What is Switching ?
- Switching is the most valuable asset of computer networking.
- Everytime in computer network you have access the internet or another computer network outside your immediate location, or your messages are sent through a maze of transmission media and connection devices.
- The mechanism for exchange of information between different computer networks and network segments is called switching in Networking.
- On the other words we can say that any type signal or data element directing or Switching toward a particular hardware address or hardware pieces.
- Hardware devices that can be used for switching or transferring data from one location to another that can use multiple layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
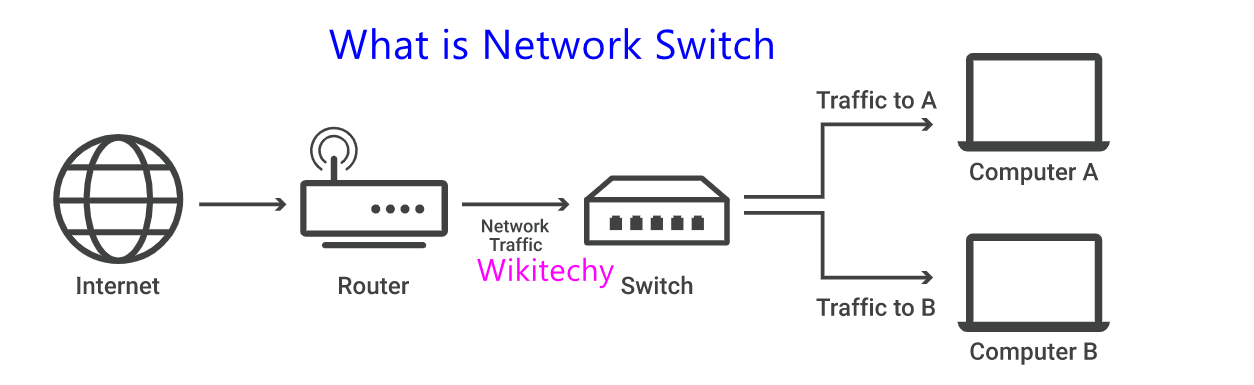
Types of Switching Techniques
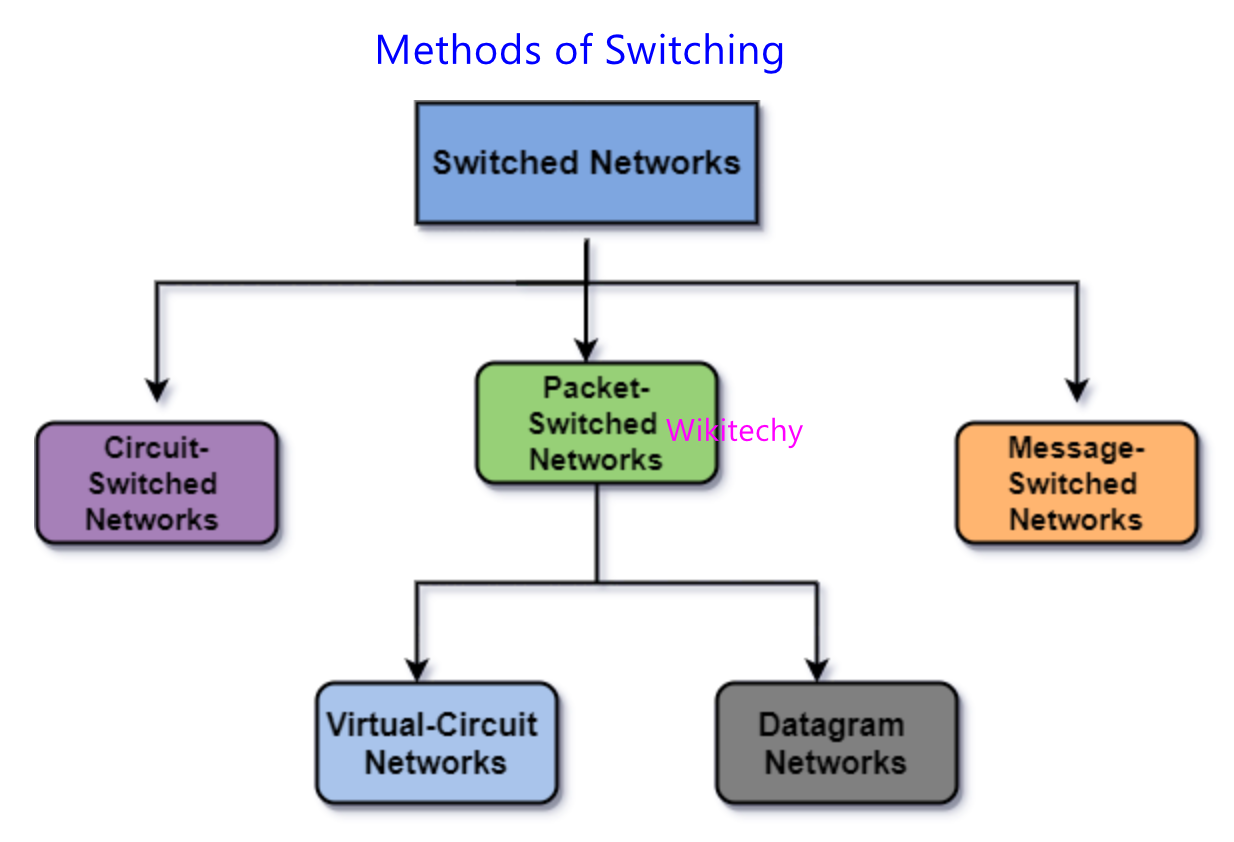
- There are basically three types of switching methods are available.
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
- Message Switching
Circuit Switching
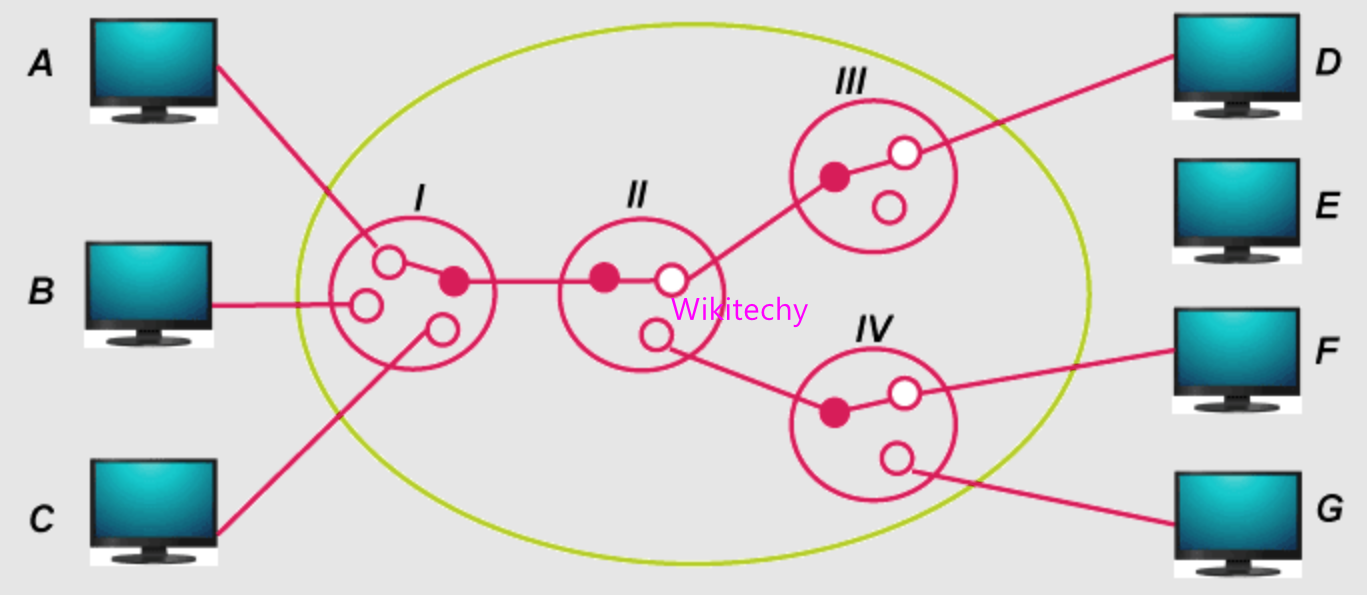
- Circuit-switching is the real-time connection-oriented system. In Circuit Switching a dedicated channel (or circuit) is set up for a single connection between the sender and recipient during the communication session.
- In telephone communication system, the normal voice call is the example of Circuit Switching. The telephone service provider maintain a unbroken link for each telephone call.
- Circuit switching is pass through three phases, that are circuit establishment, data transfer and circuit disconnect.

