- Variables in python are the containers for storing data values.
- It gets mapped to that instance, they are reference, or pointers, to an object in memory which means that whenever a variable is assigned to an instance.
- Python is not statically typed, unlike other languages like C/C++/JAVA.
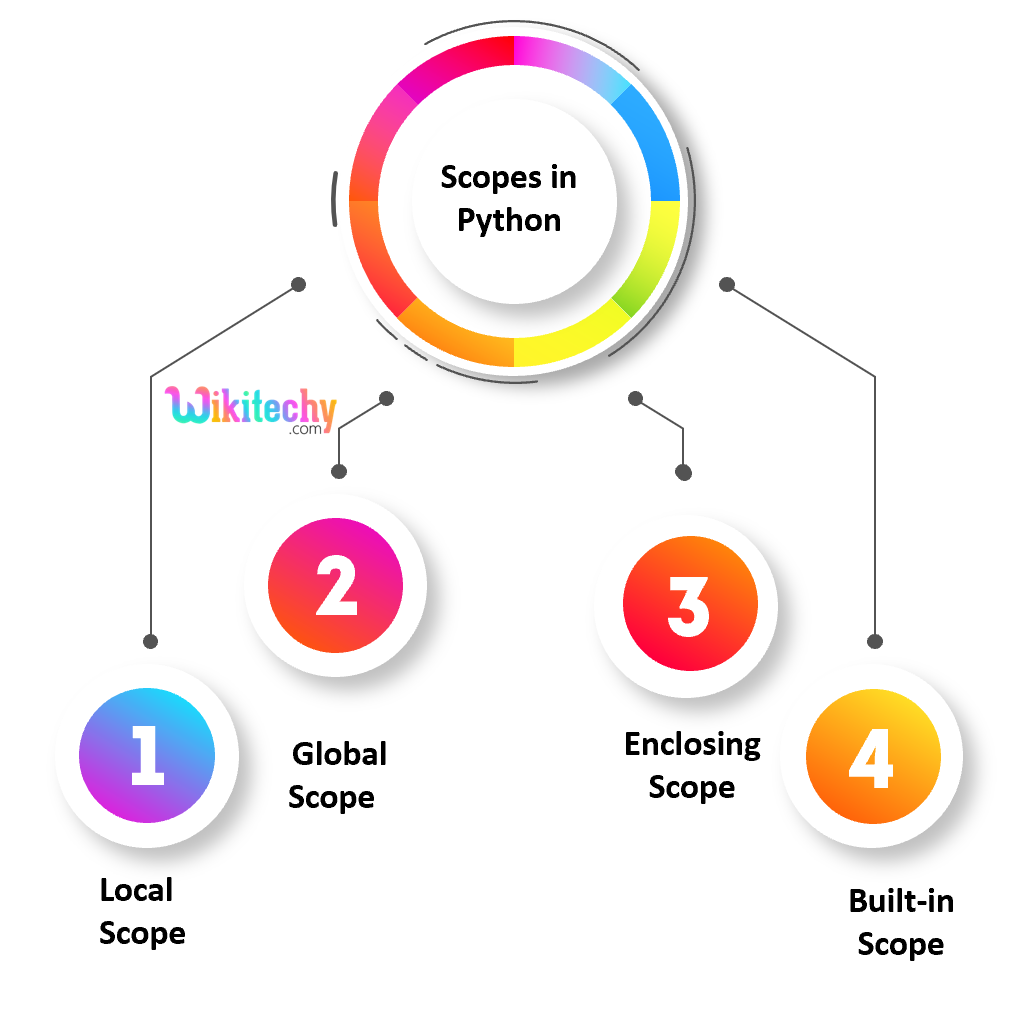
- Scope of a variable is the location where we can find a variable and also access it if required.
- In python there are four types of scopes they are, Local Scope, Global Scope, Enclosing Scope and Built-in Scope.
- Global variables are the ones that are defined and declared outside, not specified to any function.
- In current function a local scope refers to the local objects were available.
- Global scope refers to the objects available throughout the code execution since their inception.
- In program a module-level scope refers to the global objects of the current module accessible.
- In program an outermost scope refers to all the built-in names callable and objects in this scope are searched last to find the name referenced.
Sample Code : Global Scope
Output

