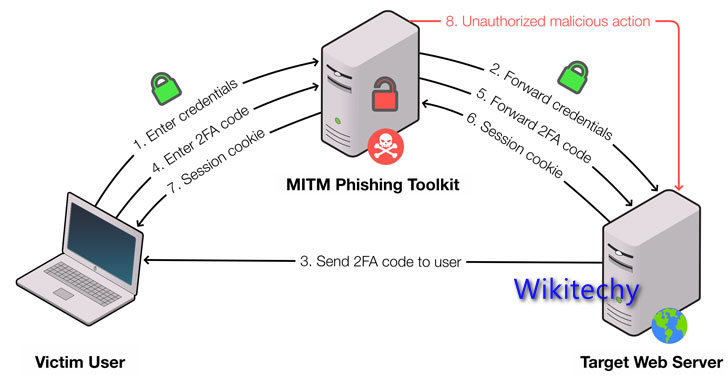
Phishing attacks
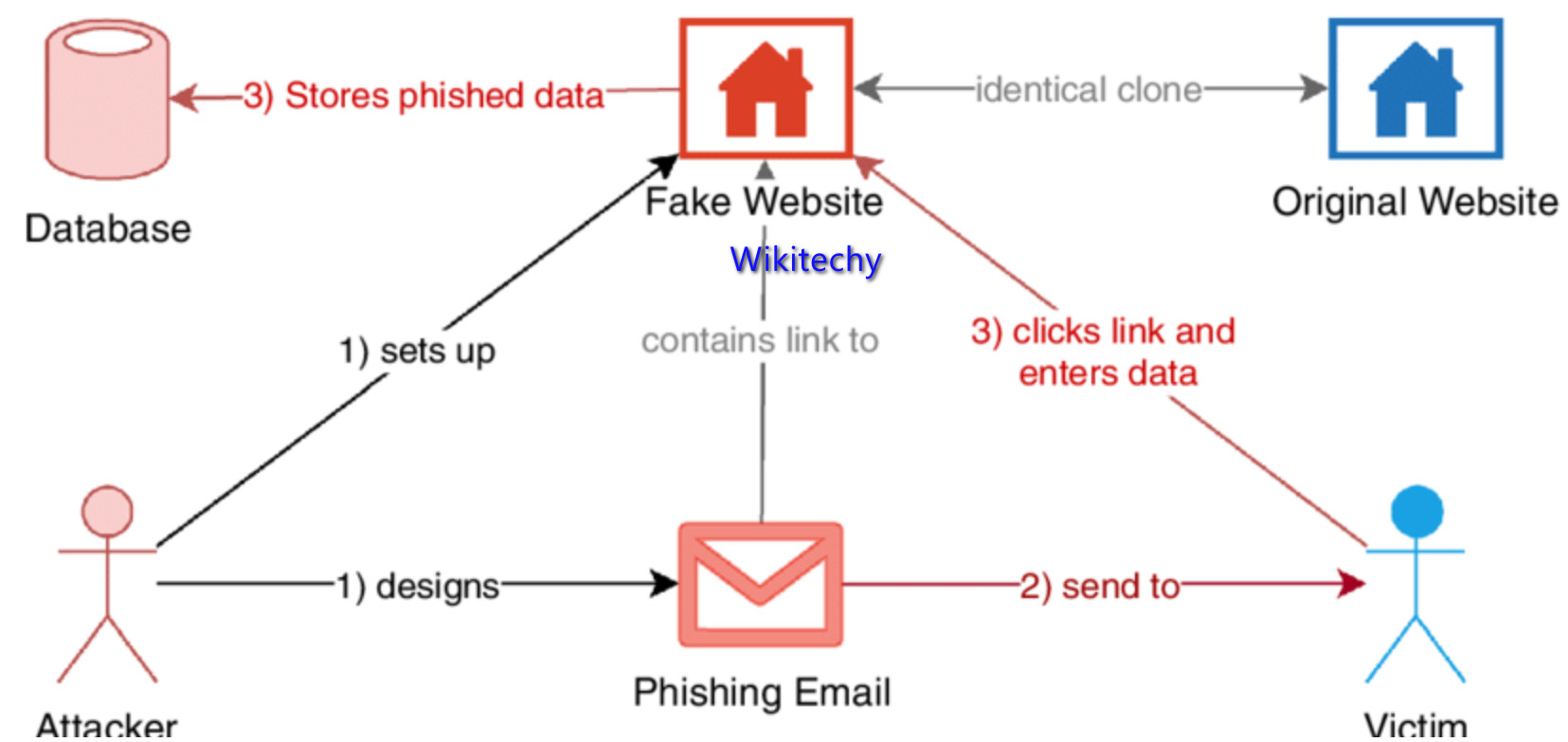
- Phishing is based on the concept of ‘deception’ where the attacker uses disguised emails, apps and websites to scam recipients, gather personal information and access sensitive data.
