Write an efficient C++ program to find the sum of contiguous subarray within a one-dimensional array of numbers which has the largest sum.
Kadane’s Algorithm:
Initialize:
max_so_far = 0
max_ending_here = 0
Loop for each element of the array
(a) max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i]
(b) if(max_ending_here < 0)
max_ending_here = 0
(c) if(max_so_far < max_ending_here)
max_so_far = max_ending_here
return max_so_far
[ad type=”banner”]
Explanation:
Simple idea of the Kadane’s algorithm is to look for all positive contiguous segments of the array (max_ending_here is used for this). And keep track of maximum sum contiguous segment among all positive segments (max_so_far is used for this). Each time we get a positive sum compare it with max_so_far and update max_so_far if it is greater than max_so_far
Lets take the example:
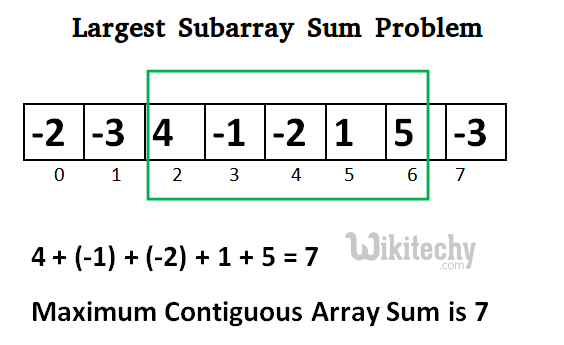
{-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3}
max_so_far = max_ending_here = 0
for i=0, a[0] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
for i=1, a[1] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
Set max_ending_here = 0 because max_ending_here < 0
for i=2, a[2] = 4
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (4)
max_ending_here = 4
max_so_far is updated to 4 because max_ending_here greater
than max_so_far which was 0 till now
for i=3, a[3] = -1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-1)
max_ending_here = 3
for i=4, a[4] = -2
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-2)
max_ending_here = 1
for i=5, a[5] = 1
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (1)
max_ending_here = 2
for i=6, a[6] = 5
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (5)
max_ending_here = 7
max_so_far is updated to 7 because max_ending_here is
greater than max_so_far
for i=7, a[7] = -3
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + (-3)
max_ending_here = 4
Program:
Output :
Maximum contiguous sum is 7[ad type=”banner”]
Above program can be optimized further, if we compare max_so_far with max_ending_here only if max_ending_here is greater than 0.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Algorithmic Paradigm: Dynamic Programming
The implementation handles the case when all numbers in array are negative.
Output :
Maximum contiguous sum is 7[ad type=”banner”]
To print the subarray with the maximum sum, we maintain indices whenever we get the maximum sum.
Output :
Maximum contiguous sum is 7 Starting index 2 Ending index 6