Write a C function to count number of nodes in a given singly linked list.
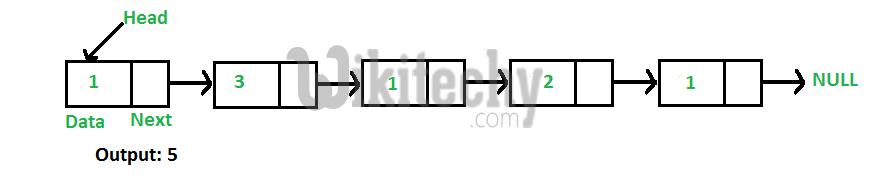
For example, the function should return 5 for linked list 1->3->1->2->1.
Iterative Solution
1) Initialize count as 0
2) Initialize a node pointer, current = head.
3) Do following while current is not NULL
a) current = current -> next
b) count++;
4) Return count
Java Programming:
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) { data = d; next = null; }
}
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCount()
{
Node temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp != null)
{
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Count of nodes is " +
llist.getCount());
}
}
[ad type=”banner”]
Output:
count of nodes is 5
Recursive Solution
int getCount(head)
1) If head is NULL, return 0.
2) Else return 1 + getCount(head->next)
Java Programming:
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) { data = d; next = null; }
}
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
public void push(int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
public int getCountRec(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
return 1 + getCountRec(node.next);
}
public int getCount()
{
return getCountRec(head);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(1);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(1);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Count of nodes is " +
llist.getCount());
}
}
[ad type=”banner”]
Output:
count of nodes is 5
