What is Routing ?
- Routing refers to establishing the routes that data packets take on their way to a particular destination.
- This term can be applied to data traveling on the Internet, over 3G or 4G networks, or over similar networks used for telecom and other digital communications setups. Routing can also take place within proprietary networks.

How Routing Protocols Work

- Every network Routing protocol performs three basic functions:
- Discovery – Identify other routers on the network.
- Route Management – Keep track of all the possible destinations (for network messages) along with some data describing the pathway of each.
- Path Determination – Make dynamic decisions for where to send each network message.
There are 3 types of Routing
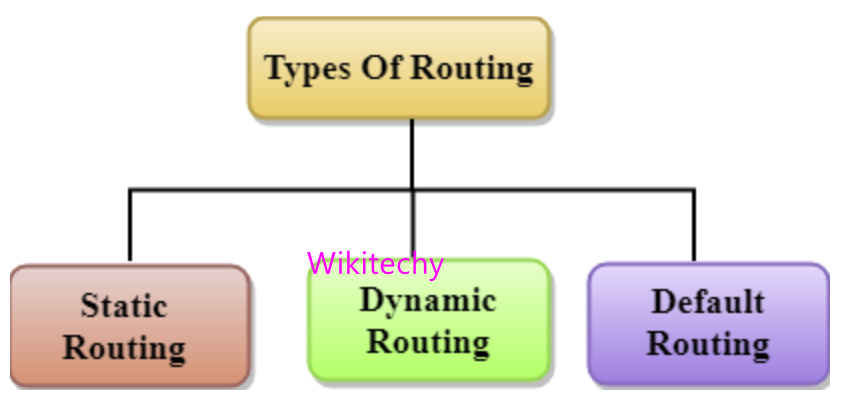
- Static Routing
- Dafault Routing
- Dynamic Routing
Static Routing
- Static Routing is a process in which we have to manually add routes in Routing table.

Advantages
- No Routing overhead for router CPU which means a cheaper router can be used to do Routing.
- It adds security because only administrator can allow Routing to particular networks only.
- No bandwidth usage between routers.
Disadvantages
- For a large network, it is a difficult task for administrator to manually add each route for the network in the Routing table on each router.
- The administrator should have good knowledge of the topology.
- If a new administrator comes, then he has to manually add each route so he should have very good knowledge of the routes of the topology.
Default Routing
- This method where the router is configured to send all packets towards a single router (next hop).
- It is very useful method for small networks or networks with a single entry and exit point.
- Basically this method used in addition to Static and/or Dynamic routing.
- It is generally used with stub routers. A stub router is a router which has only one route to reach all other networks.

