- PHP data types are used to hold different types of values or data.
- There are eight primitive data types which are further categorized into three types, they are:
- Scalar types
- Compound types
- Special types
Scalar data types
- Scalar data types hold only single value and it consists of four data types, they are boolean, integer, float and string.
Boolean
- Booleans are the simplest data type works like switch and holds only two values TRUE (1) or FALSE (0).
- It is often used with conditional statements were if the condition is correct, it returns TRUE otherwise FALSE.
Sample Code
Output

Integer
- Integer means numeric data, it can be either positive or negative sign.
- It holds only whole numbers, like numbers without decimal points or fractional parts.
Sample Code
Output

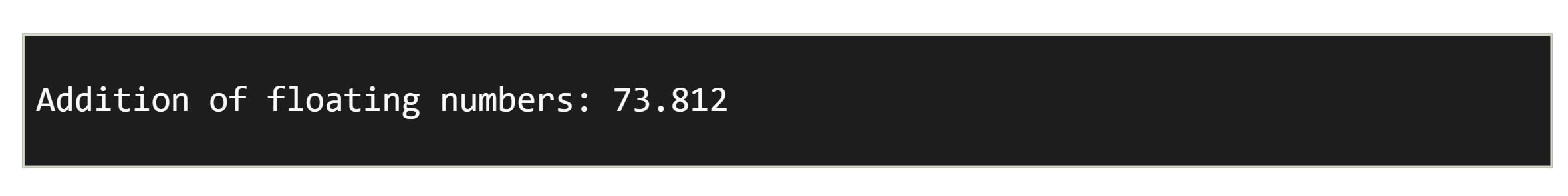
Float
- A floating-point number is a number with a decimal point and unlike integer, it can hold numbers with a fractional or decimal point, including a negative or positive sign.
Sample Code
Output
String
- String is a non-numeric data type which holds letters or any alphabets, numbers, and even special characters.
- Its value must be enclosed either within single quotes or in double quotes and both are treated differently.
Sample Code
Output

Compound data type
- Compound data type can hold multiple and it consists of two data types, they are array and object.
Array
- In single variable an array canstore multiple values of same data type.
Sample Code
Output

Object
- Objects are the instances of user-defined classes that can store both functions and values.
- It must be explicitly declared.
Sample Code
Output

Special Data Type
- Special data types consist of two types, they are Null and resource data type.
Null
- Null is a special data type that has only one value is NULL and there is a convention of writing it in capital letters as it is case sensitive.
- In special data type NULL defined a variable with no value.
Sample Code
Output

Resource:
- In PHP resources are not the exact data type and basically these are used to references to external PHP resources or store some small function calls.

