Branch and Bound | Set 3 (8 puzzle Problem)
We have introduced Branch and Bound and discussed 0/1 Knapsack problem in below posts.
- Branch and Bound | Set 1 (Introduction with 0/1 Knapsack)
- Branch and Bound | Set 2 (Implementation of 0/1 Knapsack)
In this puzzle solution of 8 puzzle problem is discussed.
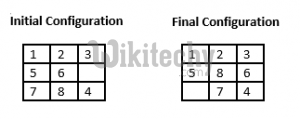
Given a 3×3 board with 8 tiles (every tile has one number from 1 to 8) and one empty space. The objective is to place the numbers on tiles to match final configuration using the empty space. We can slide four adjacent (left, right, above and below) tiles into the empty space.
For example,
1. DFS (Brute-Force)
We can perform depth-first search on state space (Set of all configurations of a given problem i.e. all states that can be reached from initial state) tree.
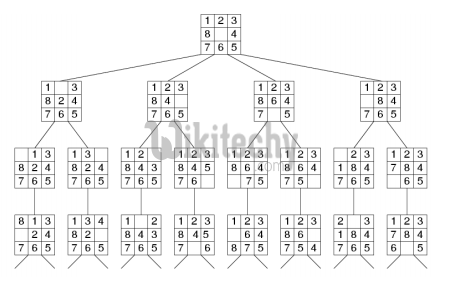
state space tree for 8 puzzle
In this solution, successive moves can take us away from the goal rather than bringing closer. The search of state space tree follows leftmost path from the root regardless of initial state. An answer node may never be found in this approach.
[ad type=”banner”]2. BFS (Brute-Force)
We can perform a Breadth-first search on state space tree. This always finds a goal state nearest to the root. But no matter what the initial state is, the algorithm attempts the same sequence of moves like DFS.
3. Branch and Bound
The search for an answer node can often be speeded by using an “intelligent” ranking function, also called an approximate cost function to avoid searching in sub-trees that do not contain an answer node. It is similar to backtracking technique but uses BFS-like search.
There are basically three types of nodes involved in Branch and Bound
1. Live node is a node that has been generated but whose children have not yet been generated.
2. E-node is a live node whose children are currently being explored. In other words, an E-node is a node currently being expanded.
3. Dead node is a generated node that is not to be expanded or explored any further. All children of a dead node have already been expanded.
Cost function:
Each node X in the search tree is associated with a cost. The cost function is useful for determining the next E-node. The next E-node is the one with least cost. The cost function is defined as,
C(X) = g(X) + h(X) where
g(X) = cost of reaching the current node
from the root
h(X) = cost of reaching an answer node from X.
[ad type=”banner”]
Ideal Cost function for 8-puzzle Algorithm :
We assume that moving one tile in any direction will have 1 unit cost. Keeping that in mind, we define cost function for 8-puzzle algorithm as below :
c(x) = f(x) + h(x) where
f(x) is the length of the path from root to x
(the number of moves so far) and
h(x) is the number of non-blank tiles not in
their goal position (the number of mis-
-placed tiles). There are at least h(x)
moves to transform state x to a goal state
An algorithm is available for getting an approximation of h(x) which is a unknown value.
Complete Algorithm:
/* Algorithm LCSearch uses c(x) to find an answer node
* LCSearch uses Least() and Add() to maintain the list
of live nodes
* Least() finds a live node with least c(x), deletes
it from the list and returns it
* Add(x) adds x to the list of live nodes
* Implement list of live nodes as a min heap */
struct list_node
{
list_node *next;
// Helps in tracing path when answer is found
list_node *parent;
float cost;
}
algorithm LCSearch(list_node *t)
{
// Search t for an answer node
// Input: Root node of tree t
// Output: Path from answer node to root
if (*t is an answer node)
{
print(*t);
return;
}
E = t; // E-node
Initialize the list of live nodes to be empty;
while (true)
{
for each child x of E
{
if x is an answer node
{
print the path from x to t;
return;
}
Add (x); // Add x to list of live nodes;
x->parent = E; // Pointer for path to root
}
if there are no more live nodes
{
print ("No answer node");
return;
}
// Find a live node with least estimated cost
E = Least();
// The found node is deleted from the list of
// live nodes
}
}
Below diagram shows the path followed by above algorithm to reach final configuration from given initial configuration of 8-Puzzle. Note that only nodes having least value of cost function are expanded.
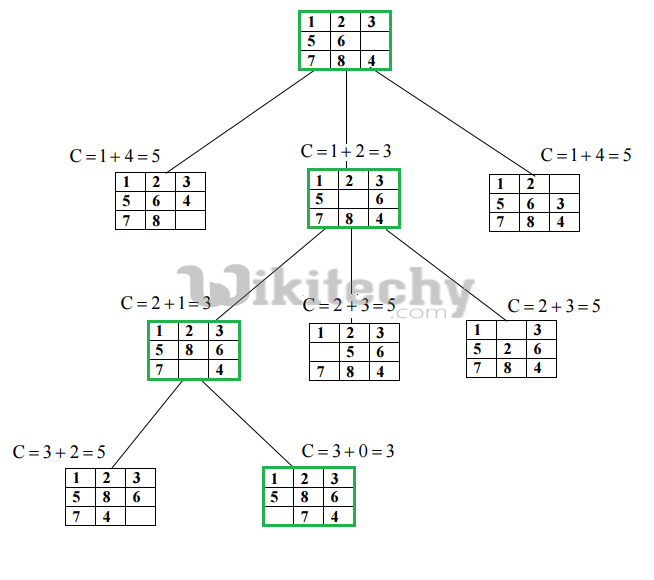
Output :
1 2 3 5 6 0 7 8 4 1 2 3 5 0 6 7 8 4 1 2 3 5 8 6 7 0 4 1 2 3 5 8 6 0 7 4[ad type=”banner”]