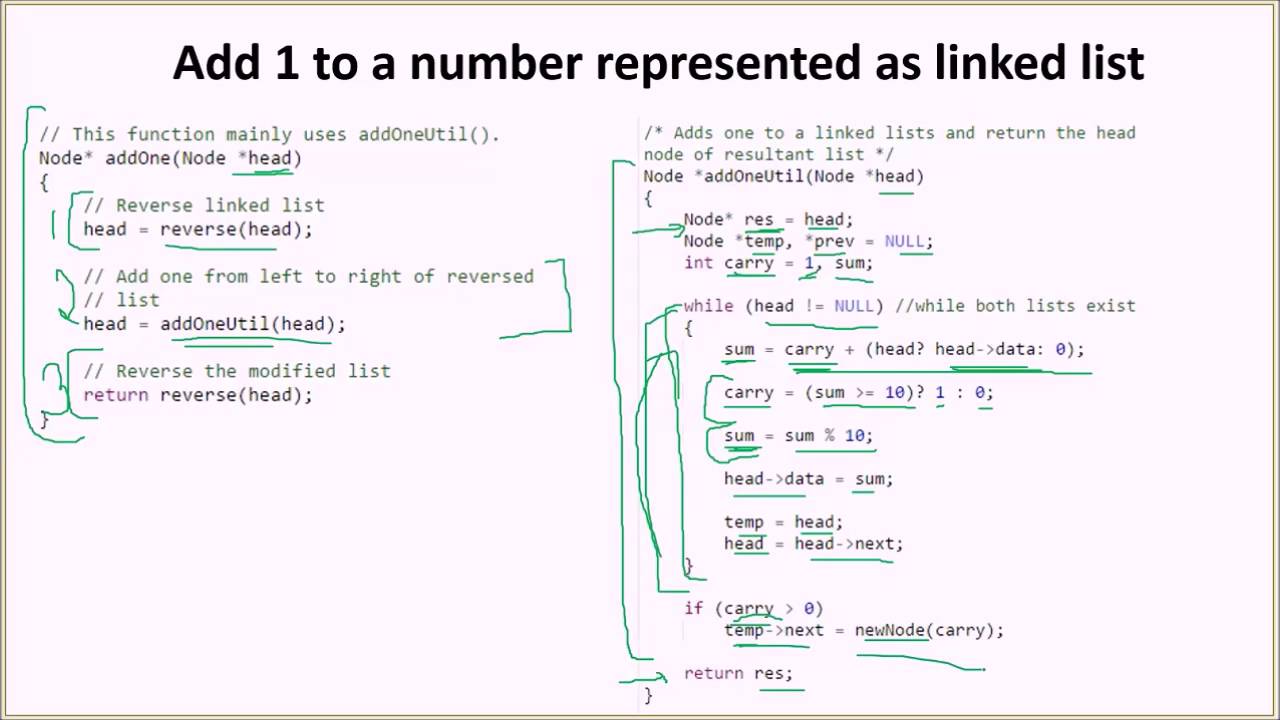
Number is represented in linked list such that each digit corresponds to a node in linked list. Add 1 to it. For example 1999 is represented as (1-> 9-> 9 -> 9) and adding 1 to it should change it to (2->0->0->0)
Below are the steps :
- Reverse given linked list. For example, 1-> 9-> 9 -> 9 is converted to 9-> 9 -> 9 ->1.
- Start traversing linked list from leftmost node and add 1 to it. If there is a carry, move to the next node. Keep moving to the next node while there is a carry.
- Reverse modified linked list and return head.
C++ prpgramming:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
Node *reverse(Node *head)
{
Node * prev = NULL;
Node * current = head;
Node * next;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
Node *addOneUtil(Node *head)
{
Node* res = head;
Node *temp, *prev = NULL;
int carry = 1, sum;
while (head != NULL)
{
sum = carry + head->data;
carry = (sum >= 10)? 1 : 0;
sum = sum % 10;
head->data = sum;
temp = head;
head = head->next;
}
if (carry > 0)
temp->next = newNode(carry);
return res;
}
Node* addOne(Node *head)
{
head = reverse(head);
head = addOneUtil(head);
return reverse(head);
}
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(void)
{
Node *head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(9);
head->next->next = newNode(9);
head->next->next->next = newNode(9);
printf("List is ");
printList(head);
head = addOne(head);
printf("\nResultant list is ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
List is 1999
Resultant list is 2000
Recursive Implementation:
We can recursively reach the last node and forward carry to previous nodes. Recursive solution doesn’t require reversing of linked list. We can also use a stack in place of recursion to temporarily hold nodes.
C++ Programming:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
int addWithCarry(Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return 1;
int res = head->data + addWithCarry(head->next);
head->data = (res) % 10;
return (res) / 10;
}
Node* addOne(Node *head)
{
int carry = addWithCarry(head);
if (carry)
{
Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = carry;
newNode->next = head;
return newNode;
}
return head;
}
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(void)
{
Node *head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(9);
head->next->next = newNode(9);
head->next->next->next = newNode(9);
printf("List is ");
printList(head);
head = addOne(head);
printf("\nResultant list is ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
List is 1999
Resultant list is 2000