- Fake Apps are also another new trending phishing threat, particularly for cloud environments. Once a user accepts the permission requests of a malicious app, the hacker has access to their account, data and will likely have full control.
- Phishing is one of the common types of outsider attacks, so you’ll want to keep your eyes wide open for those.
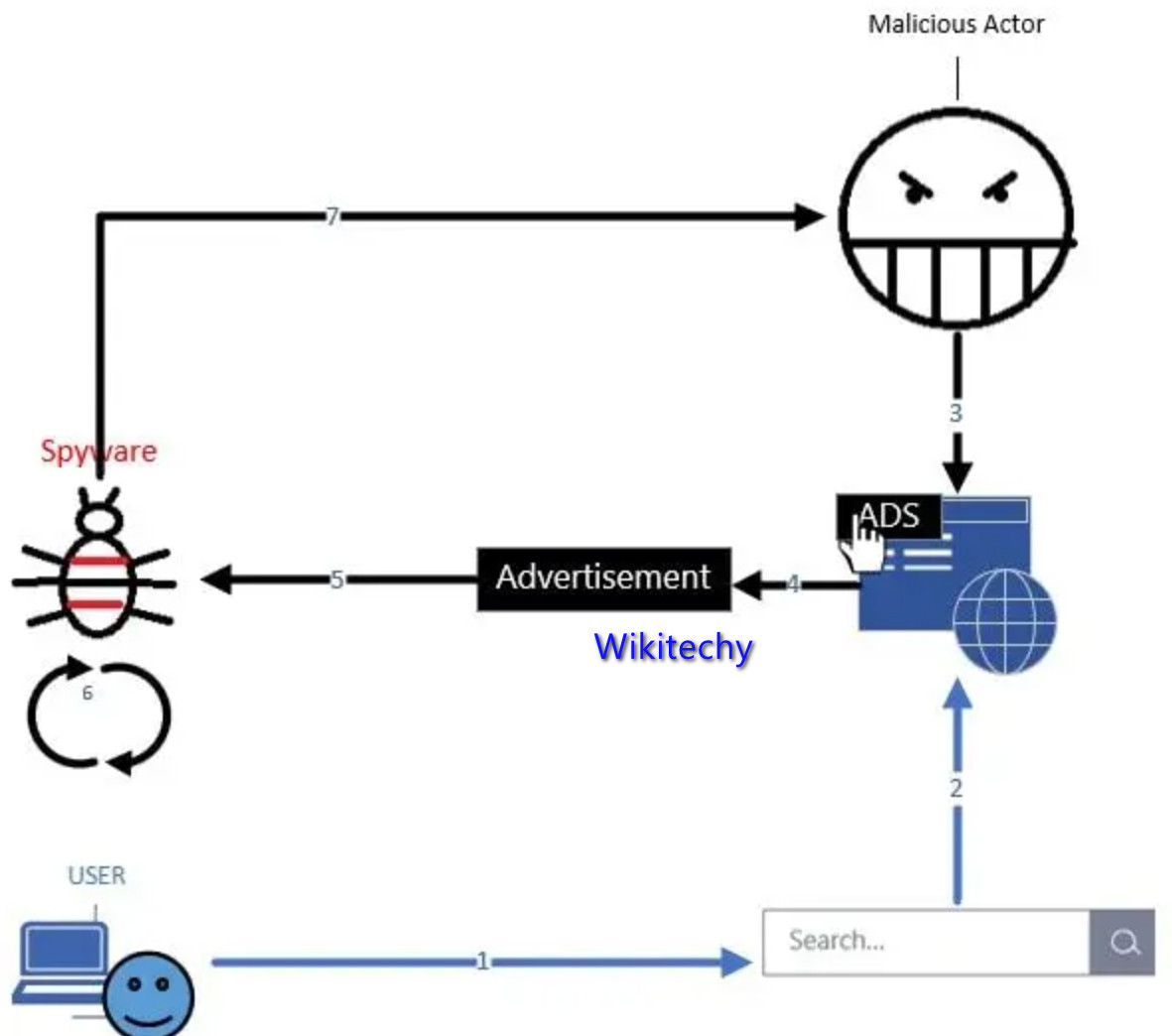
Spyware
- A spyware attack is like a regular ‘spy’ in the conventional sense. It accesses your system to collect and share your cloud data with the attacker without your knowledge.
How it can get in :
- It either accesses your data as a hidden component of open software or through traditional things like deceptive ads, websites, email, instant messages, as well as direct file-sharing connections.
- Spywares are hard to detect and use a variety of techniques to communicate back to the attacker in a way that won’t illegal the doubt of your security teams.
Domain-wide Spoofing:

- Spoofing is common form of deceit-based phishing attack in which the attacker seems to be using a company’s domain to impersonate it or any of its employees.
- This type of attack is very common in cloud environments whereby the attacker successfully bypasses access controls through deceit and steals crucial data stored on your cloud.
- In fact, according to the FTC, over 96% of companies in business today have experienced a domain spoofing attack in one form or another.