We have discussed Circular Linked List Introduction and Applications, in the previous post on Circular Linked List. In this post, traversal operation is discussed.
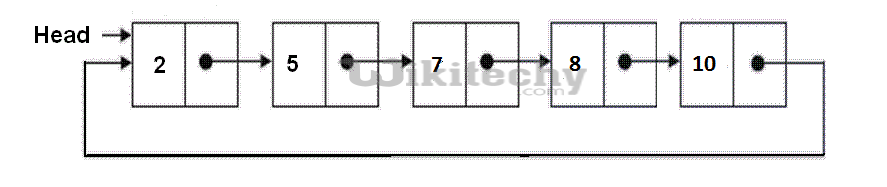
In a conventional linked list, we traverse the list from the head node and stop the traversal when we reach NULL. In a circular linked list, we stop traversal when we reach the first node again. Following is C code for linked list traversal.
void printList(struct node *first)
{
struct node *temp = first;
if (first != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != first);
}
}
[ad type=”banner”]
Complete C program to demonstrate traversal. Following is complete C program to demonstrate traversal of circular linked list.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
void push(struct node **head_ref, int data)
{
struct node *ptr1 = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *temp = *head_ref;
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *head_ref;
if (*head_ref != NULL)
{
while (temp->next != *head_ref)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = ptr1;
}
else
ptr1->next = ptr1;
*head_ref = ptr1;
}
void printList(struct node *head)
{
struct node *temp = head;
if (head != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
}
}
int main()
{
struct node *head = NULL;
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 56);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 11);
printf("Contents of Circular Linked List\n ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
Contents of Circular Linked List
11 2 56 12
[ad type=”banner”]
