- In python a namespace is a system that has a unique name for each and every object.
- An object might be a method or a variable and python itself maintains a namespace in the form of a Python dictionary.
- Inside every directory that one can have multiple directories having a file with the same name.
- The role of a namespace is like a surname, in real time example.
- Python interpreter understands what exact method or variable one is trying to point to in the code, depending upon the namespace, on similar lines.
- In this Name which means name, a unique identifier and Space which talks something related to scope.
- In python a name might be of any method or variable and space depends upon the location from where is trying to access a variable or a method.
- The namespace consists of three types, they are global namespace, built-in namespace, local namespace.
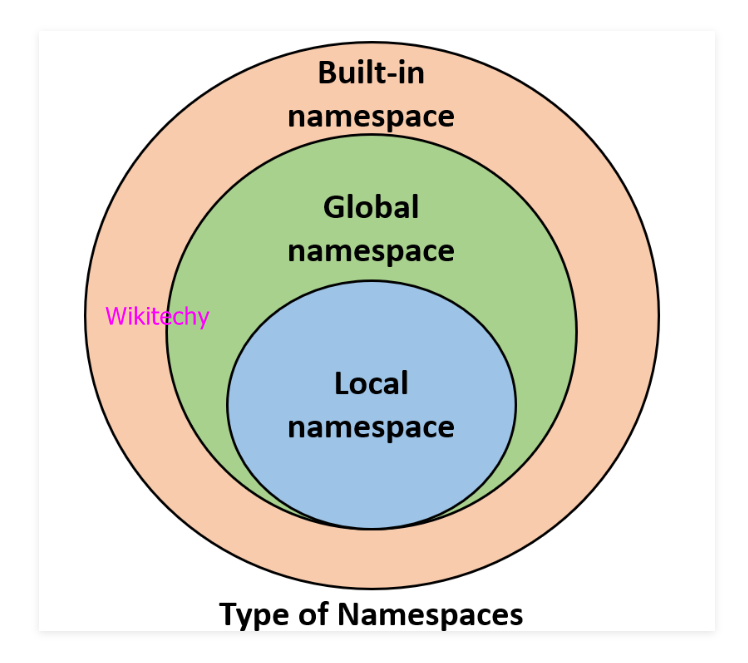
- If python interpreter runs solely without any user-defined modules, methods, classes, etc. Some functions like print (), id () is always present, these are built-in namespaces.
- If user creates a module, a global namespace gets created, later the creation of local functions creates the local namespace.
- The global namespace encompasses the local namespace and built-in namespace encompasses global namespace.
- If scope of an object ends, the lifetime of that namespace comes to an end, so the lifetime of a namespace depends upon the scope of objects.
- Hence there is no possible to access the inner namespace’s objects from an outer namespace.
Sample Code
Output