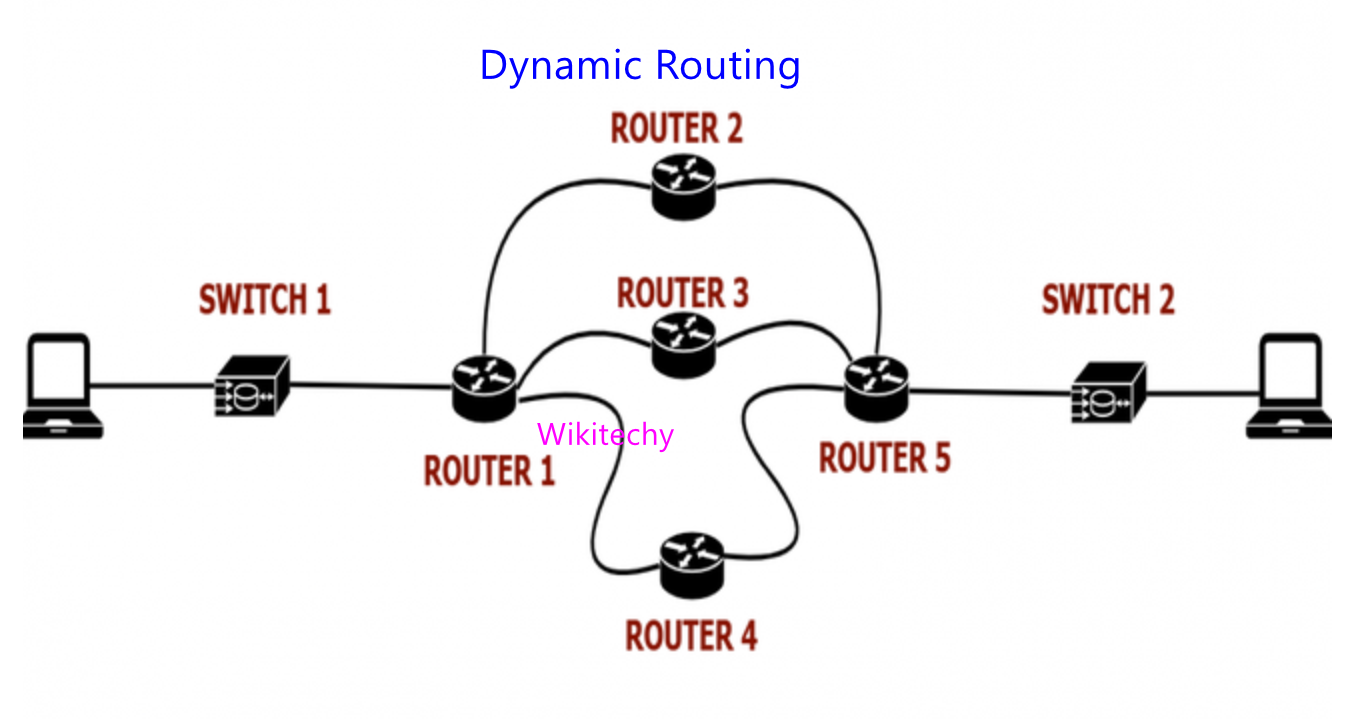
Dynamic Routing
-
- Dynamic Routing makes automatic adjustment of the routes according to the current state of the route in the Routing table.
- Dynamic Routing uses protocols to discover network destinations and the routes to reach it.
- RIP and OSPF are the best examples of dynamic Routing protocol. Automatic adjustment will be made to reach the network destination if one route goes down.
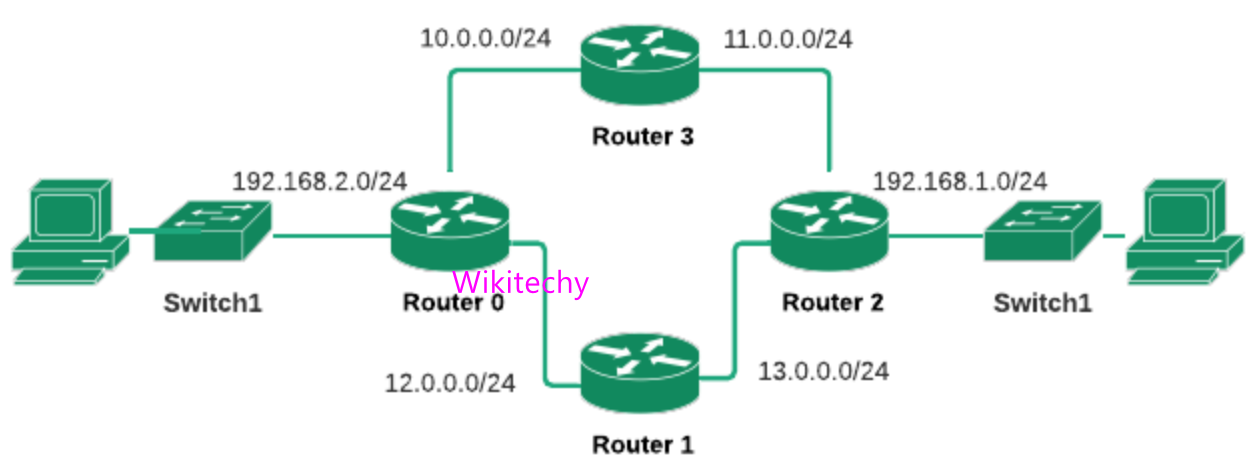
Dynamic Routing
- A dynamic protocol have following features,
- The routers should have the same dynamic protocol running in order to exchange routes.
- When a router finds a change in the topology then router advertises it to all other routers.
Advantages
- Easy to configure.
- More effective at selecting the best route to a destination remote network and also for discovering remote network.
Disadvantages
- Consumes more bandwidth for communicating with other neighbours.
- Less secure than static Routing.
