We have discussed singly and doubly linked lists in the following posts.
Introduction to Linked List & Insertion
Doubly Linked List Introduction and Insertion
Circular linked list is a linked list where all nodes are connected to form a circle. There is no NULL at the end. A circular linked list can be a singly circular linked list or doubly circular linked list.
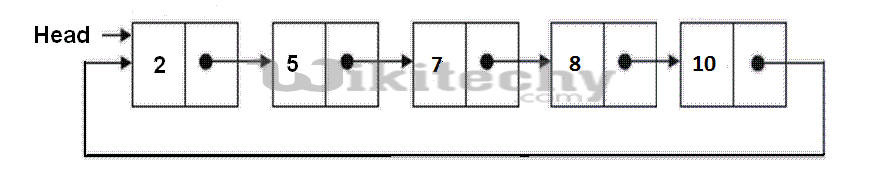
Advantages of Circular Linked Lists:
1) Any node can be a starting point. We can traverse the whole list by starting from any point. We just need to stop when the first visited node is visited again.
2) Useful for implementation of queue. Unlike this implementation, we don’t need to maintain two pointers for front and rear if we use circular linked list. We can maintain a pointer to the last inserted node and front can always be obtained as next of last.
3) Circular lists are useful in applications to repeatedly go around the list. For example, when multiple applications are running on a PC, it is common for the operating system to put the running applications on a list and then to cycle through them, giving each of them a slice of time to execute, and then making them wait while the CPU is given to another application. It is convenient for the operating system to use a circular list so that when it reaches the end of the list it can cycle around to the front of the list. (Source http://web.eecs.utk.edu/~bvz/cs140/notes/Dllists/)
4) Circular Doubly Linked Lists are used for implementation of advanced data structures like Fibonacci Heap.
[ad type=”banner”]