Packet Switching
- The basic example of Packet Switching is the Internet. In Packet Switching, data can be fragmented into suitably-sized pieces in variable length or blocks that are called packets that can be routed independently by network devices based on the destination address contained certain “formatted” header within each packet.
- The packet switched networks allow sender and recipient without reserving the circuit. Multiple paths are exist between sender and recipient in a packet switching network.
- They does not require a call setup to transfer packets between sender and recipient.

Packet Switching
- There are two type of Packet Switching connectionless or Connection-Oriented.
Connectionless Packet Switching
- It is also known as datagram switching. In this type of network each packet routed individually by network devices based on the destination address contained within each packet.
- Due to each packet is routed individually, the result is that each packet is delivered out-of-order with different paths of transmission, it depend on the networking devices like (switches and routers) at any given time.
- After reaching recipient location, the packets are reassemble to the original form.
Connection-Oriented Packet Switching
- It is also known as virtual circuit switching. In this type of Networking packets are send in sequential order over a defined route.
Message Switching
- Message switching does not set up a dedicated channel (or circuit) between the sender and recipient during the communication session.
- In Message Switching each message is treated as an independent blocks.
- In this type of networking, each message is then transmitted from first network device to second network device through the internetwork i.e. message is transmitted from the sender to intermediate device.

Message Switching
- The intermediate device stores the message for a time being, after inspects it for errors, intermediate device transmitting the message to the next node with its routing information. Because the message switching networks are called store and forward networks in networking.

